Programmable Controllers: Theory and Implementation
Programmable Controllers: Theory and Implementation
Programmable Controllers: Theory and Implementation
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
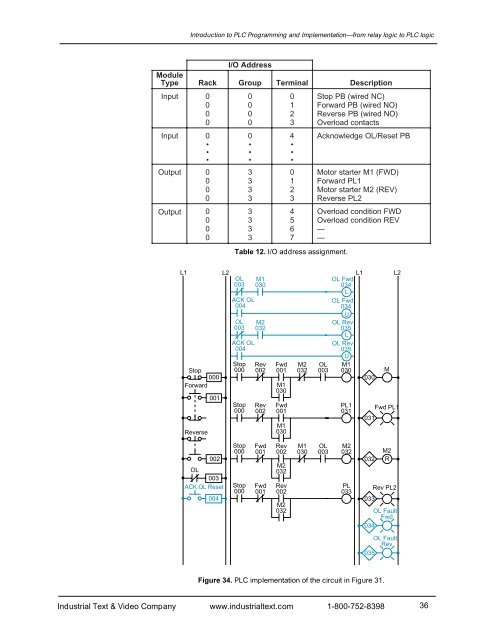
Introduction to PLC Programming <strong>and</strong> <strong>Implementation</strong>—from relay logic to PLC logicModuleTypeRackI/O AddressGroupTerminalTable 12. I/O address assignment.DescriptionInput0 0 0 Stop PB (wired NC)0 0 1 Forward PB (wired NO)0 0 2 Reverse PB (wired NO)0 0 3 Overload contactsInput0 0 4 Acknowledge OL/Reset PB• • •• • •• • •Output0 3 0 Motor starter M1 (FWD)0 3 1 Forward PL10 3 2 Motor starter M2 (REV)0 3 3 Reverse PL2Output0 3 4 Overload condition FWD0 3 5 Overload condition REV0 3 6 —0 3 7 —L1Stop000ForwardReverse001L2OL003ACK OL004OL003ACK OL004Stop000Stop000M1030M2032Rev002Rev002Fwd001M1030Fwd001M1030M2032L1OL Fwd034LOL Fwd034UOL Rev035LOL Rev035UOL M1003 030030PL1031031ML2Fwd PL1002OL003ACK OL Reset004Stop000Stop000Fwd001Fwd001Rev002M2032Rev002M2032M1030OL003M2032PL033032033M2RRev PL2OL FaultFwd034OL FaultRev035Figure 34. PLC implementation of the circuit in Figure 31.Industrial Text & Video Company www.industrialtext.com 1-800-752-839836