Acta Facultatis Ecologiae - Technická univerzita vo Zvolene
Acta Facultatis Ecologiae - Technická univerzita vo Zvolene
Acta Facultatis Ecologiae - Technická univerzita vo Zvolene
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
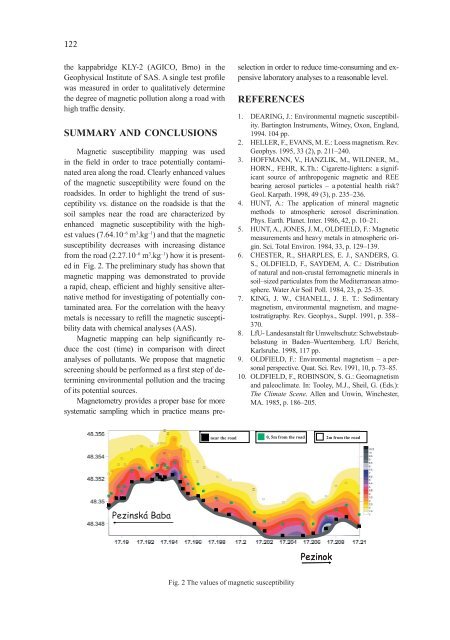
122the kappabridge KLY-2 (AGICO, Brno) in theGeophysical Institute of SAS. A single test profilewas measured in order to qualitatively determinethe degree of magnetic pollution along a road withhigh traffic density.SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONSMagnetic susceptibility mapping was usedin the field in order to trace potentially contaminatedarea along the road. Clearly enhanced valuesof the magnetic susceptibility were found on theroadsides. In order to highlight the trend of susceptibilityvs. distance on the roadside is that thesoil samples near the road are characterized byenhanced magnetic susceptibility with the highestvalues (7.64.10 –6 m 3 .kg –1 ) and that the magneticsusceptibility decreases with increasing distancefrom the road (2.27.10 –6 m 3 .kg –1 ) how it is presentedin Fig. 2. The preliminary study has shown thatmagnetic mapping was demonstrated to providea rapid, cheap, efficient and highly sensitive alternativemethod for investigating of potentially contaminatedarea. For the correlation with the heavymetals is necessary to refill the magnetic susceptibilitydata with chemical analyses (AAS).Magnetic mapping can help significantly reducethe cost (time) in comparison with directanalyses of pollutants. We propose that magneticscreening should be performed as a first step of determiningenvironmental pollution and the tracingof its potential sources.Magnetometry provides a proper base for moresystematic sampling which in practice means preselectionin order to reduce time-consuming and expensivelaboratory analyses to a reasonable level.REFERENCES1. DEARING, J.: Environmental magnetic susceptibility.Bartington Instruments, Witney, Oxon, England,1994. 104 pp.2. HELLER, F., EVANS, M. E.: Loess magnetism. Rev.Geophys. 1995, 33 (2), p. 211–240.3. HOFFMANN, V., HANZLIK, M., WILDNER, M.,HORN., FEHR, K.Th.: Cigarette-lighters: a significantsource of anthropogenic magnetic and REEbearing aerosol particles – a potential health risk?Geol. Karpath. 1998, 49 (3), p. 235–236.4. HUNT, A.: The application of mineral magneticmethods to atmospheric aerosol discrimination.Phys. Earth. Planet. Inter. 1986, 42, p. 10–21.5. HUNT, A., JONES, J. M., OLDFIELD, F.: Magneticmeasurements and heavy metals in atmospheric origin.Sci. Total Environ. 1984, 33, p. 129–139.6. CHESTER, R., SHARPLES, E. J., SANDERS, G.S., OLDFIELD, F., SAYDEM, A. C.: Distributionof natural and non-crustal ferromagnetic minerals insoil–sized particulates from the Mediterranean atmosphere.Water Air Soil Poll. 1984, 23, p. 25–35.7. KING, J. W., CHANELL, J. E. T.: Sedimentarymagnetism, environmental magnetism, and magnetostratigraphy.Rev. Geophys., Suppl. 1991, p. 358–370.8. LfU- Landesanstalt für Umweltschutz: Schwebstaubbelastungin Baden–Wuerttemberg. LfU Bericht,Karlsruhe. 1998, 117 pp.9. OLDFIELD, F.: Environmental magnetism – a personalperspective. Quat. Sci. Rev. 1991, 10, p. 73–85.10. OLDFIELD, F., ROBINSON, S. G.: Geomagnetismand paleoclimate. In: Tooley, M.J., Sheil, G. (Eds.):The Climate Scene. Allen and Unwin, Winchester,MA. 1985, p. 186–205.near the road 0, 5m from the road 2m from the roadPezinská BabaPezinokFig. 2 The values of magnetic susceptibility