- Page 2 and 3:
The Origin and Evolution of Mammals
- Page 4 and 5:
The Origin and Evolution of Mammals
- Page 6 and 7:
Preface This book arose from twin a
- Page 8 and 9:
For Mal /gosia with love and thanks
- Page 10 and 11:
Contents 1 Introduction The definit
- Page 12 and 13:
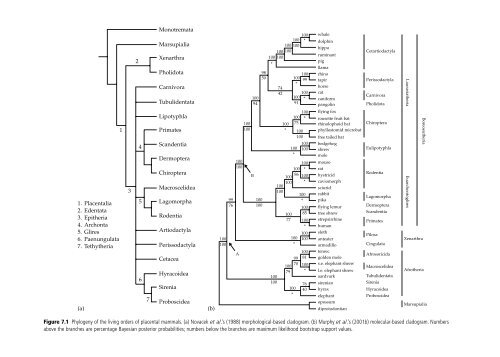
CHAPTER 1 Introduction There are ab
- Page 14 and 15:
transversely occluding molar teeth
- Page 16 and 17:
the Mesozoic mammals, is to do with
- Page 18 and 19:
a hierarchy of committees under the
- Page 20 and 21:
it means that a 200 Ma igneous rock
- Page 22 and 23:
een a more fundamental impact than
- Page 24 and 25:
Table 2.3 Classification of marsupi
- Page 26 and 27:
(a) (b) (c) humerus radius aquatic
- Page 28 and 29:
(a) Westlothiana Limnoscelis PO Wes
- Page 30 and 31:
the ankle bones to form an astragal
- Page 32 and 33:
(b) (c) (a) Casea rutena Casea broi
- Page 34 and 35:
(Fig. 3.2(f)), is actually an ophia
- Page 36 and 37:
the first one is enlarged, often to
- Page 38 and 39:
Even at their initial appearance in
- Page 40 and 41:
(a) Nikkasaurus (b) (d) Reiszia (e)
- Page 42 and 43:
Nikkasauridae The family Nikkasauri
- Page 44 and 45:
has figured large in discussions of
- Page 46 and 47:
(c) Figure 3.9 (continued). Syodon
- Page 48 and 49:
a mixture of progressively more spe
- Page 50 and 51:
animal with interdigitating, but no
- Page 52 and 53:
(e) (a) Anomocephalus Ulemica (b) S
- Page 54 and 55:
mandibulae musculature. This, as in
- Page 56 and 57:
To date the postcranial skeleton of
- Page 58 and 59:
ecognised four subgroups, based mai
- Page 60 and 61:
the presence of a deep, longitudina
- Page 62 and 63:
collected from the Lystrosaurus Ass
- Page 64 and 65:
(a) (d) (c) (b) Leontocephalus V PA
- Page 66 and 67:
(a) (c) Lycosuchus Oliveria (d) EVO
- Page 68 and 69:
separate families. Lycosuchidae (Fi
- Page 70 and 71:
consist of a large labial cusp and
- Page 72 and 73:
Procynosuchus (d) Procynosuchus (a)
- Page 74 and 75:
They constitute the monophyletic gr
- Page 76 and 77:
Although there is no mammal-like co
- Page 78 and 79:
Cynognathidae Cynognathus (Fig. 3.2
- Page 80 and 81:
(e) (f) Figure 3.22 (continued). Ma
- Page 82 and 83:
(c) (d) (a) (b) Kayentatherium EVOL
- Page 84 and 85:
Pachygenelus (e) (a) (c) Therioherp
- Page 86 and 87:
palatal, and orbitosphenoid bones,
- Page 88 and 89:
Wible and Hopson 1993). The interor
- Page 90 and 91:
published a cladogram based on rece
- Page 92 and 93:
310-320 Ma. By this time, the great
- Page 94 and 95:
are forms such as Casea itself, var
- Page 96 and 97:
lakes and swamps in the low-lying l
- Page 98 and 99:
urrowing and subsisting on a diet o
- Page 100 and 101:
Eothyris Haptodus sphenacodontine B
- Page 102 and 103:
z (a) (c) a.pt.m. M B PO P P SQ P M
- Page 104 and 105:
(b) a.pt.m. temp.m. a.pt.m. temp.m.
- Page 106 and 107:
the dentary bone above the level of
- Page 108 and 109:
the therocephalian grade was not on
- Page 110 and 111:
A balance was also achieved in the
- Page 112 and 113:
Locomotion Ancestral amniote grade
- Page 114 and 115:
screw-shaped: the front part faces
- Page 116 and 117:
For the recovery phase, the relativ
- Page 118 and 119:
SC PRC p.i.f.i tr.min (c) dp.cr ect
- Page 120 and 121:
the therocephalian pelvis and hindl
- Page 122 and 123:
spc s.sp s.sp SC PRC (d) delt T AST
- Page 124 and 125:
no significant novelties to what ha
- Page 126 and 127:
(a) (c) (e) (g) D D ex. au.m C tym
- Page 128 and 129:
(a) (c) (d) PMX (f) V n.turb mx.tur
- Page 130 and 131:
ol.b (a) (b) cer.hem gorgonopsian t
- Page 132 and 133:
(a) (b) (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) a g
- Page 134 and 135:
cold stress, the part that usually
- Page 136 and 137:
conducted the experiment of wrappin
- Page 138 and 139:
mammals themselves that the enlarge
- Page 140 and 141:
elevation of maximum aerobic activi
- Page 142 and 143:
a mammal. The difficulty with all s
- Page 144 and 145:
collection, ingestion, and assimila
- Page 146 and 147:
were edaphosaurid and caseid pelyco
- Page 148 and 149:
CHAPTER 5 The Mesozoic mammals The
- Page 150 and 151:
(a) (d) AL condylar foramina are se
- Page 152 and 153:
evidence to relate the haramiyidans
- Page 154 and 155:
postcranial skeleton, and Graybeal
- Page 156 and 157:
side of the head can be in action a
- Page 158 and 159:
the lower molars is relatively high
- Page 160 and 161:
morganucodontan teeth. However, des
- Page 162 and 163:
adjacent lower molars. A small exte
- Page 164 and 165:
(a) (b) (d) P4 P4 Plagiaulax P4 Pau
- Page 166 and 167:
American Morrison Formation genus C
- Page 168 and 169:
a self-sharpening property. As the
- Page 170 and 171:
near parasagittal gait (Fig. 5.11(e
- Page 172 and 173:
pass through the birth canal. Relat
- Page 174 and 175:
(a) 1 (b) (d) me (c) me.d 3 styl st
- Page 176 and 177:
(a) (c) Henkelotherium Crusafontia
- Page 178 and 179:
pubis is excluded from the acetabul
- Page 180 and 181:
Cretaceous, (Aptian or Albian) of M
- Page 182 and 183:
eautifully preserved placentals fro
- Page 184 and 185: subsequent specimens revealed that
- Page 186 and 187: Minimal divergence of tribosphenida
- Page 188 and 189: (c) (a) M 1 M 1 M 2 Steropodon M 2
- Page 190 and 191: (b) (a) (c) pa.d pr.d me.d Ambondro
- Page 192 and 193: crown-group therians) is accepted b
- Page 194 and 195: form of the tooth, must reflect sub
- Page 196 and 197: of feasibility that a taxon of endo
- Page 198 and 199: mammals, by creating environmental
- Page 200 and 201: the 11 species of marsupial, of whi
- Page 202 and 203: (d) (a) pa A Dasyuromorphia B C pr
- Page 204 and 205: earing two huge claws on digits thr
- Page 206 and 207: that contains the independent ances
- Page 208 and 209: (b) (d) (a) Glasbius Alphadon (c) D
- Page 210 and 211: elieved to be Late Cretaceous in ag
- Page 212 and 213: (Fig. 6.5(c)). The dentition exhibi
- Page 214 and 215: (d) Figure 6.6 (continued). Thylaco
- Page 216 and 217: (a) (c) Caroloameghina and Procarol
- Page 218 and 219: (a) (e) (d) Proargyrolagus Groeberi
- Page 220 and 221: (a) (b) Djarthia Thylacotinga (c) (
- Page 222 and 223: LIVING AND FOSSIL MARSUPIALS 211 M
- Page 224 and 225: Extinct Notoryctemorphia At present
- Page 226 and 227: (f) (g) Wakaleo Diprotodon optatum
- Page 228 and 229: fossil mammals, which might help cl
- Page 230 and 231: 30 40 50 60 Figure 6.13 Southern Go
- Page 232 and 233: the Diprotodontia also included gen
- Page 236 and 237: effectively absent. However, increa
- Page 238 and 239: Asioryctes (a) (b) (d) Cimolestes p
- Page 240 and 241: and Prokennalestes, although it doe
- Page 242 and 243: (a) Leptictidium Palaeoryctidans we
- Page 244 and 245: (a) Purgatorius (c) are part of the
- Page 246 and 247: (a) (d) (e) (g) Protoungulatum Meso
- Page 248 and 249: (a) (f) (e) Hyopsodus Phenacodus (d
- Page 250 and 251: Titanoides (pantodont) (a) (c) (b)
- Page 252 and 253: (a) (b) (d) Trogosus (tillodont) Es
- Page 254 and 255: Mioclaenus Paulacoutoia (didolodont
- Page 256 and 257: their presence. The five orders may
- Page 258 and 259: Xenungulata. Only two Late Palaeoce
- Page 260 and 261: (a) (b) (d) (c) Oxyaena Patriofelis
- Page 262 and 263: continuously growing, and form a gr
- Page 264 and 265: navicular facet, 19 or more thoraci
- Page 266 and 267: (a) (c) Phosphatherium Numidotheriu
- Page 268 and 269: coexist with other characters that
- Page 270 and 271: The salient feature of Widanelfasia
- Page 272 and 273: 1 (a) 1. Perissodactyla 2. Titanoth
- Page 274 and 275: (a) (b) BUNODONTIA or SUIFORMES SUI
- Page 276 and 277: time, which suggests that it was on
- Page 278 and 279: condition. This particular combinat
- Page 280 and 281: etween Primates, Dermoptera (colugo
- Page 282 and 283: have postcranial adaptations for ar
- Page 284 and 285:
undoubtedly related at a supraordin
- Page 286 and 287:
indisputably to occur prior to the
- Page 288 and 289:
The Late Cretaceous mammal record i
- Page 290 and 291:
interordinal divergences in the Lat
- Page 292 and 293:
diversity on Earth (Janis 1993). Fu
- Page 294 and 295:
effect of the surrounding sea. Trop
- Page 296 and 297:
was high. It lasted from 5 to 3 Ma
- Page 298 and 299:
and thus remain in their preferred
- Page 300 and 301:
agreement about exactly when within
- Page 302 and 303:
References Abdala, F. Redescription
- Page 304 and 305:
Ax, P. 1987. The phylogenetic syste
- Page 306 and 307:
Bramble, D. M. 1978. Origin of the
- Page 308 and 309:
Colbert, E.H. 1948. The mammal-like
- Page 310 and 311:
Duvall, D. 1986. A new question of
- Page 312 and 313:
Gow, C.E. 1980. The dentitions of t
- Page 314 and 315:
Ivakhnenko, M.F. 1990. The late Pal
- Page 316 and 317:
Kemp, T.S. 1988a. A note on the Mes
- Page 318 and 319:
cladogenesis in dasyurid marsupials
- Page 320 and 321:
(eds) Evolution of Tertiary mammals
- Page 322 and 323:
McKenna, M.C. and Bell, S.K. 1997.
- Page 324 and 325:
(ed) The phylogeny and classificati
- Page 326 and 327:
Ray, S. 2000.Endothiodont dicynodon
- Page 328 and 329:
Rubidge, B.S., Kitching, J.W., and
- Page 330 and 331:
Simpson, G.G. 1970. The Argyrolagid
- Page 332 and 333:
Thewissen, J.G.M. 1990. Evolution o
- Page 334 and 335:
Novacek, M.J., and McKenna, M.C. (e
- Page 336 and 337:
Index Note: Page numbers in italics
- Page 338 and 339:
Equoidea 262 Equus 262 Erethizon 28
- Page 340 and 341:
Overkill hypothesis 289, 290 Oxyaen
- Page 342:
Tulerpeton 14, 18 Tylopoda 264 Ukha