12th Congress of the European Hematology ... - Haematologica
12th Congress of the European Hematology ... - Haematologica
12th Congress of the European Hematology ... - Haematologica
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
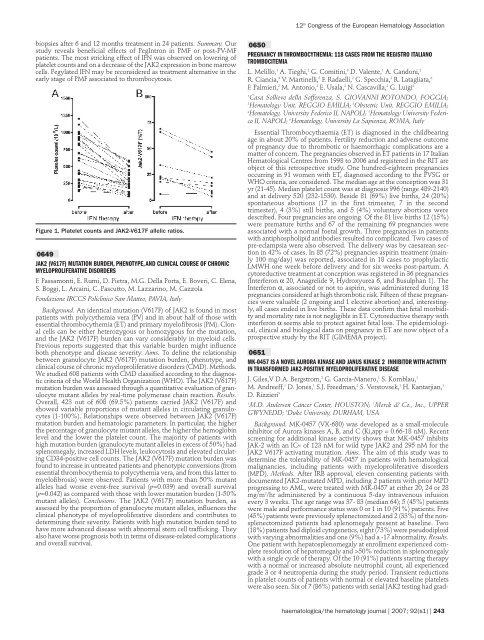
iopsies after 6 and 12 months treatment in 24 patients. Summary. Our<br />
study reveals beneficial effects <strong>of</strong> PegIntron in PMF or post-PV-MF<br />
patients. The most stricking effect <strong>of</strong> IFN was observed on lowering <strong>of</strong><br />
platelet counts and on a decrease <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> JAK2 expression in bone marrow<br />
cells. Pegylated IFN may be reconsidered as treatment alternative in <strong>the</strong><br />
early stage <strong>of</strong> PMF associated to thrombocytosis.<br />
Figure 1. Platelet counts and JAK2-V617F allelic ratios.<br />
0649<br />
JAK2 (V617F) MUTATION BURDEN, PHENOTYPE, AND CLINICAL COURSE OF CHRONIC<br />
MYELOPROLIFERATIVE DISORDERS<br />
F. Passamonti, E. Rumi, D. Pietra, M.G. Della Porta, E. Boveri, C. Elena,<br />
S. Boggi, L. Arcaini, C. Pascutto, M. Lazzarino, M. Cazzola<br />
Fondazione IRCCS Policlinico San Matteo, PAVIA, Italy<br />
Background. An identical mutation (V617F) <strong>of</strong> JAK2 is found in most<br />
patients with polycy<strong>the</strong>mia vera (PV) and in about half <strong>of</strong> those with<br />
essential thrombocy<strong>the</strong>mia (ET) and primary myel<strong>of</strong>ibrosis (PM). Clonal<br />
cells can be ei<strong>the</strong>r heterozygous or homozygous for <strong>the</strong> mutation,<br />
and <strong>the</strong> JAK2 (V617F) burden can vary considerably in myeloid cells.<br />
Previous reports suggested that this variable burden might influence<br />
both phenotype and disease severity. Aims. To define <strong>the</strong> relationship<br />
between granulocyte JAK2 (V617F) mutation burden, phenotype, and<br />
clinical course <strong>of</strong> chronic myeloproliferative disorders (CMD). Methods.<br />
We studied 608 patients with CMD classified according to <strong>the</strong> diagnostic<br />
criteria <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> World Health Organization (WHO). The JAK2 (V617F)<br />
mutation burden was assessed through a quantitative evaluation <strong>of</strong> granulocyte<br />
mutant alleles by real-time polymerase chain reaction. Results.<br />
Overall, 423 out <strong>of</strong> 608 (69.5%) patients carried JAK2 (V617F) and<br />
showed variable proportions <strong>of</strong> mutant alleles in circulating granulocytes<br />
(1-100%). Relationships were observed between JAK2 (V617F)<br />
mutation burden and hematologic parameters. In particular, <strong>the</strong> higher<br />
<strong>the</strong> percentage <strong>of</strong> granulocyte mutant alleles, <strong>the</strong> higher <strong>the</strong> hemoglobin<br />
level and <strong>the</strong> lower <strong>the</strong> platelet count. The majority <strong>of</strong> patients with<br />
high mutation burden (granulocyte mutant alleles in excess <strong>of</strong> 50%) had<br />
splenomegaly, increased LDH levels, leukocytosis and elevated circulating<br />
CD34-positive cell counts. The JAK2 (V617F) mutation burden was<br />
found to increase in untreated patients and phenotypic conversions (from<br />
essential thrombocy<strong>the</strong>mia to polycy<strong>the</strong>mia vera, and from this latter to<br />
myel<strong>of</strong>ibrosis) were observed. Patients with more than 50% mutant<br />
alleles had worse event-free survival (p=0.039) and overall survival<br />
(p=0.042) as compared with those with lower mutation burden (1-50%<br />
mutant alleles). Conclusions. The JAK2 (V617F) mutation burden, as<br />
assessed by <strong>the</strong> proportion <strong>of</strong> granulocyte mutant alleles, influences <strong>the</strong><br />
clinical phenotype <strong>of</strong> myeloproliferative disorders and contributes to<br />
determining <strong>the</strong>ir severity. Patients with high mutation burden tend to<br />
have more advanced disease with abnormal stem cell trafficking. They<br />
also have worse prognosis both in terms <strong>of</strong> disease-related complications<br />
and overall survival.<br />
12 th <strong>Congress</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>European</strong> <strong>Hematology</strong> Association<br />
0650<br />
PREGNANCY IN THROMBOCYTHEMIA: 118 CASES FROM THE REGISTRO ITALIANO<br />
TROMBOCITEMIA<br />
L. Melillo, 1 A. Tieghi, 2 G. Comitini, 3 D. Valente, 1 A. Candoni, 2<br />
R. Ciancia, 4 V. Martinelli, 5 F. Radaelli, 2 G. Specchia, 2 R. Latagliata, 6<br />
F. Palmieri, 2 M. Antonio, 2 E. Usala, 2 N. Cascavilla, 2 G. Luigi2 1 Casa Sollievo della S<strong>of</strong>ferenza, S. GIOVANNI ROTONDO, FOGGIA;<br />
2 <strong>Hematology</strong> Unit, REGGIO EMILIA; 3 Obstetric Unit, REGGIO EMILIA;<br />
4 <strong>Hematology</strong>, University Federico II, NAPOLI; 5 <strong>Hematology</strong> University Federico<br />
II, NAPOLI; 6 <strong>Hematology</strong>, University La Sapienza, ROMA, Italy<br />
Essential Thrombocythaemia (ET) is diagnosed in <strong>the</strong> childbearing<br />
age in about 20% <strong>of</strong> patients. Fertility reduction and adverse outcome<br />
<strong>of</strong> pregnancy due to thrombotic or haemorrhagic complications are a<br />
matter <strong>of</strong> concern. The pregnancies observed in ET patients in 17 Italian<br />
Hematological Centres from 1998 to 2006 and registered in <strong>the</strong> RIT are<br />
object <strong>of</strong> this retrospective study. One hundred-eighteen pregnancies<br />
occurring in 91 women with ET, diagnosed according to <strong>the</strong> PVSG or<br />
WHO criteria, are considered. The median age at <strong>the</strong> conception was 31<br />
yr (21-45). Median platelet count was at diagnosis 996 (range 489-2140)<br />
and at delivery 520 (232-1530). Beside 81 (69%) live births, 24 (20%)<br />
spontaneous abortions (17 in <strong>the</strong> first trimester, 7 in <strong>the</strong> second<br />
trimester), 4 (3%) still births, and 5 (4%) voluntary abortions were<br />
described. Four pregnancies are ongoing. Of <strong>the</strong> 81 live births 12 (15%)<br />
were premature births and 67 <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> remaining 69 pregnancies were<br />
associated with a normal foetal growth. Three pregnancies in patients<br />
with antiphospholipid antibodies resulted no complicated. Two cases <strong>of</strong><br />
pre-eclampsia were also observed. The delivery was by caesarean section<br />
in 42% <strong>of</strong> cases. In 85 (72%) pregnancies aspirin treatment (mainly<br />
100 mg/day) was reported, associated in 18 cases to prophylactic<br />
LMWH one week before delivery and for six weeks post-partum. A<br />
cytoreductive treatment at conception was registered in 36 pregnancies<br />
(Interferon α 20, Anagrelide 9, Hydroxyurea 6, and Busulphan 1). The<br />
Interferon α, associated or not to aspirin, was administered during 18<br />
pregnancies considered at high thrombotic risk. Fifteen <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong>se pregnancies<br />
were valuable (2 ongoing and 1 elective abortion) and, interestingly,<br />
all cases ended in live births. These data confirm that fetal morbidity<br />
and mortality rate is not negligible in ET. Cytoreductive <strong>the</strong>rapy with<br />
interferon α seems able to protect against fetal loss. The epidemiological,<br />
clinical and biological data on pregnancy in ET are now object <strong>of</strong> a<br />
prospective study by <strong>the</strong> RIT (GIMEMA project).<br />
0651<br />
MK-0457 IS A NOVEL AURORA KINASE AND JANUS KINASE 2 INHIBITOR WITH ACTIVITY<br />
IN TRANSFORMED JAK2-POSITIVE MYELOPROLIFERATIVE DISEASE<br />
J. Giles,V D.A. Bergstrom, 2 G. Garcia-Manero, 1 S. Kornblau, 1<br />
M. Andreeff, 1 D. Jones, 1 S.J. Freedman, 2 S. Verstovsek, 1 H. Kantarjian, 1<br />
D. Rizzieri3 1 M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, HOUSTON; 2 Merck & Co., Inc., UPPER<br />
GWYNEDD; 3 Duke University, DURHAM, USA<br />
Background. MK-0457 (VX-680) was developed as a small-molecule<br />
inhibitor <strong>of</strong> Aurora kinases A, B, and C (Ki,app = 0.66-18 nM). Recent<br />
screening for additional kinase activity shows that MK-0457 inhibits<br />
JAK-2 with an IC50 <strong>of</strong> 123 nM for wild type JAK2 and 295 nM for <strong>the</strong><br />
JAK2 V617F activating mutation. Aims. The aim <strong>of</strong> this study was to<br />
determine <strong>the</strong> tolerability <strong>of</strong> MK-0457 in patients with hematological<br />
malignancies, including patients with myeloproliferative disorders<br />
(MPD). Methods. After IRB approval, eleven consenting patients with<br />
documented JAK2-mutated MPD, including 2 patients with prior MPD<br />
progressing to AML, were treated with MK-0457 at ei<strong>the</strong>r 20, 24 or 28<br />
mg/m 2 /hr administered by a continuous 5-day intravenous infusion<br />
every 3 weeks. The age range was 37- 83 (median 64); 5 (45%) patients<br />
were male and performance status was 0 or 1 in 10 (91%) patients. Five<br />
(45%) patients were previously splenectomized and 2 (33%) <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> nonsplenectomized<br />
patients had splenomegaly present at baseline. Two<br />
(18%) patients had diploid cytogenetics, eight (73%) were pseudodiploid<br />
with varying abnormalities and one (9%) had a -17 abnormality. Results.<br />
One patient with hepatosplenomegaly at enrollment experienced complete<br />
resolution <strong>of</strong> hepatomegaly and >50% reduction in splenomegaly<br />
with a single cycle <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong>rapy. Of <strong>the</strong> 10 (91%) patients starting <strong>the</strong>rapy<br />
with a normal or increased absolute neutrophil count, all experienced<br />
grade 3 or 4 neutropenia during <strong>the</strong> study period. Transient reductions<br />
in platelet counts <strong>of</strong> patients with normal or elevated baseline platelets<br />
were also seen. Six <strong>of</strong> 7 (86%) patients with serial JAK2 testing had grad-<br />
haematologica/<strong>the</strong> hematology journal | 2007; 92(s1) | 243