Timing, hosts and locations of (grouped) events of NanoImpactNet
Timing, hosts and locations of (grouped) events of NanoImpactNet
Timing, hosts and locations of (grouped) events of NanoImpactNet
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
NanoSafetyCluster - Compendium 2012<br />
1 Summary<br />
NanoHouse project in some words:<br />
NanoHouse collaborative project is founded by the European<br />
Commission in the frame <strong>of</strong> FP7 programs: NMP-2009-1.3-1 &<br />
ENV2009.3.1.3.2 “Activities towards the development <strong>of</strong><br />
appropriate solutions for the use, recycling <strong>and</strong>/or final<br />
treatment <strong>of</strong> nanotechnology-based products.<br />
This project started January 2010 for a duration <strong>of</strong> 42 months<br />
(until 06/2013) <strong>and</strong> a total budget <strong>of</strong> 3.1 M€.<br />
The current <strong>and</strong> projected applications <strong>of</strong> Engineered<br />
NanoParticles (ENPs) span a very wide range <strong>of</strong> industrial <strong>and</strong><br />
consumer sectors such as : biomedicine, pharmaceuticals,<br />
cosmetics, new sources <strong>of</strong> energy, environmental analysis <strong>and</strong><br />
remediation, material science . At the same time, the potential<br />
impact <strong>of</strong> these new materials their production <strong>and</strong> their lifecycle<br />
implications on the places where people live on<br />
Environmental Health <strong>and</strong> Safety (EHS) is a key issue regarding<br />
the future acceptability <strong>and</strong> sustainability <strong>of</strong> nanoproducts. In<br />
this perspective, buildings <strong>and</strong> individual houses are critical in<br />
that they constitute the major surrounding <strong>of</strong> people in<br />
developed countries.<br />
The NanoHOUSE project concentrate on this issue <strong>and</strong> aims at<br />
promoting a responsible <strong>and</strong> sustainable development <strong>of</strong><br />
2 Background<br />
Nanosciences <strong>and</strong> Nanotechnologies (N&N) provide many<br />
opportunities to significantly improve materials properties <strong>and</strong><br />
sustainability. The current <strong>and</strong> projected applications <strong>of</strong><br />
Engineered NanoParticles (ENPs) span a very wide range <strong>of</strong><br />
industrial <strong>and</strong> consumer sectors such as: biomedicine,<br />
pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, new sources <strong>of</strong> energy,<br />
environmental analysis <strong>and</strong> remediation, material sciences<br />
At the same time, the potential impact <strong>of</strong> these new materials<br />
their production <strong>and</strong> their life-cycle implications on the places<br />
where people live on human health <strong>and</strong> the environment is<br />
viewed with apprehension by citizens. A growing body <strong>of</strong><br />
scientific evidence indicates that exposure to some ENPs can<br />
lead to harmful effects. In the Nanotechnology Action Plan 2004<br />
(COM(2004) 338), the European Commission highlighted that<br />
“R&D need to take into account the impacts <strong>of</strong> nanotechnology<br />
throughout the whole <strong>of</strong> their life-cycle”. In the “Nanosciences<br />
<strong>and</strong> nanotechnologies: An action plan for Europe 2005-2009<br />
(2005)” it is emphasized as well: “Health, safety <strong>and</strong><br />
environmental risks that may be associated with products <strong>and</strong><br />
applications <strong>of</strong> N&N need to be addressed upfront <strong>and</strong><br />
throughout their life cycle”. Therefore, the environmental <strong>and</strong><br />
health consequences <strong>of</strong> these materials, their production <strong>and</strong><br />
nanomaterials in building industry through a Life Cycle<br />
Thinking approach.<br />
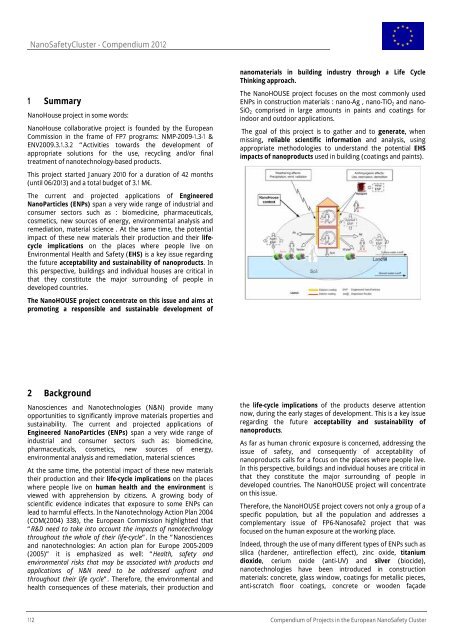
The NanoHOUSE project focuses on the most commonly used<br />
ENPs in construction materials : nano-Ag , nano-TiO 2 <strong>and</strong> nano-<br />
SiO 2 comprised in large amounts in paints <strong>and</strong> coatings for<br />
indoor <strong>and</strong> outdoor applications.<br />
The goal <strong>of</strong> this project is to gather <strong>and</strong> to generate, when<br />
missing, reliable scientific information <strong>and</strong> analysis, using<br />
appropriate methodologies to underst<strong>and</strong> the potential EHS<br />
impacts <strong>of</strong> nanoproducts used in building (coatings <strong>and</strong> paints).<br />
the life-cycle implications <strong>of</strong> the products deserve attention<br />
now, during the early stages <strong>of</strong> development. This is a key issue<br />
regarding the future acceptability <strong>and</strong> sustainability <strong>of</strong><br />
nanoproducts.<br />
As far as human chronic exposure is concerned, addressing the<br />
issue <strong>of</strong> safety, <strong>and</strong> consequently <strong>of</strong> acceptability <strong>of</strong><br />
nanoproducts calls for a focus on the places where people live.<br />
In this perspective, buildings <strong>and</strong> individual houses are critical in<br />
that they constitute the major surrounding <strong>of</strong> people in<br />
developed countries. The NanoHOUSE project will concentrate<br />
on this issue.<br />
Therefore, the NanoHOUSE project covers not only a group <strong>of</strong> a<br />
specific population, but all the population <strong>and</strong> addresses a<br />
complementary issue <strong>of</strong> FP6-Nanosafe2 project that was<br />
focused on the human exposure at the working place.<br />
Indeed, through the use <strong>of</strong> many different types <strong>of</strong> ENPs such as<br />
silica (hardener, antireflection effect), zinc oxide, titanium<br />
dioxide, cerium oxide (anti-UV) <strong>and</strong> silver (biocide),<br />
nanotechnologies have been introduced in construction<br />
materials: concrete, glass window, coatings for metallic pieces,<br />
anti-scratch floor coatings, concrete or wooden façade<br />
112 Compendium <strong>of</strong> Projects in the European NanoSafety Cluster