Kapitel 4 - Rendering und Visibilität - ICSY
Kapitel 4 - Rendering und Visibilität - ICSY
Kapitel 4 - Rendering und Visibilität - ICSY
Sie wollen auch ein ePaper? Erhöhen Sie die Reichweite Ihrer Titel.
YUMPU macht aus Druck-PDFs automatisch weboptimierte ePaper, die Google liebt.
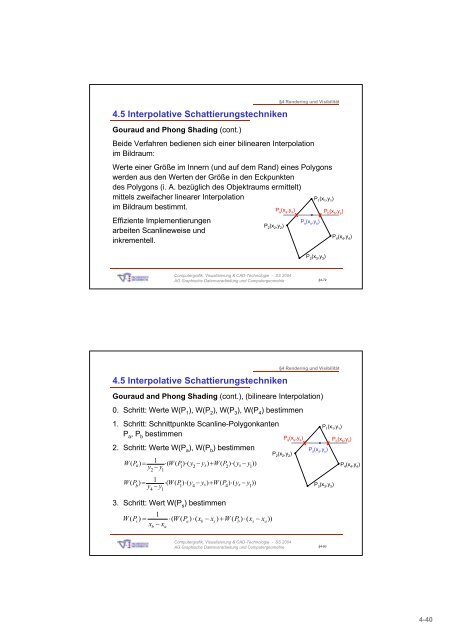
4.5 Interpolative Schattierungstechniken<br />
§4 <strong>Rendering</strong> <strong>und</strong> Visibilität<br />
Gouraud and Phong Shading (cont.)<br />
Beide Verfahren bedienen sich einer bilinearen Interpolation<br />
im Bildraum:<br />
Werte einer Größe im Innern (<strong>und</strong> auf dem Rand) eines Polygons<br />
werden aus den Werten der Größe in den Eckpunkten<br />
des Polygons (i. A. bezüglich des Objektraums ermittelt)<br />
mittels zweifacher linearer Interpolation<br />
P 1<br />
(x 1<br />
,y 1<br />
)<br />
im Bildraum bestimmt.<br />
Effiziente Implementierungen<br />
arbeiten Scanlineweise <strong>und</strong><br />
inkrementell.<br />
P 2<br />
(x 2<br />
,y 2<br />
)<br />
P a<br />
(x a<br />
,y s<br />
)<br />
P s<br />
(x s<br />
,y s<br />
)<br />
P 3<br />
(x 3<br />
,y 3<br />
)<br />
P b<br />
(x b<br />
,y s<br />
)<br />
P 4<br />
(x 4<br />
,y 4<br />
)<br />
Computergrafik, Visualisierung & CAD-Technologie - SS 2004<br />
AG Graphische Datenverarbeitung <strong>und</strong> Computergeometrie<br />
§4-79<br />
4.5 Interpolative Schattierungstechniken<br />
§4 <strong>Rendering</strong> <strong>und</strong> Visibilität<br />
Gouraud and Phong Shading (cont.), (bilineare Interpolation)<br />
0. Schritt: Werte W(P 1 ), W(P 2 ), W(P 3 ), W(P 4 ) bestimmen<br />
1. Schritt: Schnittpunkte Scanline-Polygonkanten<br />
P a , P b bestimmen<br />
2. Schritt: Werte W(P a ), W(P b ) bestimmen<br />
WP ( ) =<br />
1<br />
⋅( WP ( )( ⋅ y− y) + WP ( )( ⋅ y−y))<br />
y − y<br />
a 1 2 s 2 s 1<br />
2 1<br />
WP ( ) =<br />
1<br />
⋅( WP ( )( ⋅ y− y) ( )( ))<br />
b<br />
1 4 s + WP ⋅ y<br />
4 s−y<br />
y − y<br />
1<br />
4 1<br />
3. Schritt: Wert W(P s ) bestimmen<br />
1<br />
W( Ps ) = ⋅( W( Pa)( ⋅ xb<br />
− xs) + W( Pb)( ⋅ xs −xa))<br />
x − x<br />
b<br />
a<br />
P 2<br />
(x 2<br />
,y 2<br />
)<br />
P a<br />
(x a<br />
,y s<br />
)<br />
P s<br />
(x s<br />
,y s<br />
)<br />
P 1<br />
(x 1<br />
,y 1<br />
)<br />
P 3<br />
(x 3<br />
,y 3<br />
)<br />
P b<br />
(x b<br />
,y s<br />
)<br />
P 4<br />
(x 4<br />
,y 4<br />
)<br />
Computergrafik, Visualisierung & CAD-Technologie - SS 2004<br />
AG Graphische Datenverarbeitung <strong>und</strong> Computergeometrie<br />
§4-80<br />
4-40