Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
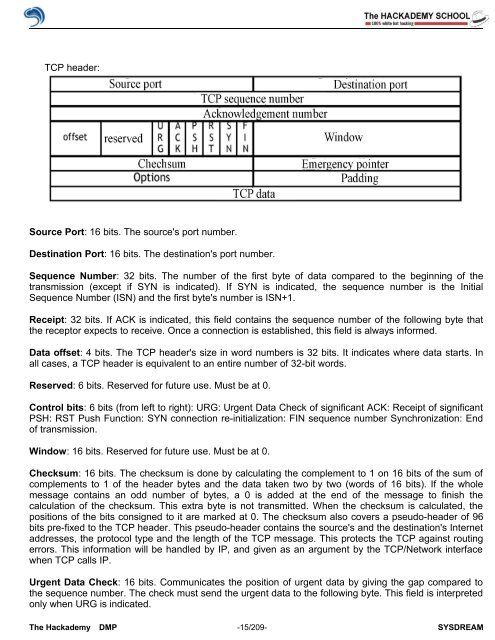
TCP header:<br />
Source Port: 16 bits. The source's port number.<br />
Destination Port: 16 bits. The destination's port number.<br />
Sequence Number: 32 bits. The number <strong>of</strong> the first byte <strong>of</strong> data compared to the beginning <strong>of</strong> the<br />
transmission (except if SYN is indicated). If SYN is indicated, the sequence number is the Initial<br />
Sequence Number (ISN) and the first byte's number is ISN+1.<br />
Receipt: 32 bits. If ACK is indicated, this field contains the sequence number <strong>of</strong> the following byte that<br />
the receptor expects to receive. Once a connection is established, this field is always informed.<br />
Data <strong>of</strong>fset: 4 bits. The TCP header's size in word numbers is 32 bits. It indicates where data starts. In<br />
all cases, a TCP header is equivalent to an entire number <strong>of</strong> 32-bit words.<br />
Reserved: 6 bits. Reserved for future use. Must be at 0.<br />
Control bits: 6 bits (from left to right): URG: Urgent Data Check <strong>of</strong> significant ACK: Receipt <strong>of</strong> significant<br />
PSH: RST Push Function: SYN connection re-initialization: FIN sequence number Synchronization: End<br />
<strong>of</strong> transmission.<br />
Window: 16 bits. Reserved for future use. Must be at 0.<br />
Checksum: 16 bits. The checksum is done by calculating the complement to 1 on 16 bits <strong>of</strong> the sum <strong>of</strong><br />
complements to 1 <strong>of</strong> the header bytes and the data taken two by two (words <strong>of</strong> 16 bits). If the whole<br />
message contains an odd number <strong>of</strong> bytes, a 0 is added at the end <strong>of</strong> the message to finish the<br />
calculation <strong>of</strong> the checksum. This extra byte is not transmitted. When the checksum is calculated, the<br />
positions <strong>of</strong> the bits consigned to it are marked at 0. The checksum also covers a pseudo-header <strong>of</strong> 96<br />
bits pre-fixed to the TCP header. This pseudo-header contains the source's and the destination's Internet<br />
addresses, the protocol type and the length <strong>of</strong> the TCP message. This protects the TCP against routing<br />
errors. This information will be handled by IP, and given as an argument by the TCP/Network interface<br />
when TCP calls IP.<br />
Urgent Data Check: 16 bits. Communicates the position <strong>of</strong> urgent data by giving the gap compared to<br />
the sequence number. The check must send the urgent data to the following byte. This field is interpreted<br />
only when URG is indicated.<br />
The <strong>Hack</strong>ademy DMP -15/209- SYSDREAM