Product Manual
Product Manual
Product Manual
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
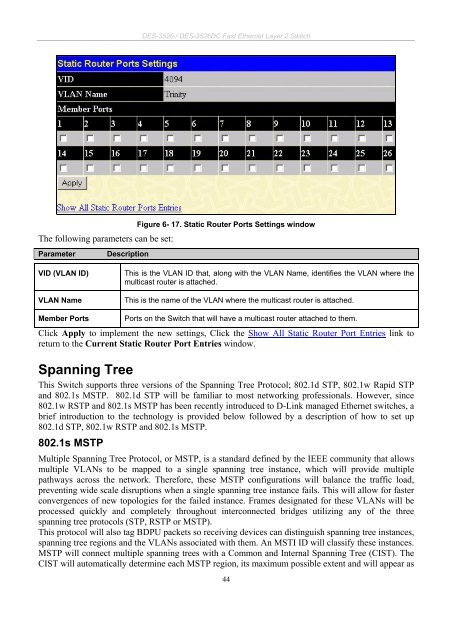
The following parameters can be set:<br />
Parameter Description<br />
DES-3526 / DES-3526DC Fast Ethernet Layer 2 Switch<br />
Figure 6- 17. Static Router Ports Settings window<br />
VID (VLAN ID) This is the VLAN ID that, along with the VLAN Name, identifies the VLAN where the<br />
multicast router is attached.<br />
VLAN Name This is the name of the VLAN where the multicast router is attached.<br />
Member Ports Ports on the Switch that will have a multicast router attached to them.<br />
Click Apply to implement the new settings, Click the Show All Static Router Port Entries link to<br />
return to the Current Static Router Port Entries window.<br />
Spanning Tree<br />
This Switch supports three versions of the Spanning Tree Protocol; 802.1d STP, 802.1w Rapid STP<br />
and 802.1s MSTP. 802.1d STP will be familiar to most networking professionals. However, since<br />
802.1w RSTP and 802.1s MSTP has been recently introduced to D-Link managed Ethernet switches, a<br />
brief introduction to the technology is provided below followed by a description of how to set up<br />
802.1d STP, 802.1w RSTP and 802.1s MSTP.<br />
802.1s MSTP<br />
Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol, or MSTP, is a standard defined by the IEEE community that allows<br />
multiple VLANs to be mapped to a single spanning tree instance, which will provide multiple<br />
pathways across the network. Therefore, these MSTP configurations will balance the traffic load,<br />
preventing wide scale disruptions when a single spanning tree instance fails. This will allow for faster<br />
convergences of new topologies for the failed instance. Frames designated for these VLANs will be<br />
processed quickly and completely throughout interconnected bridges utilizing any of the three<br />
spanning tree protocols (STP, RSTP or MSTP).<br />
This protocol will also tag BDPU packets so receiving devices can distinguish spanning tree instances,<br />
spanning tree regions and the VLANs associated with them. An MSTI ID will classify these instances.<br />
MSTP will connect multiple spanning trees with a Common and Internal Spanning Tree (CIST). The<br />
CIST will automatically determine each MSTP region, its maximum possible extent and will appear as<br />
44