This environmental impact assessment for Kriegers flak ... - Vattenfall
This environmental impact assessment for Kriegers flak ... - Vattenfall
This environmental impact assessment for Kriegers flak ... - Vattenfall
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
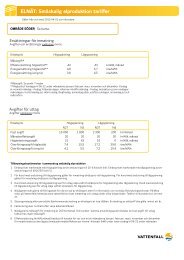
66 PRESENTATION OF THE AREA<br />
11.1.1 General in<strong>for</strong>mation about <strong>Kriegers</strong><br />
Flak<br />
<strong>Kriegers</strong> Flak is a raised seabed/submarine bank in the<br />
southern Baltic Sea. Water depth within central parts<br />
of the area is 16-17 metres, increasing to 20-25 metres<br />
at the borders. Outside the area the depth increases<br />
sharply to 40 metres or more. The seabed is made up<br />
of sediments from the last ice age on top of sediments<br />
from the cretaceous period.<br />
The border between the top of the sedimentary bedrock<br />
and the quaternary deposits is located within the<br />
actual area at a depth of between 50 and 60 metres.<br />
The upper part of the layer, deposited be<strong>for</strong>e the<br />
quaternary period, consists of limestone, comparable<br />
to glacially de<strong>for</strong>med lime at nearby Møns Klint in<br />
Denmark. The nearest core drilling to great depth is<br />
at Smygehuk between the Danish and the Swedish<br />
economic zones, and marked Smygehuk I (Lat.N55°<br />
18’ 16.22”, Long. E13° 03’ 02.25”).<br />
There, the top 350 metres of the sedimentary<br />
Overview of <strong>Kriegers</strong> Flak with isochrones showing the water depth. The yellow line indicates the<br />
border between the Swedish and the Danish economic zones (GEUS Report 2004/97).<br />
bedrock consist of white, soft limestone with a rich<br />
occurrence of ß int (up to 30%) in the upper part, but<br />
declining with depth and only sporadically occurring<br />
on greater depths than 150 metres. The changeover<br />
between quaternary sediment and the sedimentary<br />
bedrock was found to be at a depth of 42 metres below<br />
the surface, which indicates that the top level of the<br />
pre-quaternary deposits are likely to show small variations<br />
in depth and there<strong>for</strong>e assumed to be horizontal<br />
within the present area. Characteristics and quality <strong>for</strong><br />
the upper layer of the bedrock is in line with the evaluations<br />
of the drillings Smygehuk I.<br />
The composition and powerfulness of the removed<br />
sediment layers from the last ice age depend partly on<br />
the water depth and partly on local water conditions<br />
(currents, speed of water etc). In shallow waters, i.e.<br />
the central area of <strong>Kriegers</strong> Flak, quaternary sediments<br />
are found with powerfulness of generally less than<br />
20 meters, while the sediment powerfulness south of<br />
Krieger Flak (Arcona basin) is more than 40 meters.