annual report annual report annual report annual report 2005
annual report annual report annual report annual report 2005
annual report annual report annual report annual report 2005
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
104<br />
RADIOBIOLOGY<br />
DNA INTER-STRAND CROSSLINKS ARE INDUCED IN CELLS<br />
PRE-LABELLED WITH 5-BROMO-2’-DEOXYURIDINE<br />
AND EXPOSED TO UVC RADIATION<br />
Andrzej Wójcik 1,2/ , Agnieszka Bochenek 1/ , Anna Lankoff 1/ , Halina Lisowska 1/ , Anna Padjas 3/ ,<br />
Clemens von Sonntag 4,5/ , Günter Obe 6/<br />
1/<br />
Institute of Biology, Świętokrzyska Academy, Kielce, Poland<br />
2/<br />
Institute of Nuclear Chemistry and Technology, Warszawa, Poland<br />
3/<br />
Holycross Cancer Center, Kielce, Poland<br />
4/<br />
The Max Planck Institute for Bioinorganic Chemistry, Mülheim an der Ruhr, Germany<br />
5/<br />
Leibniz-Institut für Oberflächenmodifizierung (IOM), Leipzig, Germany<br />
6/<br />
Institute of Genetics, University of Duisburg-Essen, Essen, Germany<br />
It has been observed previously that 5-bromo-2’-deoxyuridine<br />
(BrdU) potentiates the effect of UVC<br />
radiation on the level of sister chromatid exchanges.<br />
It is not known which type of DNA damage<br />
is responsible for this enhancing effect and we<br />
have proposed this to be the DNA inter-strand<br />
crosslink (ICL) [1] which, theoretically, may arise<br />
in cells that are labelled with BrdU for one round<br />
of replication and exposed to UVC radiation. This<br />
notion was based on the fact that irradiation of<br />
BrdU-labelled DNA with UV leads not only to the<br />
formation of a uracilyl radical but also of a bromine<br />
atom which can oxidise a purine base of the<br />
DNA strand opposed to the uracilyl radical. Thus,<br />
two radicals at opposing strands are formed and<br />
this can easily lead to the formation of an ICL.<br />
The aim of the present investigation was to verify<br />
if ICLs are indeed formed in this irradiation scenario.<br />
CHO-K1 cells were pre-labelled with BrdU<br />
and exposed to UVC. ICLs were detected by the<br />
modified version of the comet assay that relies on<br />
the reduction of induced DNA migration in the<br />
agarose gel. Carboplatin was used as a positive<br />
control. The results fully supported this hypothesis:<br />
exposure to BrdU+UVC reduced the level<br />
of damage induced by gamma radiation and measured<br />
in the comet assay in a manner similar to<br />
carboplatin, a platinum compound which is a potent<br />
inducer of both ICLs and intra-strand crosslinks.<br />
In order to confirm the results of the comet<br />
assay in a different system, we have tested the sensitivity<br />
of CL-V4B cells towards BrdU+UVC.<br />
These cells have a mutated Rad51C paralog, a key<br />
enzyme in the homologous recombination repair<br />
[2,3]. Due to this, they are highly sensitive to ICLs<br />
[4]. The observation of a high level (as compared<br />
to the wild type cells) of chromosomal damage in<br />
CL-V4B cells exposed to BrdU+UVC and mitomycin<br />
C, but not to UVC alone, substantiates the<br />
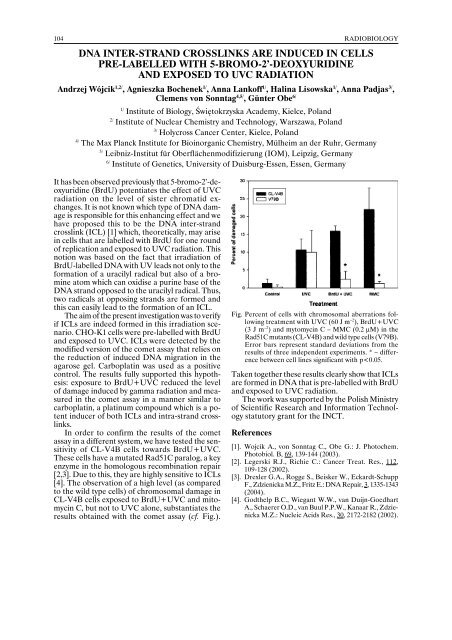
results obtained with the comet assay (cf. Fig.).<br />
Fig. Percent of cells with chromosomal aberrations following<br />
treatment with UVC (60 J m –2 ), BrdU+UVC<br />
(3 J m –2 ) and mytomycin C – MMC (0.2 µM) in the<br />
Rad51C mutants (CL-V4B) and wild type cells (V79B).<br />
Error bars represent standard deviations from the<br />
results of three independent experiments. * – difference<br />
between cell lines significant with p