annual report annual report annual report annual report 2005
annual report annual report annual report annual report 2005
annual report annual report annual report annual report 2005
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
RADIOCHEMISTRY, STABLE ISOTOPES,<br />
NUCLEAR ANALYTICAL METHODS, GENERAL CHEMISTRY<br />
93<br />
drate (Mg[(C 5 H 3 N 2 O 2 )(H 2 O)] 2·2H 2 O) is composed<br />
of monomeric molecules in which the magnesium(II)<br />
ion at the centre of symmetry is coordinated<br />
by two ligand molecules, each via its N,O<br />
bonding moiety [Mg-N 2.177(2) Å, Mg-O 2.041(1)<br />
Å]. The ligand molecules and the metal ion form<br />
a trans-planar configuration (rms 0.0001 Å). Two<br />
water oxygen atoms [Mg-O 2.091(1) Å], above and<br />
below the plane, complete a slightly distorted octahedron<br />
(Figs.1 and 2). A network of hydrogen bonds<br />
operating between the solvation water molecules<br />
acting as donors and unbonded carboxylate oxygen<br />
atoms and unbonded hetero-ring nitrogen<br />
atoms holds the monomers together.<br />
X-ray diffraction data collection was carried out<br />
on a KUMA KM4 four circle diffractometer at the<br />
Institute of Nuclear Chemistry and Technology.<br />
Structure solution and refinement was performed<br />
using SHELXL programme package.<br />
CRYSTAL CHEMISTRY OF COORDINATION COMPOUNDS<br />
WITH HETEROCYCLIC CARBOXYLATE LIGANDS.<br />
PART LVI. THE CRYSTAL AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURES<br />
OF TWO CALCIUM(II) COMPLEXES<br />
WITH IMIDAZOLE-4,5-DICARBOXYLATE AND WATER LIGANDS<br />
Wojciech Starosta, Janusz Leciejewicz, Thathan Premkumar 1/ , Subbian Govindarajan 1/<br />
1/<br />
Department of Chemistry, Bharathiar University, Coimbatore, Tamilnadu, India<br />
Fig.2. The packing diagram of Ca(4,5-IDA)(H 2 O) 4·H 2 O<br />
showing the alignment of the molecular layers along<br />
the c axis.<br />
late oxygen atom O3 [d(Ca-O3)=2.325(1) Å], the<br />
hetero-ring nitrogen atom [d(Ca-N2)=2.523(1)Å]<br />
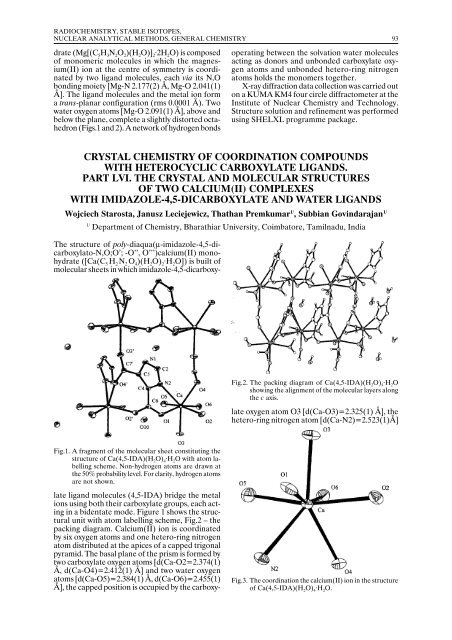
Fig.1. A fragment of the molecular sheet constituting the<br />
structure of Ca(4,5-IDA)(H 2 O) 4·H 2 O with atom labelling<br />
scheme. Non-hydrogen atoms are drawn at<br />
the 50% probability level. For clarity, hydrogen atoms<br />
are not shown.<br />
The structure of poly-diaqua(µ-imidazole-4,5-dicarboxylato-N,O;O’;<br />
-O’’, O’’’)calcium(II) monohydrate<br />
([Ca(C 5 H 2 N 2 O 4 )(H 2 O) 2·H 2 O]) is built of<br />
molecular sheets in which imidazole-4,5-dicarboxylate<br />
ligand molecules (4,5-IDA) bridge the metal<br />
ions using both their carboxylate groups, each acting<br />
in a bidentate mode. Figure 1 shows the structural<br />
unit with atom labelling scheme, Fig.2 – the<br />
packing diagram. Calcium(II) ion is coordinated<br />
by six oxygen atoms and one hetero-ring nitrogen<br />
atom distributed at the apices of a capped trigonal<br />
pyramid. The basal plane of the prism is formed by<br />
two carboxylate oxygen atoms [d(Ca-O2=2.374(1)<br />
Å, d(Ca-O4)=2.412(1) Å] and two water oxygen<br />
atoms [d(Ca-O5)=2.384(1) Å, d(Ca-O6)=2.455(1)<br />
Å], the capped position is occupied by the carboxy-<br />
Fig.3. The coordination the calcium(II) ion in the structure<br />
of Ca(4,5-IDA)(H 2<br />
O) 4·H 2<br />
O.