Segmentation of 3D Tubular Tree Structures in Medical Images ...
Segmentation of 3D Tubular Tree Structures in Medical Images ...
Segmentation of 3D Tubular Tree Structures in Medical Images ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
5.2. Method 79<br />
(a) MIP <strong>of</strong> the<br />
dataset us<strong>in</strong>g a liver<br />
mask.<br />
(b) F<strong>in</strong>al segmentation<br />
<strong>of</strong> all trees.<br />
(c) TDF response.<br />
(d) Extracted tubular<br />
structures.<br />
(e) Reconstructed tree structures.<br />
(f) Segmented trees.<br />
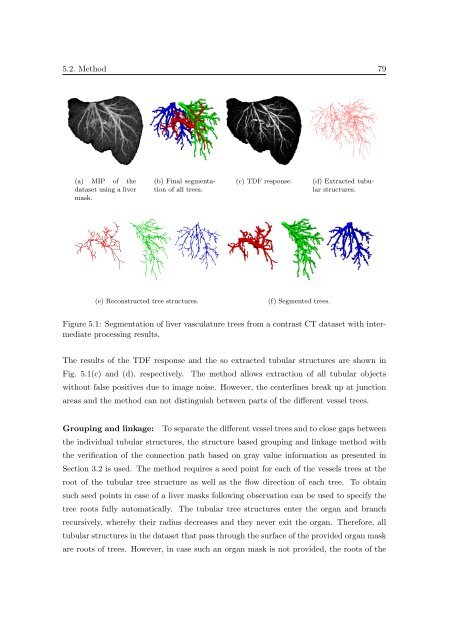
Figure 5.1: <strong>Segmentation</strong> <strong>of</strong> liver vasculature trees from a contrast CT dataset with <strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
process<strong>in</strong>g results.<br />
The results <strong>of</strong> the TDF response and the so extracted tubular structures are shown <strong>in</strong><br />
Fig. 5.1(c) and (d), respectively. The method allows extraction <strong>of</strong> all tubular objects<br />
without false positives due to image noise. However, the centerl<strong>in</strong>es break up at junction<br />
areas and the method can not dist<strong>in</strong>guish between parts <strong>of</strong> the different vessel trees.<br />
Group<strong>in</strong>g and l<strong>in</strong>kage: To separate the different vessel trees and to close gaps between<br />
the <strong>in</strong>dividual tubular structures, the structure based group<strong>in</strong>g and l<strong>in</strong>kage method with<br />
the verification <strong>of</strong> the connection path based on gray value <strong>in</strong>formation as presented <strong>in</strong><br />
Section 3.2 is used. The method requires a seed po<strong>in</strong>t for each <strong>of</strong> the vessels trees at the<br />
root <strong>of</strong> the tubular tree structure as well as the flow direction <strong>of</strong> each tree. To obta<strong>in</strong><br />
such seed po<strong>in</strong>ts <strong>in</strong> case <strong>of</strong> a liver masks follow<strong>in</strong>g observation can be used to specify the<br />
tree roots fully automatically. The tubular tree structures enter the organ and branch<br />
recursively, whereby their radius decreases and they never exit the organ. Therefore, all<br />
tubular structures <strong>in</strong> the dataset that pass through the surface <strong>of</strong> the provided organ mask<br />
are roots <strong>of</strong> trees. However, <strong>in</strong> case such an organ mask is not provided, the roots <strong>of</strong> the