Segmentation of 3D Tubular Tree Structures in Medical Images ...
Segmentation of 3D Tubular Tree Structures in Medical Images ...
Segmentation of 3D Tubular Tree Structures in Medical Images ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
6.2. Method 101<br />
(a)<br />
(b)<br />
(c)<br />
(d)<br />
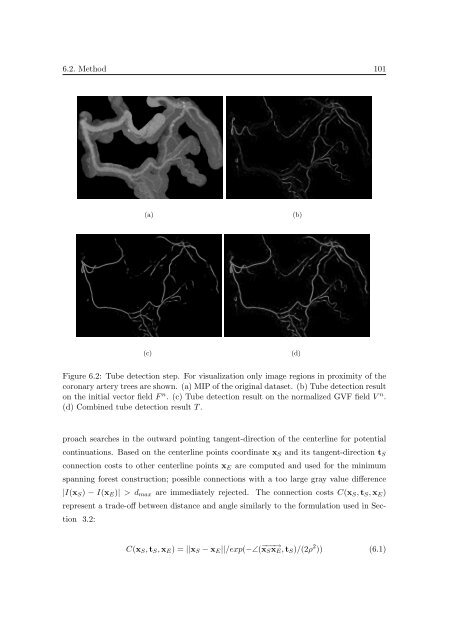
Figure 6.2: Tube detection step. For visualization only image regions <strong>in</strong> proximity <strong>of</strong> the<br />
coronary artery trees are shown. (a) MIP <strong>of</strong> the orig<strong>in</strong>al dataset. (b) Tube detection result<br />
on the <strong>in</strong>itial vector field F n . (c) Tube detection result on the normalized GVF field V n .<br />
(d) Comb<strong>in</strong>ed tube detection result T .<br />
proach searches <strong>in</strong> the outward po<strong>in</strong>t<strong>in</strong>g tangent-direction <strong>of</strong> the centerl<strong>in</strong>e for potential<br />
cont<strong>in</strong>uations. Based on the centerl<strong>in</strong>e po<strong>in</strong>ts coord<strong>in</strong>ate x S and its tangent-direction t S<br />
connection costs to other centerl<strong>in</strong>e po<strong>in</strong>ts x E are computed and used for the m<strong>in</strong>imum<br />
spann<strong>in</strong>g forest construction; possible connections with a too large gray value difference<br />
|I(x S ) − I(x E )| > d max are immediately rejected. The connection costs C(x S , t S , x E )<br />
represent a trade-<strong>of</strong>f between distance and angle similarly to the formulation used <strong>in</strong> Section<br />
3.2:<br />
C(x S , t S , x E ) = ||x S − x E ||/exp(−∠( −−−→ x S x E , t S )/(2ρ 2 )) (6.1)