Segmentation of 3D Tubular Tree Structures in Medical Images ...
Segmentation of 3D Tubular Tree Structures in Medical Images ...
Segmentation of 3D Tubular Tree Structures in Medical Images ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
3.4. Experiments 57<br />
(a) (b) (c)<br />
(d) Image based group<strong>in</strong>g/l<strong>in</strong>kage.<br />
(e) Structure based group<strong>in</strong>g/l<strong>in</strong>kage.<br />
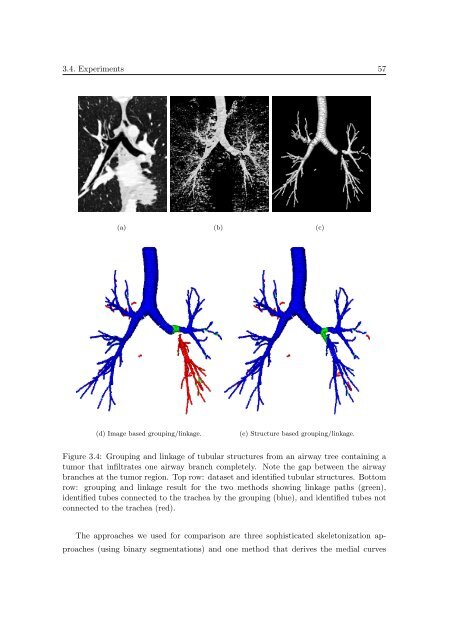
Figure 3.4: Group<strong>in</strong>g and l<strong>in</strong>kage <strong>of</strong> tubular structures from an airway tree conta<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g a<br />
tumor that <strong>in</strong>filtrates one airway branch completely. Note the gap between the airway<br />
branches at the tumor region. Top row: dataset and identified tubular structures. Bottom<br />
row: group<strong>in</strong>g and l<strong>in</strong>kage result for the two methods show<strong>in</strong>g l<strong>in</strong>kage paths (green),<br />
identified tubes connected to the trachea by the group<strong>in</strong>g (blue), and identified tubes not<br />
connected to the trachea (red).<br />
The approaches we used for comparison are three sophisticated skeletonization approaches<br />
(us<strong>in</strong>g b<strong>in</strong>ary segmentations) and one method that derives the medial curves