Chapter-1 / Physiological Foundations - WHNLive Public Library
Chapter-1 / Physiological Foundations - WHNLive Public Library
Chapter-1 / Physiological Foundations - WHNLive Public Library
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
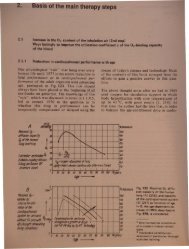
~~itItINitIIJq/s N 31 54 52~IBIP~-.t 81 mmHg/linprxttIUI't 10.79 IrPa%454035 ~/30125/V201510• .///'5 #easl.Jrement before thelim!,orocedl.Jrlj sessIon.0P02-trf ..Fig. 55 Dependence of the "non-responderrate" V of the 36 h 02MT procedure on theinitial value of the PiO" . The entire sample.,-artwas a total of 137 indiViduals; controls andpatients betvveen 1977 and 1980; at the beginning,process management not yet optimal.Result: The greater the increase inP02 betvveen the starting level and themeasaJ~ement level during the first session,the lower the failure rateInfluence of the initial increase in the P02-artunder O 2 inhalation. Closely connected to thisis the rise in the P02-art under the conditionsnamed, in relation to the initial resting value.The greater this rise, the lower the nonresponderrate, as in Fig. 54. It follows from thisthat patients with, for example, a low restinglevel and a relatively high increase under inhalation,can still be treated with a chance ofsuccess if the target level of 120--125 mmHg(16.0-16.7 kPa) is not reached under inhalation.Influence of the starting level of the P02- artbefore the procedure. If the values we obtainedare arranged according to the starting level ofthe P0 2 - art before the procedure and the nonresponderrate considered to this, then it can beseen, as in Fig. 55, that the nonresponder ratecorrelated positively with the resting level. Thelower the initial value, the greater the chancesof success. This is the statistical evidence thatyouthful P0 2 - art levels are no indication fortreatment.The procedure's slim chances in individualswith an initially high resting value are easy tounderstand. It is not possible for the 02MT toincrease the P0 2 - art levels to considerably abovethose which exist in youthful persons withhealthy lungs. An increase can be attainedwhen these levels have dropped, in old age orfrom another cause. Then, however, and ourresults show this, the increase is all the better,the greater this drop is. Particularly, patientin whom the P02- art resting level has sunkbelow the age-dependent "expected level" andwho are therefore primarily in need of help,have good prospects for success, if the conditionsresulting from the other influencing factorsare fulfilled.1.1.8.7 Further causes for lung-conditioned partial therapy nonresponders; distribution disorders;proportion of the arteriovenous shunt volumeThe causes of the reduction in the P0 2 -art andthe corresponding increases in the mean diffusion-effectivealveoloarterial O2 partial pressuredifference APo 2with increasing age are to befound less in the deterioration of the ventilationparameters with age, as in Fig. 56, andmore in the increase in the following functionaldisorders [32, 80):1. Diffusion disorder: disturbed proportion between02 diffu ion capacity DL and perfuion (pulmonary blood flow) Q.2. VA /Q distribution disorder: di turbed proportionbetween alveolar ventilation' andperfusion Q.3. DL /Q distribution disorder: di turb d proportionbetween O 2 diffu ion apa it DLand perfu ion Q.4. Increa ed arteriov nou shunt volum .The perfu ion Q of th lun apillari nimportant rol in th fun ti nal di . Iti th refor u,nd rstandabl th t th