Chapter-1 / Physiological Foundations - WHNLive Public Library
Chapter-1 / Physiological Foundations - WHNLive Public Library
Chapter-1 / Physiological Foundations - WHNLive Public Library
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
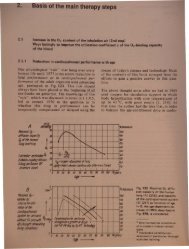
otllm'lv.2 h th ju tifi d pro p ct of favorablytnflue.ncin th furth r cou of th infarction. Ult bl m u . In 1971 w ugge ted forth. [144] th t th dose of g-strophanthin beupplemented by a lysosome stabilizer (e.g.m ~h lpredni olone) in order to hamper cytolysISand cytolytic chain reaction. By means ofthe treatment of 270 infarct patients with theuggested combination, Dohrmann achieved adrop in the mortality rate from 38 to 16 %[152 153] in his unselected patient sample inthe .Evangelisches Waldkrankenhaus Spandau,~e~lm (West). After these particular reports,It IS enough for the further therapeutic actionin this critical time-span of such practical importanc~)to refer to the comprehensive) morerecent hterature on clinical infarction therapy[154]. The experiences gathered in the last fewyears entitle us to estimate that the wide use ofthe discussed results of Dohrmann)s and ourgroups could lead to a drastic drop in infarctlethality. The way to this is to abandon [155]the old-fashioned pharmacological ideas on thelacking efficacy of the perlingually administeredg-strophanthin.Strophanthin is also of significance for othermedical disciplines) in addition to its use inmyocardiac infarction) particularly in situationswhere there is la~tacidosis) e. g. in sports medicine.According to as yet unpublished selfexperimentsby my co-worker W. Klemm)sporting performance capacity is increased inthe anaerobic boundary region (with lactateaccumulation). The same performance could beachieved on a bicycle ergometer at a lowerheart frequency after perlingual administrationof one Strodival capsule.From the above consideration we can recognizeseveral treatment phases of the acute myocardiacinfarction with differences regardingsuitable measures, effects and the chances ofsuccess. Table 8 gives an overview of these.The consequences of the O2 deficiency in alarge volume of muscle tissue have been particularlythoroughly investigated in myocardial infarction.Thus Fig. 88 can give an idea of thejoint destruction of finer blood vessels in alarge-focal necrosis in the final stage of the infarction[156]. A comparison of this figure withthe X-ray arteriography) Fig. 82, is very informativeand shows that a mechanism veryclose to nature is triggered in the cancer tissuewith the modern CMT concept.O 2inhalation is one of the tandard measuresin the therapy of acute infarct. An improvementin the O 2 tatu, a fast and a trong apo ible) i thereby trived for. Our P02 m a -urement lead to berevperhap be achieved if,lowing paragraph, a 0plemented simultaneoUllytion and a further raising 0blood fluidity were therebyunder unfavorable circulatory co:DdjitU1_It also seemed necessary to go .discussion of the complex p1roc_gering, course and therapy ofcardiac infarction, because ewith one of the main causes 0time and because a great change . OCClltWpresent in ideas about the mec:halUsm iI...,and the suitable counter-measureWith the meaningful use of vanan02MT it should be possible greathe probability of suffering a myoalldiiac-'"farction. A prophylaxis of a myocarditd infllTetionwhich attacks the primary ca e·when it is possible decisively to re ceprobability of O2 deficiency in emuscle) lasting for some minutes, which t~·Pil'Sthe infarction [Ill, 157]. One of the mfective means of avoiding such O2 deficieconditions is the use of 02MT and (or) exer .training in order to raise the O2 status wblicbhas been critically worsened in increasing age ordue to distress.In the rehabilitation phase following myocardialinfarction it seems possible to reduce considerablythe risk ofreinfarctions and to shorten theperiod of recuperation) e.g. by application ofthe 36 h 02MT procedure) GK 4-1. The patient'sstress capacity increases considerableven during this procedure) in correlation torise in the P02_art measured without additioO2 application) or in the l1-value. This fast . crease in the strain capacity is of specific sign· cance for rehabilitation after a myocardia infarction'until now treatment here has hadtread a tightrope between triggering a recurreninfarction due to too much strain and an unnecessarilyslow return to a suitable wa of li~in the case in question due to too little train.This tightrope is broadened and the ri k to thpatient thereby ignificantly reduced b meanof the discovered initial mobilization f thinfarct patient, which) in the e ample in Fi .89) occurs after the first e ion of the h02MT procedure. Thu th m bilization ffof the 02MT ignifie a d i iv aid t ha iIitationafter myo ardial infar tion hi hhould b tak n up with a littl dip ibl by all m di inal bran h n rn d iththi probl m. In rd r that thi d m ndmor a il und t d and pt dr port h r th rv ti n m d in