- Page 2 and 3:
ADVANCES INWATER TREATMENTANDENVIRO
- Page 5 and 6:
ELSEVIER SCIENCE PUBLISHERS LTDCrow
- Page 7 and 8: PART VI—RIVERS AND RIVER MANAGEME
- Page 9 and 10: FOREWORDThe quality of the environm
- Page 12: PART IPolicy matters
- Page 16 and 17: ENVIRONMENTAL STEWARDSHIP: THE ROLE
- Page 18 and 19: ENVIRONMENTAL STEWARDSHIP: THE ROLE
- Page 20 and 21: ENVIRONMENTAL STEWARDSHIP: THE ROLE
- Page 22 and 23: ENVIRONMENTAL STEWARDSHIP: THE ROLE
- Page 24 and 25: ENVIRONMENTAL STEWARDSHIP: THE ROLE
- Page 26: ENVIRONMENTAL STEWARDSHIP: THE ROLE
- Page 29: 18 WATER TREATMENTTable 1: Comparis
- Page 32 and 33: EUROPEAN DRINKING WATER STANDARDS 2
- Page 34 and 35: Chapter 3COST ESTIMATION OF DIFFERE
- Page 36 and 37: COST OF DIFFERENT WATER QUALITY PRO
- Page 38 and 39: COST OF DIFFERENT WATER QUALITY PRO
- Page 40: COST OF DIFFERENT WATER QUALITY PRO
- Page 43 and 44: 32 WATER TREATMENTThe Act enabled t
- Page 45 and 46: 34 WATER TREATMENTSome of the descr
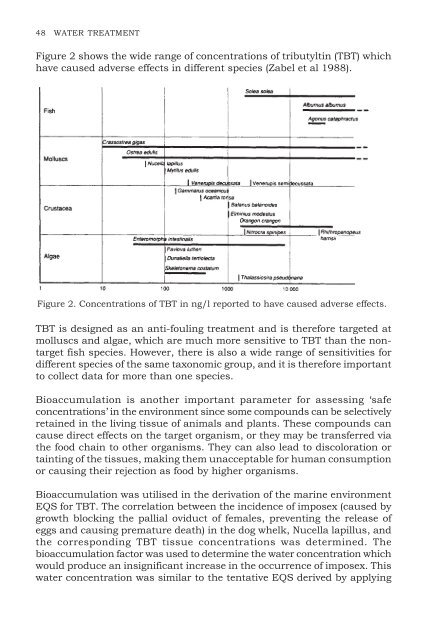
- Page 47 and 48: 36 WATER TREATMENTTable III: Parame
- Page 49 and 50: 38 WATER TREATMENT8.3 Deficiencies
- Page 51 and 52: 40 WATER TREATMENTAPPENDIXSCHEDULE
- Page 54 and 55: Chapter 5CONTROL OF DANGEROUSSUBSTA
- Page 56 and 57: CONTROL OF DANGEROUS SUBSTANCES IN
- Page 60 and 61: CONTROL OF DANGEROUS SUBSTANCES IN
- Page 62 and 63: CONTROL OF DANGEROUS SUBSTANCES IN
- Page 64: CONTROL OF DANGEROUS SUBSTANCES IN
- Page 68 and 69: Chapter 6THE GREATER LYON EMERGENCY
- Page 70 and 71: GREATER LYON EMERGENCY WATER INSTAL
- Page 72 and 73: Chapter 7EXPERT SYSTEMS FOR THEEXPL
- Page 74 and 75: EXPERT SYSTEMS FOR PURIFICATION STA
- Page 76: EXPERT SYSTEMS FOR PURIFICATION STA
- Page 80 and 81: Chapter 8APPLYING TECHNOLOGY TO THE
- Page 82 and 83: APPLYING TECHNOLOGY IN A PRIVATISED
- Page 84: APPLYING TECHNOLOGY IN A PRIVATISED
- Page 87 and 88: 76 WATER TREATMENTPublic awareness
- Page 89 and 90: 78 WATER TREATMENTcontrol system. T
- Page 91 and 92: 80 WATER TREATMENTFIGURE 2
- Page 93 and 94: 82 WATER TREATMENTFilter 1 continue
- Page 95 and 96: 84 WATER TREATMENTThe tank was cons
- Page 97 and 98: 86 WATER TREATMENTThe supernatant l
- Page 100 and 101: Chapter 10PLANT MONITORING ANDCONTR
- Page 102 and 103: PLANT MONITORING AND CONTROL SYSTEM
- Page 104 and 105: PLANT MONITORING AND CONTROL SYSTEM
- Page 106 and 107: PLANT MONITORING AND CONTROL SYSTEM
- Page 108 and 109:
PLANT MONITORING AND CONTROL SYSTEM
- Page 110 and 111:
PLANT MONITORING AND CONTROL SYSTEM
- Page 112 and 113:
PLANT MONITORING AND CONTROL SYSTEM
- Page 114:
PLANT MONITORING AND CONTROL SYSTEM
- Page 117 and 118:
106 WATER TREATMENTFIG. 2 COMBINING
- Page 119 and 120:
108 WATER TREATMENT- Operational co
- Page 121 and 122:
110 WATER TREATMENTFIG. 6 PS1 PUMP
- Page 123 and 124:
112 WATER TREATMENThrs to prevent r
- Page 125 and 126:
114 WATER TREATMENTDecision support
- Page 128 and 129:
Chapter 12GAS LIQUID MIXING AND MAS
- Page 130 and 131:
GAS LIQUID MIXING AND MASS TRANSFER
- Page 132 and 133:
GAS LIQUID MIXING AND MASS TRANSFER
- Page 134 and 135:
5. Waste Water Processing Technique
- Page 136 and 137:
GAS LIQUID MIXING AND MASS TRANSFER
- Page 138 and 139:
In summary, to quote reference 10,
- Page 140:
PART IVControl and measurementtechn
- Page 143 and 144:
132 WATER TREATMENTThese perceived
- Page 145 and 146:
134 WATER TREATMENTSuch deteriorati
- Page 147 and 148:
136 WATER TREATMENTresources throug
- Page 149 and 150:
138 WATER TREATMENTMobile equipment
- Page 152 and 153:
Chapter 14MEASUREMENTS OF MASSTRANS
- Page 154 and 155:
MEASUREMENTS OF MASS TRANSFER IN A
- Page 156 and 157:
MEASUREMENTS OF MASS TRANSFER IN A
- Page 158 and 159:
MEASUREMENTS OF MASS TRANSFER IN A
- Page 160 and 161:
MEASUREMENTS OF MASS TRANSFER IN A
- Page 162 and 163:
MEASUREMENTS OF MASS TRANSFER IN A
- Page 164 and 165:
MEASUREMENTS OF MASS TRANSFER IN A
- Page 166:
PART VTreatment: innovation andappl
- Page 169 and 170:
158 WATER TREATMENTiii)iv)The progr
- Page 171 and 172:
160 WATER TREATMENTof its generatio
- Page 173 and 174:
162 WATER TREATMENTA last point of
- Page 176 and 177:
Chapter 16COLLECTION EFFICIENCY OFL
- Page 178 and 179:
COLLECTION EFFICIENCY OF LIQUID/LIQ
- Page 180 and 181:
COLLECTION EFFICIENCY OF LIQUID/LIQ
- Page 182 and 183:
COLLECTION EFFICIENCY OF LIQUID/LIQ
- Page 184 and 185:
Chapter 17UNDERSTANDING THE FOULING
- Page 186 and 187:
FOULING PHENOMENON IN CROSS-FLOW MI
- Page 188 and 189:
FOULING PHENOMENON IN CROSS-FLOW MI
- Page 190 and 191:
FOULING PHENOMENON IN CROSS-FLOW MI
- Page 192 and 193:
Chapter 18ADSORPTION OFTRIHALOMETHA
- Page 194 and 195:
ADSORPTION OF TRIHALOMETHANES ON TO
- Page 196 and 197:
ADSORPTION OF TRIHALOMETHANES ON TO
- Page 198 and 199:
ADSORPTION OF TRIHALOMETHANES ON TO
- Page 200 and 201:
ADSORPTION OF TRIHALOMETHANES ON TO
- Page 202 and 203:
Chapter 19DEVELOPMENTS IN IONEXCHAN
- Page 204 and 205:
DEVELOPMENTS IN ION EXCHANGE DENITR
- Page 206 and 207:
DEVELOPMENTS IN ION EXCHANGE DENITR
- Page 208:
DEVELOPMENTS IN ION EXCHANGE DENITR
- Page 211 and 212:
200 WATER TREATMENTL m = molar liqu
- Page 213 and 214:
202 WATER TREATMENTliquid-liquid ex
- Page 215 and 216:
204 WATER TREATMENTThe investigatio
- Page 217 and 218:
206 WATER TREATMENTAn additional 14
- Page 219 and 220:
208 WATER TREATMENTFig. 7b Concentr
- Page 221 and 222:
210 WATER TREATMENTTABLE 1Design pa
- Page 223 and 224:
212 WATER TREATMENTTABLE 2Performan
- Page 225 and 226:
214 WATER TREATMENTdosing of Calgon
- Page 227 and 228:
216 WATER TREATMENTGreen D W & Molo
- Page 230 and 231:
Chapter 21GREEN ENGINEERING: THE CA
- Page 232 and 233:
GREEN ENGINEERING: THE CASE OF LAND
- Page 234 and 235:
Chapter 22PREVENTION OF WATERPOLLUT
- Page 236 and 237:
NON-POINT DISCHARGES FROM URBAN ARE
- Page 238 and 239:
NON-POINT DISCHARGES FROM URBAN ARE
- Page 240 and 241:
NON-POINT DISCHARGES FROM URBAN ARE
- Page 242 and 243:
Chapter 23THE RIVER FANE FLOWREGULA
- Page 244 and 245:
RIVER FANE FLOW REGULATION SCHEME 2
- Page 246 and 247:
RIVER FANE FLOW REGULATION SCHEME 2
- Page 248 and 249:
RIVER FANE FLOW REGULATION SCHEME 2
- Page 250 and 251:
RIVER FANE FLOW REGULATION SCHEME 2
- Page 252:
RIVER FANE FLOW REGULATION SCHEME 2
- Page 256 and 257:
Chapter 24RIBBLE ESTUARY WATER QUAL
- Page 258 and 259:
RIBBLE ESTUARY WATER QUALITY IMPROV
- Page 260 and 261:
RIBBLE ESTUARY WATER QUALITY IMPROV
- Page 262 and 263:
RIBBLE ESTUARY WATER QUALITY IMPROV
- Page 264:
RIBBLE ESTUARY WATER QUALITY IMPROV
- Page 267 and 268:
256 WATER TREATMENTThe long term ef
- Page 269 and 270:
258 WATER TREATMENTIn the bottom of
- Page 271 and 272:
260 WATER TREATMENT7.1 Efficiency o
- Page 273 and 274:
262 WATER TREATMENT8. THE RESULTS8.
- Page 275 and 276:
264 WATER TREATMENTSS and AramN lev
- Page 277 and 278:
266 WATER TREATMENT8.5 RainfallRain
- Page 279 and 280:
268 WATER TREATMENTsimultaneously.