Download the ESMO 2012 Abstract Book - Oxford Journals
Download the ESMO 2012 Abstract Book - Oxford Journals
Download the ESMO 2012 Abstract Book - Oxford Journals
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
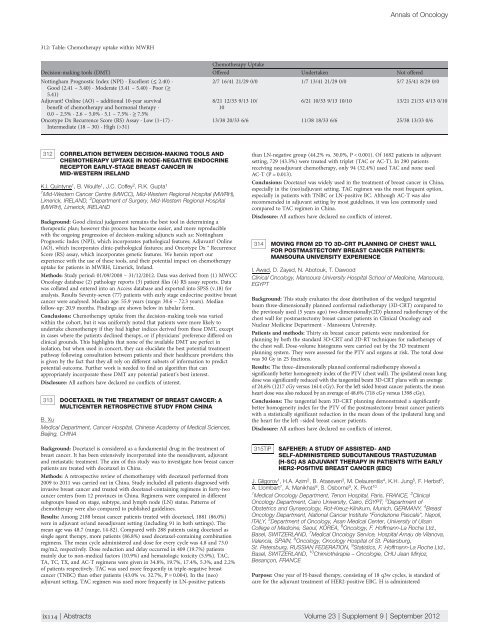
312: Table: Chemo<strong>the</strong>rapy uptake within MWRH<br />
Decision-making tools (DMT)<br />
Nottingham Prognostic Index (NPI) · Excellent (≤ 2.40) ·<br />
Good (2.41 – 3.40) · Moderate (3.41 – 5.40) · Poor (≥<br />
5.41)<br />
Adjuvant! Online (AO) – additional 10-year survival<br />
benefit of chemo<strong>the</strong>rapy and hormonal <strong>the</strong>rapy ·<br />
0.0 – 2.5% · 2.6 – 5.0% · 5.1 – 7.5% · ≥ 7.5%<br />
Oncotype Dx Recurrence Score (RS) Assay · Low (1–17) ·<br />
Intermediate (18 – 30) · High (>31)<br />
312 CORRELATION BETWEEN DECISION-MAKING TOOLS AND<br />
CHEMOTHERAPY UPTAKE IN NODE-NEGATIVE ENDOCRINE<br />
RECEPTOR EARLY-STAGE BREAST CANCER IN<br />
MID-WESTERN IRELAND<br />
K.I. Quintyne 1 , B. Woulfe 1 , J.C. Coffey 2 , R.K. Gupta 1<br />
1 Mid-Western Cancer Centre (MWCC), Mid-Western Regional Hospital (MWRH),<br />
Limerick, IRELAND, 2 Department of Surgery, Mid-Western Regional Hospital<br />
(MWRH), Limerick, IRELAND<br />
Background: Good clinical judgement remains <strong>the</strong> best tool in determining a<br />
<strong>the</strong>rapeutic plan; however this process has become easier, and more reproducible<br />
with <strong>the</strong> ongoing progression of decision-making adjuncts such as: Nottingham<br />
Prognostic Index (NPI), which incorporates pathological features; Adjuvant! Online<br />
(AO), which incorporates clinic-pathological features; and Oncotype Dx ® Recurrence<br />
Score (RS) assay, which incorporates genetic features. We herein report our<br />
experience with <strong>the</strong> use of <strong>the</strong>se tools, and <strong>the</strong>ir potential impact on chemo<strong>the</strong>rapy<br />
uptake for patients in MWRH, Limerick, Ireland.<br />
Methods: Study period: 01/09/2008 – 31/12/<strong>2012</strong>. Data was derived from (1) MWCC<br />
Oncology database (2) pathology reports (3) patient files (4) RS assay reports. Data<br />
was collated and entered into an Access database and exported into SPSS (v.18) for<br />
analysis. Results Seventy-seven (77) patients with early stage endocrine positive breast<br />
cancer were analysed. Median age: 55.9 years (range: 30.6 – 72.3 years). Median<br />
follow-up: 20.9 months. Findings are shown below in tabular form.<br />
Conclusions: Chemo<strong>the</strong>rapy uptake from <strong>the</strong> decision-making tools was varied<br />
within <strong>the</strong> cohort, but it was uniformly noted that patients were more likely to<br />
undertake chemo<strong>the</strong>rapy if <strong>the</strong>y had higher indices derived from <strong>the</strong>se DMT, except<br />
in cases where <strong>the</strong> patients declined <strong>the</strong>rapy, or if physicians’ preference differed on<br />
clinical grounds. This highlights that none of <strong>the</strong> available DMT are perfect in<br />
isolation, but when used in concert, <strong>the</strong>y can elucidate <strong>the</strong> best potential treatment<br />
pathway following consultation between patients and <strong>the</strong>ir healthcare providers; this<br />
is given by <strong>the</strong> fact that <strong>the</strong>y all rely on different subsets of information to predict<br />
potential outcome. Fur<strong>the</strong>r work is needed to find an algorithm that can<br />
appropriately incorporate <strong>the</strong>se DMT any potential patient’s best interest.<br />
Disclosure: All authors have declared no conflicts of interest.<br />
313 DOCETAXEL IN THE TREATMENT OF BREAST CANCER: A<br />
MULTICENTER RETROSPECTIVE STUDY FROM CHINA<br />
B. Xu<br />
Medical Department, Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences,<br />
Beijing, CHINA<br />
Background: Docetaxel is considered as a fundamental drug in <strong>the</strong> treatment of<br />
breast cancer. It has been extensively incorporated into <strong>the</strong> neoadjuvant, adjuvant<br />
and metastatic treatment. The aim of this study was to investigate how breast cancer<br />
patients are treated with docetaxel in China.<br />
Methods: A retrospective review of chemo<strong>the</strong>rapy with docetaxel performed from<br />
2009 to 2011 was carried out in China. Study included all patients diagnosed with<br />
invasive breast cancer and treated with docetaxel-containing regimens in forty-two<br />
cancer centers from 12 provinces in China. Regimens were compared in different<br />
subgroups based on stage, subtype, and lymph node (LN) status. Patterns of<br />
chemo<strong>the</strong>rapy were also compared to published guidelines.<br />
Results: Among 2188 breast cancer patients treated with docetaxel, 1881 (86.0%)<br />
were in adjuvant or/and neoadjuvant setting (including 91 in both settings). The<br />
mean age was 48.7 (range, 14-82). Compared with 288 patients using docetaxel as<br />
single agent <strong>the</strong>rapy, more patients (86.8%) used docetaxel-containing combination<br />
regimens. The mean cycle administered and dose for every cycle was 4.8 and 73.0<br />
mg/m2, respectively. Dose reduction and delay occurred in 409 (19.7%) patients<br />
mainly due to non-medical factors (10.9%) and hematologic toxicity (5.9%). TAC,<br />
TA, TC, TX, and AC-T regimens were given in 34.8%, 19.7%, 17.4%, 5.3%, and 2.2%<br />
of patients respectively. TAC was used more frequently in triple-negative breast<br />
cancer (TNBC) than o<strong>the</strong>r patients (43.0% vs. 32.7%, P = 0.004). In <strong>the</strong> (neo)<br />
adjuvant setting, TAC regimen was used more frequently in LN-positive patients<br />
Chemo<strong>the</strong>rapy Uptake<br />
Offered Undertaken Not offered<br />
2/7 16/41 21/29 0/0 1/7 13/41 21/29 0/0 5/7 25/41 8/29 0/0<br />
8/21 12/33 9/13 10/<br />
10<br />
Annals of Oncology<br />
6/21 10/33 9/13 10/10 13/21 21/33 4/13 0/10<br />
13/38 20/33 6/6 11/38 18/33 6/6 25/38 13/33 0/6<br />
than LN-negative group (44.2% vs. 30.0%, P < 0.001). Of 1682 patients in adjuvant<br />
setting, 729 (43.3%) were treated with triplet (TAC or AC-T). In 290 patients<br />
receiving neoadjuvant chemo<strong>the</strong>rapy, only 94 (32.4%) used TAC and none used<br />
AC-T (P = 0.013).<br />
Conclusions: Docetaxel was widely used in <strong>the</strong> treatment of breast cancer in China,<br />
especially in <strong>the</strong> (neo)adjuvant setting. TAC regimen was <strong>the</strong> most frequent option,<br />
especially in patients with TNBC or LN-positive BC. Although AC-T was also<br />
recommended in adjuvant setting by most guidelines, it was less commonly used<br />
compared to TAC regimen in China.<br />
Disclosure: All authors have declared no conflicts of interest.<br />
314 MOVING FROM 2D TO 3D-CRT PLANNING OF CHEST WALL<br />
FOR POSTMASTECTOMY BREAST CANCER PATIENTS:<br />
MANSOURA UNIVERSITY EXPERIENCE<br />
I. Awad, D. Zayed, N. Abotouk, T. Dawood<br />
Clinical Oncology, Mansoura University Hospital School of Medicine, Mansoura,<br />
EGYPT<br />
Background: This study evaluates <strong>the</strong> dose distribution of <strong>the</strong> wedged tangential<br />
beam three-dimensionally planned conformal radio<strong>the</strong>rapy (3D-CRT) compared to<br />
<strong>the</strong> previously used (5 years ago) two-dimensionally(2D) planned radio<strong>the</strong>rapy of <strong>the</strong><br />
chest wall for postmastectomy breast cancer patients in Clinical Oncology and<br />
Nuclear Medicine Department - Mansoura University.<br />
Patients and methods: Thirty six breast cancer patients were randomized for<br />
planning by both <strong>the</strong> standard 3D-CRT and 2D-RT techniques for radio<strong>the</strong>rapy of<br />
<strong>the</strong> chest wall. Dose-volume histograms were carried out by <strong>the</strong> 3D treatment<br />
planning system. They were assessed for <strong>the</strong> PTV and organs at risk. The total dose<br />
was 50 Gy in 25 fractions.<br />
Results: The three–dimensionally planned conformal radio<strong>the</strong>rapy showed a<br />
significantly better homogeneity index of <strong>the</strong> PTV (chest wall). The ipsilateral mean lung<br />
dose was significantly reduced with <strong>the</strong> tangential beam 3D-CRT plans with an average<br />
of 24.6% (1217 cGy versus 1614 cGy). For <strong>the</strong> left sided breast cancer patients, <strong>the</strong> mean<br />
heart dose was also reduced by an average of 48.6% (718 cGy versus 1398 cGy).<br />
Conclusions: The tangential beam 3D-CRT planning demonstrated a significantly<br />
better homogeneity index for <strong>the</strong> PTV of <strong>the</strong> postmastectomy breast cancer patients<br />
with a statistically significant reduction in <strong>the</strong> mean doses of <strong>the</strong> ipsilateral lung and<br />
<strong>the</strong> heart for <strong>the</strong> left –sided breast cancer patients.<br />
Disclosure: All authors have declared no conflicts of interest.<br />
315TiP SAFEHER: A STUDY OF ASSISTED- AND<br />
SELF-ADMINISTERED SUBCUTANEOUS TRASTUZUMAB<br />
(H-SC) AS ADJUVANT THERAPY IN PATIENTS WITH EARLY<br />
HER2-POSITIVE BREAST CANCER (EBC)<br />
J. Gligorov 1 , H.A. Azim 2 , B. Ataseven 3 , M. Delaurentiis 4 , K.H. Jung 5 , F. Herbst 6 ,<br />
A. Llombart 7 , A. Manikhas 8 , S. Osborne 9 , X. Pivot 10<br />
1 Medical Oncology Department, Tenon Hospital, Paris, FRANCE, 2 Clinical<br />
Oncology Department, Cairo University, Cairo, EGYPT, 3 Department of<br />
Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Rot-Kreuz-Klinikum, Munich, GERMANY, 4 Breast<br />
Oncology Department, National Cancer Institute “Fondazione Pascale”, Napoli,<br />
ITALY, 5 Department of Oncology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan<br />
College of Medicine, Seoul, KOREA, 6 Oncology, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.,<br />
Basel, SWITZERLAND, 7 Medical Oncology Service, Hospital Arnau de Vilanova,<br />
Valencia, SPAIN, 8 Oncology, Oncology Hospital of St. Petersburg,<br />
St. Petersburg, RUSSIAN FEDERATION, 9 Statistics, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.,<br />
Basel, SWITZERLAND, 10 Chimiothérapie – Oncologie, CHU Jean Minjoz,<br />
Besançon, FRANCE<br />
Purpose: One year of H-based <strong>the</strong>rapy, consisting of 18 q3w cycles, is standard of<br />
care for <strong>the</strong> adjuvant treatment of HER2-positive EBC. H is administered<br />
ix114 | <strong>Abstract</strong>s Volume 23 | Supplement 9 | September <strong>2012</strong>