APPENDICES. A systematic review and economic model of the ...
APPENDICES. A systematic review and economic model of the ...
APPENDICES. A systematic review and economic model of the ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
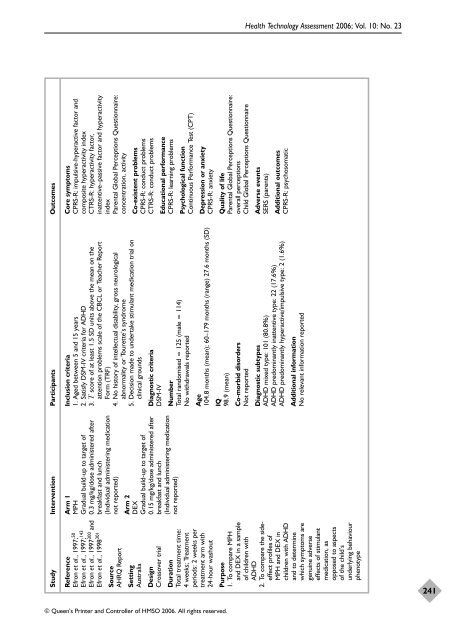
Study Intervention Participants Outcomes<br />
Core symptoms<br />
CPRS-R: impulsive-hyperactive factor <strong>and</strong><br />
composite hyperactivity index<br />
CTRS-R: hyperactivity factor,<br />
inattentive–passive factor <strong>and</strong> hyperactivity<br />
index<br />
Parental Global Perceptions Questionnaire:<br />
concentration, activity<br />
Arm 1<br />
MPH<br />
Gradual build-up to target <strong>of</strong><br />
0.3 mg/kg/dose administered after<br />
breakfast <strong>and</strong> lunch<br />
(Individual administering medication<br />
not reported)<br />
Reference<br />
Efron et al., 1997; 50<br />
Efron et al., 1997; 143<br />
Efron et al., 1997300 <strong>and</strong><br />
Efron et al., 1998 301<br />
Source<br />
AHRQ Report<br />
Co-existent problems<br />
CPRS-R: conduct problems<br />
CTRS-R: conduct problems<br />
Inclusion criteria<br />
1. Aged between 5 <strong>and</strong> 15 years<br />
2. Satisfy DSM-IV criteria for ADHD<br />
3. T score <strong>of</strong> at least 1.5 SD units above <strong>the</strong> mean on <strong>the</strong><br />
attention problems scale <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> CBCL or Teacher Report<br />
Form (TRF)<br />
4. No history <strong>of</strong> intellectual disability, gross neurological<br />
abnormality or Tourette’s syndrome<br />
5. Decision made to undertake stimulant medication trial on<br />
clinical grounds<br />
Setting<br />
Australia<br />
Diagnostic criteria<br />
DSM-IV<br />
Arm 2<br />
DEX<br />
Gradual build-up to target <strong>of</strong><br />
0.15 mg/kg/dose administered after<br />
breakfast <strong>and</strong> lunch<br />
(Individual administering medication<br />
not reported)<br />
Design<br />
Crossover trial<br />
Educational performance<br />
CPRS-R: learning problems<br />
Psychological function<br />
Continuous Performance Test (CPT)<br />
Number<br />
Total r<strong>and</strong>omised = 125 (male = 114)<br />
No withdrawals reported<br />
Age<br />
104.8 months (mean); 60–179 months (range) 27.6 months (SD)<br />
Duration<br />
Total treatment time:<br />
4 weeks; Treatment<br />
periods: 2 weeks per<br />
treatment arm with<br />
24-hour washout<br />
Depression or anxiety<br />
CPRS-R: anxiety<br />
Quality <strong>of</strong> life<br />
Parental Global Perceptions Questionnaire:<br />
overall perceptions<br />
Child Global Perceptions Questionnaire<br />
IQ<br />
98.9 (mean)<br />
© Queen’s Printer <strong>and</strong> Controller <strong>of</strong> HMSO 2006. All rights reserved.<br />
Co-morbid disorders<br />
Not reported<br />
Health Technology Assessment 2006; Vol. 10: No. 23<br />
Adverse events<br />
SERS (parents)<br />
Additional outcomes<br />
CPRS-R: psychosomatic<br />
Diagnostic subtypes<br />
ADHD mixed type: 101 (80.8%)<br />
ADHD predominantly inattentive type: 22 (17.6%)<br />
ADHD predominantly hyperactive/impulsive type: 2 (1.6%)<br />
Additional information<br />
No relevant information reported<br />
Purpose<br />
1. To compare MPH<br />
<strong>and</strong> DEX in a sample<br />
<strong>of</strong> children with<br />
ADHD<br />
2. To compare <strong>the</strong> sideeffect<br />
pr<strong>of</strong>iles <strong>of</strong><br />
MPH <strong>and</strong> DEX in<br />
children with ADHD<br />
<strong>and</strong> to determine<br />
which symptoms are<br />
genuine adverse<br />
effects <strong>of</strong> stimulant<br />
medication, as<br />
opposed to aspects<br />
<strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> child’s<br />
underlying behaviour<br />
phenotype<br />
241