Status of medicinal and aromatic plants in - Inia
Status of medicinal and aromatic plants in - Inia
Status of medicinal and aromatic plants in - Inia
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
PRESENTED PAPERS 53<br />
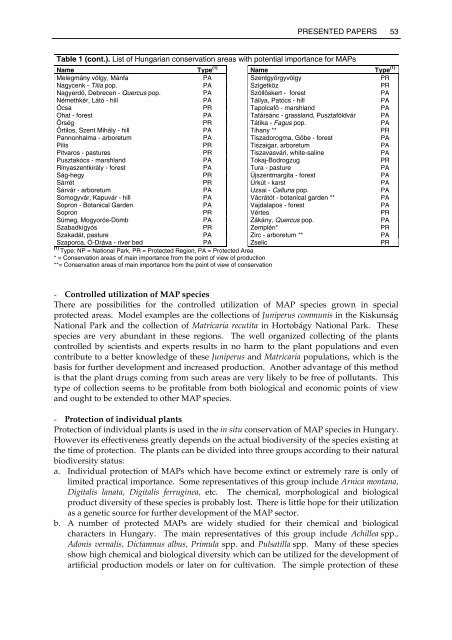
Table 1 (cont.). List <strong>of</strong> Hungarian conservation areas with potential importance for MAPs<br />
Name Type (1) Name Type (1)<br />
Melegmány völgy, Mánfa PA Szentgyörgyvölgy PR<br />
Nagycenk - Tilia pop. PA Szigetköz PR<br />
Nagyerdö, Debrecen - Quercus pop. PA Szöllôskert - forest PA<br />
Némethkér, Látó - hill PA Tállya, Patócs - hill PA<br />
Ócsa PR Tapolcafô - marshl<strong>and</strong> PA<br />
Ohat - forest PA Tatársánc - grassl<strong>and</strong>, Pusztaföldvár PA<br />
Ôrség PR Tátika - Fagus pop. PA<br />
Ôrtilos, Szent Mihály - hill PA Tihany ** PR<br />
Pannonhalma - arboretum PA Tiszadorogma, Göbe - forest PA<br />
Pilis PR Tiszaigar, arboretum PA<br />
Pitvaros - pastures PR Tiszavasvári, white-sal<strong>in</strong>e PA<br />
Pusztakócs - marshl<strong>and</strong> PA Tokaj-Bodrogzug PR<br />
R<strong>in</strong>yaszentkirály - forest PA Tura - pasture PA<br />
Ság-hegy PR Újszentmargita - forest PA<br />
Sárrét PR Úrkút - karst PA<br />
Sárvár - arboretum PA Uzsai - Calluna pop. PA<br />
Somogyvár, Kapuvár - hill PA Vácrátót - botanical garden ** PA<br />
Sopron - Botanical Garden PA Vajdalapos - forest PA<br />
Sopron PR Vértes PR<br />
Sümeg, Mogyorós-Domb PA Zákány, Quercus pop. PA<br />
Szabadkígyós PR Zemplén* PR<br />
Szakadát, pasture PA Zirc - arboretum ** PA<br />
Szaporca, Ó-Dráva - river bed PA Zselic PR<br />
(1)<br />
Type: NP = National Park, PR = Protected Region, PA = Protected Area<br />
* = Conservation areas <strong>of</strong> ma<strong>in</strong> importance from the po<strong>in</strong>t <strong>of</strong> view <strong>of</strong> production<br />
**= Conservation areas <strong>of</strong> ma<strong>in</strong> importance from the po<strong>in</strong>t <strong>of</strong> view <strong>of</strong> conservation<br />
- Controlled utilization <strong>of</strong> MAP species<br />
There are possibilities for the controlled utilization <strong>of</strong> MAP species grown <strong>in</strong> special<br />
protected areas. Model examples are the collections <strong>of</strong> Juniperus communis <strong>in</strong> the Kiskunság<br />
National Park <strong>and</strong> the collection <strong>of</strong> Matricaria recutita <strong>in</strong> Hortobágy National Park. These<br />
species are very abundant <strong>in</strong> these regions. The well organized collect<strong>in</strong>g <strong>of</strong> the <strong>plants</strong><br />
controlled by scientists <strong>and</strong> experts results <strong>in</strong> no harm to the plant populations <strong>and</strong> even<br />
contribute to a better knowledge <strong>of</strong> these Juniperus <strong>and</strong> Matricaria populations, which is the<br />
basis for further development <strong>and</strong> <strong>in</strong>creased production. Another advantage <strong>of</strong> this method<br />
is that the plant drugs com<strong>in</strong>g from such areas are very likely to be free <strong>of</strong> pollutants. This<br />
type <strong>of</strong> collection seems to be pr<strong>of</strong>itable from both biological <strong>and</strong> economic po<strong>in</strong>ts <strong>of</strong> view<br />
<strong>and</strong> ought to be extended to other MAP species.<br />
- Protection <strong>of</strong> <strong>in</strong>dividual <strong>plants</strong><br />
Protection <strong>of</strong> <strong>in</strong>dividual <strong>plants</strong> is used <strong>in</strong> the <strong>in</strong> situ conservation <strong>of</strong> MAP species <strong>in</strong> Hungary.<br />
However its effectiveness greatly depends on the actual biodiversity <strong>of</strong> the species exist<strong>in</strong>g at<br />
the time <strong>of</strong> protection. The <strong>plants</strong> can be divided <strong>in</strong>to three groups accord<strong>in</strong>g to their natural<br />
biodiversity status:<br />
a. Individual protection <strong>of</strong> MAPs which have become ext<strong>in</strong>ct or extremely rare is only <strong>of</strong><br />
limited practical importance. Some representatives <strong>of</strong> this group <strong>in</strong>clude Arnica montana,<br />
Digitalis lanata, Digitalis ferrug<strong>in</strong>ea, etc. The chemical, morphological <strong>and</strong> biological<br />
product diversity <strong>of</strong> these species is probably lost. There is little hope for their utilization<br />
as a genetic source for further development <strong>of</strong> the MAP sector.<br />
b. A number <strong>of</strong> protected MAPs are widely studied for their chemical <strong>and</strong> biological<br />
characters <strong>in</strong> Hungary. The ma<strong>in</strong> representatives <strong>of</strong> this group <strong>in</strong>clude Achillea spp.,<br />
Adonis vernalis, Dictamnus albus, Primula spp. <strong>and</strong> Pulsatilla spp. Many <strong>of</strong> these species<br />
show high chemical <strong>and</strong> biological diversity which can be utilized for the development <strong>of</strong><br />
artificial production models or later on for cultivation. The simple protection <strong>of</strong> these