The role of metacognitive skills in learning to solve problems
The role of metacognitive skills in learning to solve problems
The role of metacognitive skills in learning to solve problems
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Study II: learn<strong>in</strong>g revisited 97<br />
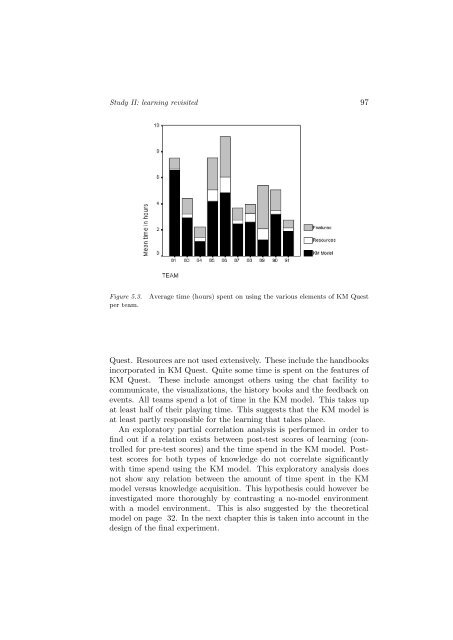
Figure 5.3.<br />
per team.<br />
Average time (hours) spent on us<strong>in</strong>g the various elements <strong>of</strong> KM Quest<br />
Quest. Resources are not used extensively. <strong>The</strong>se <strong>in</strong>clude the handbooks<br />
<strong>in</strong>corporated <strong>in</strong> KM Quest. Quite some time is spent on the features <strong>of</strong><br />
KM Quest. <strong>The</strong>se <strong>in</strong>clude amongst others us<strong>in</strong>g the chat facility <strong>to</strong><br />
communicate, the visualizations, the his<strong>to</strong>ry books and the feedback on<br />
events. All teams spend a lot <strong>of</strong> time <strong>in</strong> the KM model. This takes up<br />
at least half <strong>of</strong> their play<strong>in</strong>g time. This suggests that the KM model is<br />
at least partly responsible for the learn<strong>in</strong>g that takes place.<br />
An explora<strong>to</strong>ry partial correlation analysis is performed <strong>in</strong> order <strong>to</strong><br />
f<strong>in</strong>d out if a relation exists between post-test scores <strong>of</strong> learn<strong>in</strong>g (controlled<br />
for pre-test scores) and the time spend <strong>in</strong> the KM model. Posttest<br />
scores for both types <strong>of</strong> knowledge do not correlate significantly<br />
with time spend us<strong>in</strong>g the KM model. This explora<strong>to</strong>ry analysis does<br />
not show any relation between the amount <strong>of</strong> time spent <strong>in</strong> the KM<br />
model versus knowledge acquisition. This hypothesis could however be<br />
<strong>in</strong>vestigated more thoroughly by contrast<strong>in</strong>g a no-model environment<br />
with a model environment. This is also suggested by the theoretical<br />
model on page 32. In the next chapter this is taken <strong>in</strong><strong>to</strong> account <strong>in</strong> the<br />
design <strong>of</strong> the f<strong>in</strong>al experiment.