The role of metacognitive skills in learning to solve problems
The role of metacognitive skills in learning to solve problems
The role of metacognitive skills in learning to solve problems
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Study III: added value <strong>of</strong> the task model 121<br />
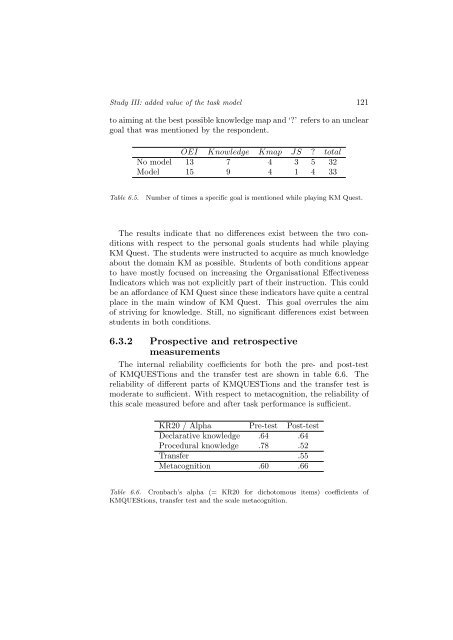
<strong>to</strong> aim<strong>in</strong>g at the best possible knowledge map and ‘?’ refers <strong>to</strong> an unclear<br />
goal that was mentioned by the respondent.<br />
OEI Knowledge Kmap JS ? <strong>to</strong>tal<br />
No model 13 7 4 3 5 32<br />
Model 15 9 4 1 4 33<br />
Table 6.5.<br />
Number <strong>of</strong> times a specific goal is mentioned while play<strong>in</strong>g KM Quest.<br />
<strong>The</strong> results <strong>in</strong>dicate that no differences exist between the two conditions<br />
with respect <strong>to</strong> the personal goals students had while play<strong>in</strong>g<br />
KM Quest. <strong>The</strong> students were <strong>in</strong>structed <strong>to</strong> acquire as much knowledge<br />
about the doma<strong>in</strong> KM as possible. Students <strong>of</strong> both conditions appear<br />
<strong>to</strong> have mostly focused on <strong>in</strong>creas<strong>in</strong>g the Organisational Effectiveness<br />
Indica<strong>to</strong>rs which was not explicitly part <strong>of</strong> their <strong>in</strong>struction. This could<br />
be an affordance <strong>of</strong> KM Quest s<strong>in</strong>ce these <strong>in</strong>dica<strong>to</strong>rs have quite a central<br />
place <strong>in</strong> the ma<strong>in</strong> w<strong>in</strong>dow <strong>of</strong> KM Quest. This goal overrules the aim<br />
<strong>of</strong> striv<strong>in</strong>g for knowledge. Still, no significant differences exist between<br />
students <strong>in</strong> both conditions.<br />
6.3.2 Prospective and retrospective<br />
measurements<br />
<strong>The</strong> <strong>in</strong>ternal reliability coefficients for both the pre- and post-test<br />
<strong>of</strong> KMQUESTions and the transfer test are shown <strong>in</strong> table 6.6. <strong>The</strong><br />
reliability <strong>of</strong> different parts <strong>of</strong> KMQUESTions and the transfer test is<br />
moderate <strong>to</strong> sufficient. With respect <strong>to</strong> metacognition, the reliability <strong>of</strong><br />
this scale measured before and after task performance is sufficient.<br />
KR20 / Alpha Pre-test Post-test<br />
Declarative knowledge .64 .64<br />
Procedural knowledge .78 .52<br />
Transfer .55<br />
Metacognition .60 .66<br />
Table 6.6. Cronbach’s alpha (= KR20 for dicho<strong>to</strong>mous items) coefficients <strong>of</strong><br />
KMQUEStions, transfer test and the scale metacognition.