The role of metacognitive skills in learning to solve problems
The role of metacognitive skills in learning to solve problems
The role of metacognitive skills in learning to solve problems
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Study III: added value <strong>of</strong> the task model 111<br />
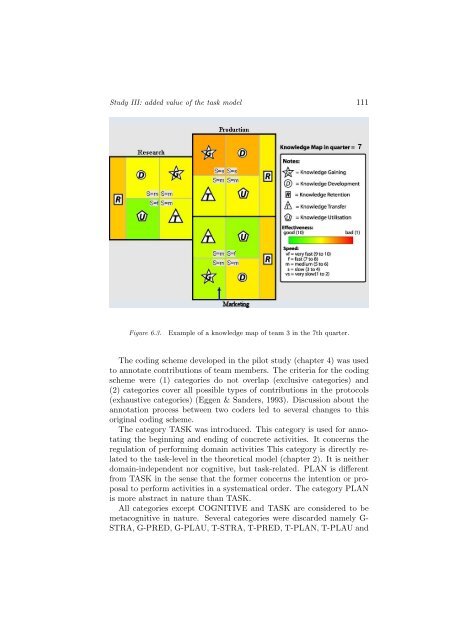
Figure 6.3.<br />
Example <strong>of</strong> a knowledge map <strong>of</strong> team 3 <strong>in</strong> the 7th quarter.<br />
<strong>The</strong> cod<strong>in</strong>g scheme developed <strong>in</strong> the pilot study (chapter 4) was used<br />
<strong>to</strong> annotate contributions <strong>of</strong> team members. <strong>The</strong> criteria for the cod<strong>in</strong>g<br />
scheme were (1) categories do not overlap (exclusive categories) and<br />
(2) categories cover all possible types <strong>of</strong> contributions <strong>in</strong> the pro<strong>to</strong>cols<br />
(exhaustive categories) (Eggen & Sanders, 1993). Discussion about the<br />
annotation process between two coders led <strong>to</strong> several changes <strong>to</strong> this<br />
orig<strong>in</strong>al cod<strong>in</strong>g scheme.<br />
<strong>The</strong> category TASK was <strong>in</strong>troduced. This category is used for annotat<strong>in</strong>g<br />
the beg<strong>in</strong>n<strong>in</strong>g and end<strong>in</strong>g <strong>of</strong> concrete activities. It concerns the<br />
regulation <strong>of</strong> perform<strong>in</strong>g doma<strong>in</strong> activities This category is directly related<br />
<strong>to</strong> the task-level <strong>in</strong> the theoretical model (chapter 2). It is neither<br />
doma<strong>in</strong>-<strong>in</strong>dependent nor cognitive, but task-related. PLAN is different<br />
from TASK <strong>in</strong> the sense that the former concerns the <strong>in</strong>tention or proposal<br />
<strong>to</strong> perform activities <strong>in</strong> a systematical order. <strong>The</strong> category PLAN<br />
is more abstract <strong>in</strong> nature than TASK.<br />
All categories except COGNITIVE and TASK are considered <strong>to</strong> be<br />
<strong>metacognitive</strong> <strong>in</strong> nature. Several categories were discarded namely G-<br />
STRA, G-PRED, G-PLAU, T-STRA, T-PRED, T-PLAN, T-PLAU and