The role of metacognitive skills in learning to solve problems
The role of metacognitive skills in learning to solve problems
The role of metacognitive skills in learning to solve problems
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
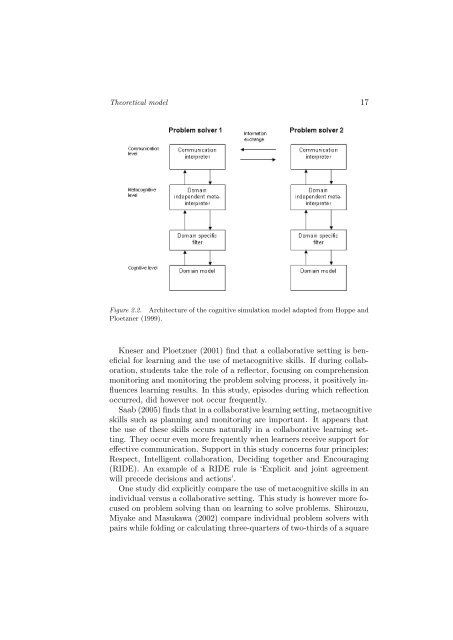
<strong>The</strong>oretical model 17<br />
Figure 2.2. Architecture <strong>of</strong> the cognitive simulation model adapted from Hoppe and<br />
Ploetzner (1999).<br />
Kneser and Ploetzner (2001) f<strong>in</strong>d that a collaborative sett<strong>in</strong>g is beneficial<br />
for learn<strong>in</strong>g and the use <strong>of</strong> <strong>metacognitive</strong> <strong>skills</strong>. If dur<strong>in</strong>g collaboration,<br />
students take the <strong>role</strong> <strong>of</strong> a reflec<strong>to</strong>r, focus<strong>in</strong>g on comprehension<br />
moni<strong>to</strong>r<strong>in</strong>g and moni<strong>to</strong>r<strong>in</strong>g the problem solv<strong>in</strong>g process, it positively <strong>in</strong>fluences<br />
learn<strong>in</strong>g results. In this study, episodes dur<strong>in</strong>g which reflection<br />
occurred, did however not occur frequently.<br />
Saab (2005) f<strong>in</strong>ds that <strong>in</strong> a collaborative learn<strong>in</strong>g sett<strong>in</strong>g, <strong>metacognitive</strong><br />
<strong>skills</strong> such as plann<strong>in</strong>g and moni<strong>to</strong>r<strong>in</strong>g are important. It appears that<br />
the use <strong>of</strong> these <strong>skills</strong> occurs naturally <strong>in</strong> a collaborative learn<strong>in</strong>g sett<strong>in</strong>g.<br />
<strong>The</strong>y occur even more frequently when learners receive support for<br />
effective communication. Support <strong>in</strong> this study concerns four pr<strong>in</strong>ciples:<br />
Respect, Intelligent collaboration, Decid<strong>in</strong>g <strong>to</strong>gether and Encourag<strong>in</strong>g<br />
(RIDE). An example <strong>of</strong> a RIDE rule is ‘Explicit and jo<strong>in</strong>t agreement<br />
will precede decisions and actions’.<br />
One study did explicitly compare the use <strong>of</strong> <strong>metacognitive</strong> <strong>skills</strong> <strong>in</strong> an<br />
<strong>in</strong>dividual versus a collaborative sett<strong>in</strong>g. This study is however more focused<br />
on problem solv<strong>in</strong>g than on learn<strong>in</strong>g <strong>to</strong> <strong>solve</strong> <strong>problems</strong>. Shirouzu,<br />
Miyake and Masukawa (2002) compare <strong>in</strong>dividual problem <strong>solve</strong>rs with<br />
pairs while fold<strong>in</strong>g or calculat<strong>in</strong>g three-quarters <strong>of</strong> two-thirds <strong>of</strong> a square