The role of metacognitive skills in learning to solve problems
The role of metacognitive skills in learning to solve problems
The role of metacognitive skills in learning to solve problems
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Study III: added value <strong>of</strong> the task model 137<br />
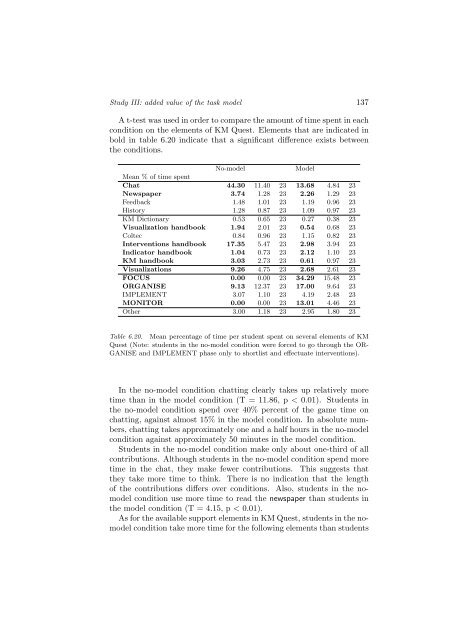
A t-test was used <strong>in</strong> order <strong>to</strong> compare the amount <strong>of</strong> time spent <strong>in</strong> each<br />
condition on the elements <strong>of</strong> KM Quest. Elements that are <strong>in</strong>dicated <strong>in</strong><br />
bold <strong>in</strong> table 6.20 <strong>in</strong>dicate that a significant difference exists between<br />
the conditions.<br />
No-model<br />
Model<br />
Mean % <strong>of</strong> time spent<br />
Chat 44.30 11.40 23 13.68 4.84 23<br />
Newspaper 3.74 1.28 23 2.26 1.29 23<br />
Feedback 1.48 1.01 23 1.19 0.96 23<br />
His<strong>to</strong>ry 1.28 0.87 23 1.09 0.97 23<br />
KM Dictionary 0.53 0.65 23 0.27 0.38 23<br />
Visualization handbook 1.94 2.01 23 0.54 0.68 23<br />
Coltec 0.84 0.96 23 1.15 0.82 23<br />
Interventions handbook 17.35 5.47 23 2.98 3.94 23<br />
Indica<strong>to</strong>r handbook 1.04 0.73 23 2.12 1.10 23<br />
KM handbook 3.03 2.73 23 0.61 0.97 23<br />
Visualizations 9.26 4.75 23 2.68 2.61 23<br />
FOCUS 0.00 0.00 23 34.29 15.48 23<br />
ORGANISE 9.13 12.37 23 17.00 9.64 23<br />
IMPLEMENT 3.07 1.10 23 4.19 2.48 23<br />
MONITOR 0.00 0.00 23 13.01 4.46 23<br />
Other 3.00 1.18 23 2.95 1.80 23<br />
Table 6.20. Mean percentage <strong>of</strong> time per student spent on several elements <strong>of</strong> KM<br />
Quest (Note: students <strong>in</strong> the no-model condition were forced <strong>to</strong> go through the OR-<br />
GANISE and IMPLEMENT phase only <strong>to</strong> shortlist and effectuate <strong>in</strong>terventions).<br />
In the no-model condition chatt<strong>in</strong>g clearly takes up relatively more<br />
time than <strong>in</strong> the model condition (T = 11.86, p < 0.01). Students <strong>in</strong><br />
the no-model condition spend over 40% percent <strong>of</strong> the game time on<br />
chatt<strong>in</strong>g, aga<strong>in</strong>st almost 15% <strong>in</strong> the model condition. In absolute numbers,<br />
chatt<strong>in</strong>g takes approximately one and a half hours <strong>in</strong> the no-model<br />
condition aga<strong>in</strong>st approximately 50 m<strong>in</strong>utes <strong>in</strong> the model condition.<br />
Students <strong>in</strong> the no-model condition make only about one-third <strong>of</strong> all<br />
contributions. Although students <strong>in</strong> the no-model condition spend more<br />
time <strong>in</strong> the chat, they make fewer contributions. This suggests that<br />
they take more time <strong>to</strong> th<strong>in</strong>k. <strong>The</strong>re is no <strong>in</strong>dication that the length<br />
<strong>of</strong> the contributions differs over conditions. Also, students <strong>in</strong> the nomodel<br />
condition use more time <strong>to</strong> read the newspaper than students <strong>in</strong><br />
the model condition (T = 4.15, p < 0.01).<br />
As for the available support elements <strong>in</strong> KM Quest, students <strong>in</strong> the nomodel<br />
condition take more time for the follow<strong>in</strong>g elements than students