- Page 1 and 2: VRIJE UNIVERSITEIT Rotational Raman
- Page 5 and 6: Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Obser
- Page 7 and 8: 1 Introduction 1.1 Observing skylig
- Page 9 and 10: Introduction 3 Extracting the wealt
- Page 11 and 12: Introduction 5 and Spurr, 1997, Vou
- Page 13: Introduction 7 energy: E rot (v,J)
- Page 17 and 18: Introduction 11 scattered radiance
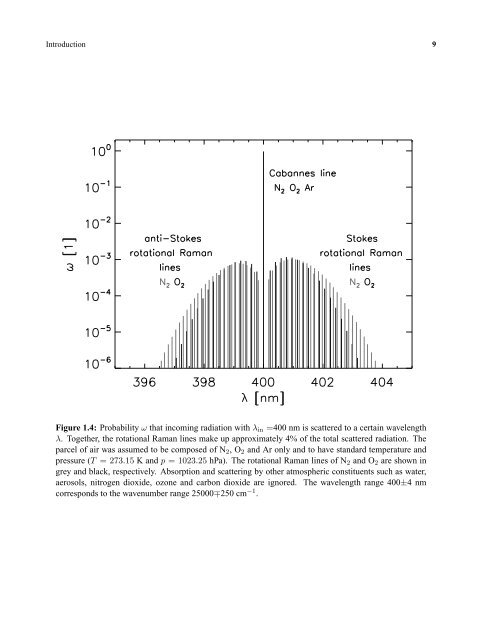
- Page 19 and 20: Introduction 13 approximation in wh
- Page 21 and 22: Introduction 15 scattering have bee
- Page 23 and 24: 2 A doubling-adding method to inclu
- Page 25 and 26: A doubling-adding method to include
- Page 27 and 28: A doubling-adding method to include
- Page 29 and 30: A doubling-adding method to include
- Page 31 and 32: A doubling-adding method to include
- Page 33 and 34: A doubling-adding method to include
- Page 35 and 36: A doubling-adding method to include
- Page 37 and 38: A doubling-adding method to include
- Page 39 and 40: A doubling-adding method to include
- Page 41 and 42: A doubling-adding method to include
- Page 43: A doubling-adding method to include
- Page 46 and 47: 40 Chapter 3 nm with a spectral res
- Page 48 and 49: 42 Chapter 3 contributions of lower
- Page 50 and 51: 44 Chapter 3 if we use the effectiv
- Page 52 and 53: 46 Chapter 3 This in turn results i
- Page 54 and 55: 48 Chapter 3 This may be shown in a
- Page 56 and 57: 50 Chapter 3 The forward and adjoin
- Page 58 and 59: 52 Chapter 3 Here, ∆ = diag [1, 1
- Page 60 and 61: 54 Chapter 3 Figure 3.3: Relative R
- Page 62 and 63: 56 Chapter 3 biases the simulation
- Page 64 and 65:
58 Chapter 3 3.4.2 Approximation me
- Page 66 and 67:
60 Chapter 3 where I ram,app and I
- Page 68 and 69:
62 Chapter 3 3.5 Simulation of pola
- Page 70 and 71:
64 Chapter 3 Figure 3.10: Relative
- Page 72 and 73:
66 Chapter 3 dependence on the vert
- Page 74 and 75:
68 Chapter 3 Figure 3.13: Same as F
- Page 76 and 77:
70 Chapter 3 3.6 Summary A vector r
- Page 78 and 79:
72 Chapter 3 where λ is the wavele
- Page 80 and 81:
74 Chapter 3 where S l is the expan
- Page 82 and 83:
76 Chapter 3 3.C Appendix: Evaluati
- Page 85 and 86:
4 Accurate modeling of spectral fin
- Page 87 and 88:
Accurate modeling of spectral fine-
- Page 89 and 90:
Accurate modeling of spectral fine-
- Page 91 and 92:
Accurate modeling of spectral fine-
- Page 93 and 94:
Accurate modeling of spectral fine-
- Page 95 and 96:
Accurate modeling of spectral fine-
- Page 97 and 98:
Accurate modeling of spectral fine-
- Page 99 and 100:
Accurate modeling of spectral fine-
- Page 101 and 102:
Accurate modeling of spectral fine-
- Page 103 and 104:
5 Retrieval of cloud properties fro
- Page 105 and 106:
Retrieval of cloud properties from
- Page 107 and 108:
Retrieval of cloud properties from
- Page 109 and 110:
Retrieval of cloud properties from
- Page 111 and 112:
Retrieval of cloud properties from
- Page 113 and 114:
Retrieval of cloud properties from
- Page 115 and 116:
Retrieval of cloud properties from
- Page 117 and 118:
Retrieval of cloud properties from
- Page 119 and 120:
Retrieval of cloud properties from
- Page 121 and 122:
Retrieval of cloud properties from
- Page 123 and 124:
Retrieval of cloud properties from
- Page 125 and 126:
References Aben, I., F. Helderman,
- Page 127 and 128:
References 121 Ellery, A., D. Wynn-
- Page 129 and 130:
References 123 Lacis, A. A., J. Cho
- Page 131 and 132:
References 125 Schulz, F., K. Stamn
- Page 133 and 134:
Summary A spectrum of sunlight that
- Page 135 and 136:
Summary 129 Earth radiance spectrum
- Page 137 and 138:
Samenvatting Het door de aardatmosf
- Page 139 and 140:
Samenvatting 133 met een vector-mod
- Page 141:
List of publications Peer-reviewed