Rotational Raman scattering in the Earth's atmosphere ... - SRON
Rotational Raman scattering in the Earth's atmosphere ... - SRON
Rotational Raman scattering in the Earth's atmosphere ... - SRON
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
28 Chapter 2<br />
Table 2.1: US standard <strong>atmosphere</strong> [NOAA, 1976]. We ignored aerosols, water vapor and trace gases<br />
except ozone. Given are mean temperature T , average air density, and volume mix<strong>in</strong>g ratios for N 2 , O 2 ,<br />
Ar and O 3 . For ozone we assume a volume mix<strong>in</strong>g ratio of 1.33 × 10 −6 <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> upper layer (#2) and<br />
0.35 × 10 −6 <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> lower layer (#1), which corresponds to a total column of about 360 Dobson units.<br />
layer T n air N 2 O 2 Ar O 3<br />
# [K] [molec.cm −3 ] [%] [%] [%] [ppmv]<br />
1 240 2 × 10 19 78.09 20.95 0.93 0.35<br />
2 260 6 × 10 17 78.09 20.95 0.93 1.33<br />
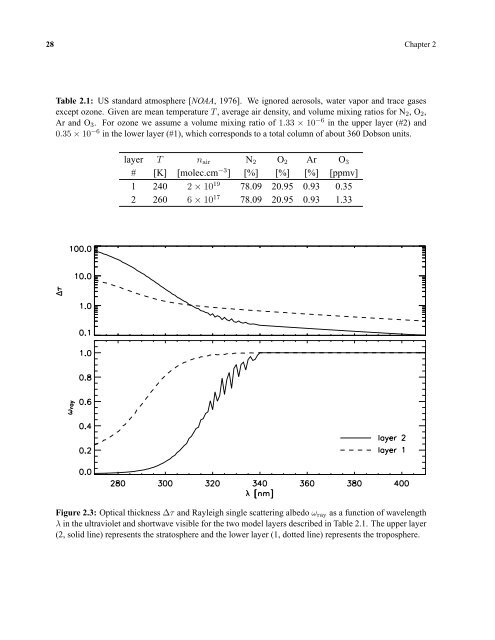
Figure 2.3: Optical thickness ∆τ and Rayleigh s<strong>in</strong>gle <strong>scatter<strong>in</strong>g</strong> albedo ω ray as a function of wavelength<br />
λ <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> ultraviolet and shortwave visible for <strong>the</strong> two model layers described <strong>in</strong> Table 2.1. The upper layer<br />
(2, solid l<strong>in</strong>e) represents <strong>the</strong> stratosphere and <strong>the</strong> lower layer (1, dotted l<strong>in</strong>e) represents <strong>the</strong> troposphere.