Bangladesh Country Investment Plan - Feed the Future
Bangladesh Country Investment Plan - Feed the Future
Bangladesh Country Investment Plan - Feed the Future
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
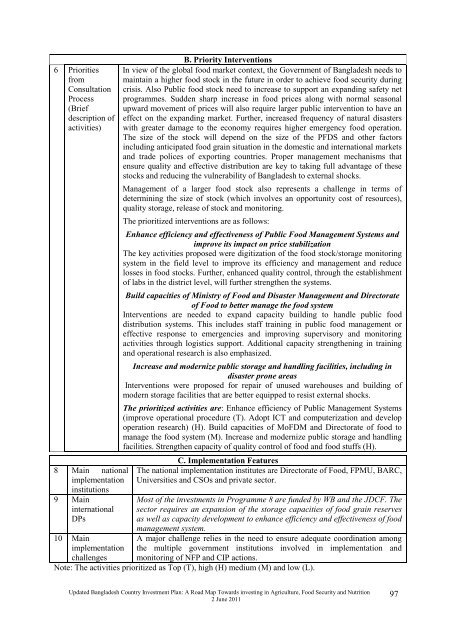
6 Priorities<br />
from<br />
Consultation<br />
Process<br />
(Brief<br />
description of<br />
activities)<br />
8 Main national<br />
implementation<br />
institutions<br />
9 Main<br />
international<br />
DPs<br />
10 Main<br />
implementation<br />
challenges<br />
B. Priority Interventions<br />
In view of <strong>the</strong> global food market context, <strong>the</strong> Government of <strong>Bangladesh</strong> needs to<br />
maintain a higher food stock in <strong>the</strong> future in order to achieve food security during<br />
crisis. Also Public food stock need to increase to support an expanding safety net<br />
programmes. Sudden sharp increase in food prices along with normal seasonal<br />
upward movement of prices will also require larger public intervention to have an<br />
effect on <strong>the</strong> expanding market. Fur<strong>the</strong>r, increased frequency of natural disasters<br />
with greater damage to <strong>the</strong> economy requires higher emergency food operation.<br />
The size of <strong>the</strong> stock will depend on <strong>the</strong> size of <strong>the</strong> PFDS and o<strong>the</strong>r factors<br />
including anticipated food grain situation in <strong>the</strong> domestic and international markets<br />
and trade polices of exporting countries. Proper management mechanisms that<br />
ensure quality and effective distribution are key to taking full advantage of <strong>the</strong>se<br />
stocks and reducing <strong>the</strong> vulnerability of <strong>Bangladesh</strong> to external shocks.<br />
Management of a larger food stock also represents a challenge in terms of<br />
determining <strong>the</strong> size of stock (which involves an opportunity cost of resources),<br />
quality storage, release of stock and monitoring.<br />
The prioritized interventions are as follows:<br />
Enhance efficiency and effectiveness of Public Food Management Systems and<br />
improve its impact on price stabilization<br />
The key activities proposed were digitization of <strong>the</strong> food stock/storage monitoring<br />
system in <strong>the</strong> field level to improve its efficiency and management and reduce<br />
losses in food stocks. Fur<strong>the</strong>r, enhanced quality control, through <strong>the</strong> establishment<br />
of labs in <strong>the</strong> district level, will fur<strong>the</strong>r streng<strong>the</strong>n <strong>the</strong> systems.<br />
Build capacities of Ministry of Food and Disaster Management and Directorate<br />
of Food to better manage <strong>the</strong> food system<br />
Interventions are needed to expand capacity building to handle public food<br />
distribution systems. This includes staff training in public food management or<br />
effective response to emergencies and improving supervisory and monitoring<br />
activities through logistics support. Additional capacity streng<strong>the</strong>ning in training<br />
and operational research is also emphasized.<br />
Increase and modernize public storage and handling facilities, including in<br />
disaster prone areas<br />
Interventions were proposed for repair of unused warehouses and building of<br />
modern storage facilities that are better equipped to resist external shocks.<br />
The prioritized activities are: Enhance efficiency of Public Management Systems<br />
(improve operational procedure (T). Adopt ICT and computerization and develop<br />
operation research) (H). Build capacities of MoFDM and Direct orate of food to<br />
manage <strong>the</strong> food system (M). Increase and modernize public storage and handling<br />
facilities. Streng<strong>the</strong>n capacity of quality control of food and food stuffs (H).<br />
C. Implementation Features<br />
The national implementation institutes are Directorate of Food, FPMU, BARC,<br />
Universities and CSOs and private sector.<br />
Most of <strong>the</strong> investments in Programme 8 are funded by WB and <strong>the</strong> JDCF. The<br />
sector requires an expansion of <strong>the</strong> storage capacities of food grain reserves<br />
as well as capacity development to enhance efficiency and effectiveness of food<br />
management system.<br />
A major challenge relies in <strong>the</strong> need to ensure adequate coordination among<br />
<strong>the</strong> multiple government institutions involved in implementation and<br />
monitoring of NFP and CIP actions.<br />
Note: The activities prioritized as Top (T), high (H) medium (M) and low (L).<br />
Updated <strong>Bangladesh</strong> <strong>Country</strong> <strong>Investment</strong> <strong>Plan</strong>: A Road Map Towards investing in Agriculture, Food Security and Nutrition<br />
2 June 2011<br />
97