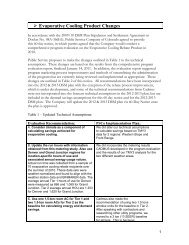
Biomass Feasibility Project Final Report - Xcel Energy
Biomass Feasibility Project Final Report - Xcel Energy
Biomass Feasibility Project Final Report - Xcel Energy
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
central Minnesota to burn biomass in the form of DDGs or crop wastes. But Central Minnesota<br />
Ethanol Cooperative in Little Falls fuels a gasifier with waste wood from nearby millwork plants<br />
and sawmills. The choice of fuel for any specific opportunity will ultimately be decided by its<br />
availability and price, not by a priori notions of its appropriateness.<br />
Having said that, we suspect that in most cases biomass fuel selection still will depend on the<br />
predominant biomass types in the immediate area. The relationships among those biomass<br />
resources and all the types of infrastructure necessary to a biomass power plant are<br />
complicated but critical. The suite of maps in gopher will help the user gain an understanding of<br />
resource availability alongside existing infrastructure.<br />
BIOMASS POWER’S CHALLENGES AND RESPONSES<br />
Given the complexity of developing effective bio-power projects, we try to make it easier by<br />
answering the challenges of biomass power development in Minnesota with some solutions to<br />
them. Some challenges arise from the properties of biomass itself, while others arise from<br />
limitations in technologies, markets, and institutions. Some challenges will be overcome with<br />
advances in technology or changes in policy. Other challenges may have to await changes in<br />
biomass’s cost relative to fossil fuels – not just lower biomass generation costs through the use of<br />
more efficient handling and conversion technologies, but also the higher fossil fuel prices that<br />
seem inevitable in the current world situation. <strong>Biomass</strong> applications are businesses that face<br />
typical business challenges. But they also have so many contact points with the ecology and<br />
with society at large that also present challenges to public policy makers.<br />
BUSINESS DEVELOPMENT CHALLENGES<br />
There is nothing unique about most challenges facing biomass power developers. They are<br />
familiar to entrepreneurs in any emerging technologies:<br />
• High input costs<br />
• Competition for supplies<br />
• Securing supplies<br />
• Information gaps<br />
• High capital costs<br />
• Increased risk in financing new<br />
technologies<br />
• Permitting and regulation<br />
• High transaction costs<br />
• Monetizing non-financial benefits<br />
• Marketing byproducts<br />
High Cost of <strong>Biomass</strong> Fuels<br />
When comparing current market prices, most biomass fuels cost more than coal, the<br />
predominant fuel used in electric power generation. One may wonder how that can be when<br />
so many biomass fuels are wastes. The answer is the high cost of energy and effort expended in<br />
collecting, transporting, and processing biomass into usable fuel delivered to the power plant.<br />
Compared to coal, biomass is a dispersed resource that doesn’t lend itself to efficient<br />
transportation and handling within our current system. Additionally, the infrastructure for<br />
delivering coal quickly and efficiently is the product of various local, state, and federal<br />
incentives to support its development over many decades.<br />
Page 138<br />
Identifying Effective <strong>Biomass</strong> Strategies:<br />
Quantifying Minnesota’s Resources and Evaluating Future Opportunities