Solid Radioactive Waste Strategy Report.pdf - UK EPR
Solid Radioactive Waste Strategy Report.pdf - UK EPR
Solid Radioactive Waste Strategy Report.pdf - UK EPR
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>EPR</strong> <strong>UK</strong><br />
N° NESH-G/2008/en/0123<br />
REV. A PAGE 10 / 257<br />
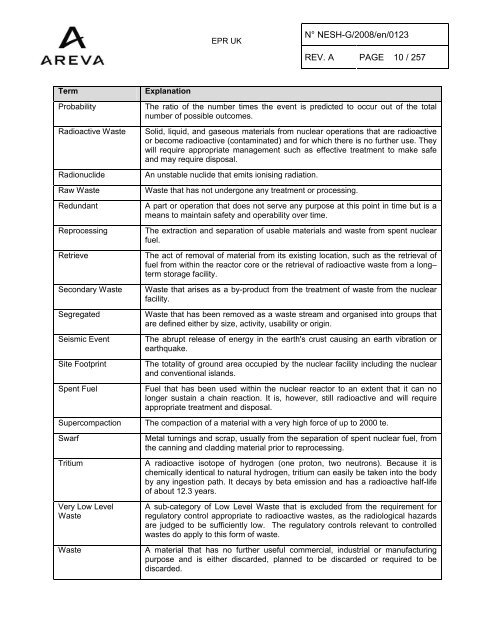
Term<br />
Probability<br />
<strong>Radioactive</strong> <strong>Waste</strong><br />
Radionuclide<br />
Raw <strong>Waste</strong><br />
Redundant<br />
Reprocessing<br />
Retrieve<br />
Secondary <strong>Waste</strong><br />
Segregated<br />
Seismic Event<br />
Site Footprint<br />
Spent Fuel<br />
Supercompaction<br />
Swarf<br />
Tritium<br />
Very Low Level<br />
<strong>Waste</strong><br />
<strong>Waste</strong><br />
Explanation<br />
The ratio of the number times the event is predicted to occur out of the total<br />
number of possible outcomes.<br />
<strong>Solid</strong>, liquid, and gaseous materials from nuclear operations that are radioactive<br />
or become radioactive (contaminated) and for which there is no further use. They<br />
will require appropriate management such as effective treatment to make safe<br />
and may require disposal.<br />
An unstable nuclide that emits ionising radiation.<br />
<strong>Waste</strong> that has not undergone any treatment or processing.<br />
A part or operation that does not serve any purpose at this point in time but is a<br />
means to maintain safety and operability over time.<br />
The extraction and separation of usable materials and waste from spent nuclear<br />
fuel.<br />
The act of removal of material from its existing location, such as the retrieval of<br />
fuel from within the reactor core or the retrieval of radioactive waste from a long–<br />
term storage facility.<br />
<strong>Waste</strong> that arises as a by-product from the treatment of waste from the nuclear<br />
facility.<br />
<strong>Waste</strong> that has been removed as a waste stream and organised into groups that<br />
are defined either by size, activity, usability or origin.<br />
The abrupt release of energy in the earth's crust causing an earth vibration or<br />
earthquake.<br />
The totality of ground area occupied by the nuclear facility including the nuclear<br />
and conventional islands.<br />
Fuel that has been used within the nuclear reactor to an extent that it can no<br />
longer sustain a chain reaction. It is, however, still radioactive and will require<br />
appropriate treatment and disposal.<br />
The compaction of a material with a very high force of up to 2000 te.<br />
Metal turnings and scrap, usually from the separation of spent nuclear fuel, from<br />
the canning and cladding material prior to reprocessing.<br />
A radioactive isotope of hydrogen (one proton, two neutrons). Because it is<br />
chemically identical to natural hydrogen, tritium can easily be taken into the body<br />
by any ingestion path. It decays by beta emission and has a radioactive half-life<br />
of about 12.3 years.<br />
A sub-category of Low Level <strong>Waste</strong> that is excluded from the requirement for<br />
regulatory control appropriate to radioactive wastes, as the radiological hazards<br />
are judged to be sufficiently low. The regulatory controls relevant to controlled<br />
wastes do apply to this form of waste.<br />
A material that has no further useful commercial, industrial or manufacturing<br />
purpose and is either discarded, planned to be discarded or required to be<br />
discarded.