Solid Radioactive Waste Strategy Report.pdf - UK EPR
Solid Radioactive Waste Strategy Report.pdf - UK EPR
Solid Radioactive Waste Strategy Report.pdf - UK EPR
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>EPR</strong> <strong>UK</strong><br />
N° NESH-G/2008/en/0123<br />
REV. A PAGE 9 / 257<br />
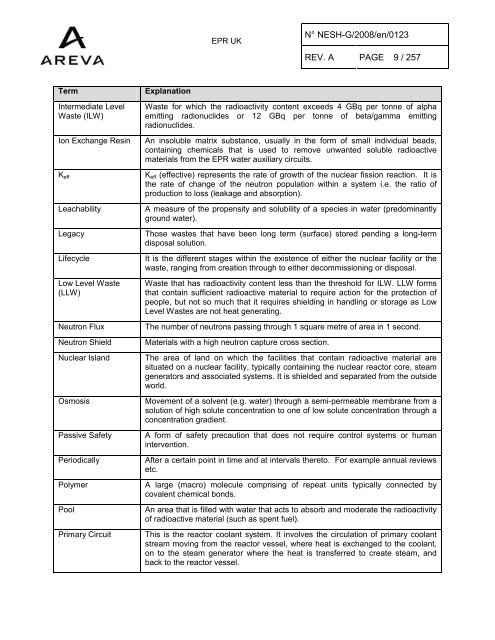
Term<br />
Intermediate Level<br />
<strong>Waste</strong> (ILW)<br />
Ion Exchange Resin<br />
K eff<br />
Leachability<br />
Legacy<br />
Lifecycle<br />
Low Level <strong>Waste</strong><br />
(LLW)<br />
Neutron Flux<br />
Neutron Shield<br />
Nuclear Island<br />
Osmosis<br />
Passive Safety<br />
Periodically<br />
Polymer<br />
Pool<br />
Primary Circuit<br />
Explanation<br />
<strong>Waste</strong> for which the radioactivity content exceeds 4 GBq per tonne of alpha<br />
emitting radionuclides or 12 GBq per tonne of beta/gamma emitting<br />
radionuclides.<br />
An insoluble matrix substance, usually in the form of small individual beads,<br />
containing chemicals that is used to remove unwanted soluble radioactive<br />
materials from the <strong>EPR</strong> water auxiliary circuits.<br />
K eff (effective) represents the rate of growth of the nuclear fission reaction. It is<br />
the rate of change of the neutron population within a system i.e. the ratio of<br />
production to loss (leakage and absorption).<br />
A measure of the propensity and solubility of a species in water (predominantly<br />
ground water).<br />
Those wastes that have been long term (surface) stored pending a long-term<br />
disposal solution.<br />
It is the different stages within the existence of either the nuclear facility or the<br />
waste, ranging from creation through to either decommissioning or disposal.<br />
<strong>Waste</strong> that has radioactivity content less than the threshold for ILW. LLW forms<br />
that contain sufficient radioactive material to require action for the protection of<br />
people, but not so much that it requires shielding in handling or storage as Low<br />
Level <strong>Waste</strong>s are not heat generating.<br />
The number of neutrons passing through 1 square metre of area in 1 second.<br />
Materials with a high neutron capture cross section.<br />
The area of land on which the facilities that contain radioactive material are<br />
situated on a nuclear facility, typically containing the nuclear reactor core, steam<br />
generators and associated systems. It is shielded and separated from the outside<br />
world.<br />
Movement of a solvent (e.g. water) through a semi-permeable membrane from a<br />
solution of high solute concentration to one of low solute concentration through a<br />
concentration gradient.<br />
A form of safety precaution that does not require control systems or human<br />
intervention.<br />
After a certain point in time and at intervals thereto. For example annual reviews<br />
etc.<br />
A large (macro) molecule comprising of repeat units typically connected by<br />
covalent chemical bonds.<br />
An area that is filled with water that acts to absorb and moderate the radioactivity<br />
of radioactive material (such as spent fuel).<br />
This is the reactor coolant system. It involves the circulation of primary coolant<br />
stream moving from the reactor vessel, where heat is exchanged to the coolant,<br />
on to the steam generator where the heat is transferred to create steam, and<br />
back to the reactor vessel.