- Page 1 and 2:
Grace Catalog 2008
- Page 3 and 4:
여백입니다.
- Page 5 and 6:
analytical hplc Evaporative Light S
- Page 7 and 8:
analytical hplc Alltech ® 3300 ELS
- Page 9 and 10:
analytical hplc ELSD Performance Be
- Page 11 and 12:
analytical hplc Alltech ® ELSD 800
- Page 13 and 14:
analytical hplc LC/MS Nitrogen Gene
- Page 15 and 16:
analytical hplc Autosamplers Alltec
- Page 17 and 18:
analytical hplc Column Heaters Allt
- Page 19 and 20:
analytical hplc HPLC Pumps Alltech
- Page 21 and 22:
analytical hplc HPLC Pumps Alltech
- Page 23 and 24:
analytical hplc Data Systems EZChro
- Page 25 and 26:
analytical hplc Analytical HPLC Col
- Page 27 and 28:
analytical hplc Grace (Jones) Genes
- Page 29 and 30:
analytical hplc Columns for Small M
- Page 31 and 32:
analytical hplc Grace ® HPLC Hardw
- Page 33 and 34:
analytical hplc System Type 2 Low V
- Page 35 and 36:
analytical hplc Grace ® VisionHT
- Page 37 and 38:
analytical hplc Grace ® VisionHT
- Page 39 and 40:
analytical hplc Alltech ® Alltima
- Page 41 and 42:
analytical hplc Alltech ® Alltima
- Page 43 and 44:
analytical hplc Alltech ® Alltima
- Page 45 and 46:
analytical hplc Alltech ® Prevail
- Page 47 and 48:
analytical hplc Alltech ® Prevail
- Page 49 and 50:
analytical hplc Reverse Elution Ord
- Page 51 and 52:
analytical hplc GraceSmart Columns
- Page 53 and 54:
analytical hplc Alltech ® Brava C
- Page 55 and 56:
analytical hplc Alltech ® Alltima
- Page 57 and 58:
analytical hplc Alltech ® Apollo
- Page 59 and 60:
analytical hplc Alltech ® Adsorbos
- Page 61 and 62:
analytical hplc Grom Sil Columns 0
- Page 63 and 64:
analytical hplc Grom Amino Acid Co
- Page 65 and 66:
analytical hplc Jones Genesis ® Co
- Page 67 and 68:
analytical hplc Alltech ® OPA Amin
- Page 69 and 70:
analytical hplc Vydac ® Venture ®
- Page 71 and 72:
analytical hplc Vydac ® 201TP (con
- Page 73 and 74:
analytical hplc Astec Chirobiotic
- Page 75 and 76:
analytical hplc Jordi Columns Norma
- Page 77 and 78:
analytical hplc Macherey-Nagel Nucl
- Page 79 and 80:
analytical hplc Polymer Labs Column
- Page 81 and 82:
analytical hplc Shodex ® ODP2 HP C
- Page 83 and 84:
analytical hplc ZirChrom ® Columns
- Page 85 and 86:
analytical hplc Vydac ® MS Introdu
- Page 87 and 88:
analytical hplc Vydac ® MS Columns
- Page 89 and 90:
analytical hplc Vydac ® Everest ®
- Page 91 and 92:
analytical hplc Vydac ® 214TP C4 V
- Page 93 and 94:
analytical hplc Vydac ® ProZap C1
- Page 95 and 96:
analytical hplc Vydac ® Venture ®
- Page 97 and 98:
analytical hplc Alltech ® ProSpher
- Page 99 and 100:
analytical hplc Alltech ® Anion Co
- Page 101 and 102:
analytical hplc Alltech ® Anion Co
- Page 103 and 104:
analytical hplc Hamilton ® Anion,
- Page 105 and 106:
analytical hplc Alltech ® Surfacta
- Page 107 and 108:
analytical hplc Empty HPLC Hardware
- Page 109 and 110:
analytical hplc Stainless Steel Fri
- Page 111 and 112:
analytical hplc Prefilters Direct-C
- Page 113 and 114:
analytical hplc Two-Piece High-Pres
- Page 115 and 116:
analytical hplc High-Pressure Adapt
- Page 117 and 118:
analytical hplc High- and Low-Press
- Page 119 and 120:
analytical hplc Low-Pressure Adapte
- Page 121 and 122:
analytical hplc Fitting and Accesso
- Page 123 and 124:
analytical hplc Mobile Phase Inlet
- Page 125 and 126:
analytical hplc Mobile Phase Delive
- Page 127 and 128:
analytical hplc Kontes Ultra-Ware
- Page 129 and 130:
analytical hplc Alltech ® Online D
- Page 131 and 132:
analytical hplc Alltech ® Adjustab
- Page 133 and 134:
analytical hplc ASI Pump Replacemen
- Page 135 and 136:
analytical hplc Hamilton ® Priming
- Page 137 and 138:
analytical hplc Rheodyne ® Model 8
- Page 139 and 140:
analytical hplc Rheodyne ® RheBuil
- Page 141 and 142:
analytical hplc Rheodyne ® ChromTR
- Page 143 and 144:
analytical hplc Alltech ® SelectPR
- Page 145 and 146:
analytical hplc Hamilton ® Miniatu
- Page 147 and 148:
Prep | Flash | TLC Preparative Chro
- Page 149 and 150:
prep | flash | tlc Preparative Chro
- Page 151 and 152:
prep | flash | tlc Spring Column O
- Page 153 and 154:
prep | flash | tlc GraceAlpha Sili
- Page 155 and 156:
prep | flash | tlc GraceAlpha Colu
- Page 157 and 158:
prep | flash | tlc Vydac ® MS 300
- Page 159 and 160:
prep | flash | tlc Vydac ® TP Colu
- Page 161 and 162:
prep | flash | tlc Alltech ® Prep
- Page 163 and 164:
prep | flash | tlc Spring Column H
- Page 165 and 166:
prep | flash | tlc Spring Column H
- Page 167 and 168:
prep | flash | tlc Axial SFC Column
- Page 169 and 170:
prep | flash | tlc Axial SFC Column
- Page 171 and 172:
prep | flash | tlc Process Scale Co
- Page 173 and 174:
prep | flash | tlc Multipacker ® P
- Page 175 and 176:
prep | flash | tlc Bulk Chromatogra
- Page 177 and 178:
prep | flash | tlc Vydac ® Media 3
- Page 179 and 180:
prep | flash | tlc Davisil ® Media
- Page 181 and 182:
prep | flash | tlc Davisil ® Media
- Page 183 and 184:
prep | flash | tlc Pumps, Injectors
- Page 185 and 186:
prep | flash | tlc GraceResolv Hig
- Page 187 and 188:
prep | flash | tlc GraceResolv Sil
- Page 189 and 190:
prep | flash | tlc TLC Plates Davis
- Page 191 and 192:
prep | flash | tlc TLC Plates Mache
- Page 193 and 194:
prep | flash | tlc Analtech TLC Pla
- Page 195 and 196:
prep | flash | tlc Sprayers Compres
- Page 197 and 198:
prep | flash | tlc TLC Accessories
- Page 199 and 200:
GC GC Instruments. . . . . . . . .
- Page 201 and 202:
gas chromatography Preconfigured SR
- Page 203 and 204:
gas chromatography SRI Accessories
- Page 205 and 206:
gas chromatography PeakSimple for
- Page 207 and 208:
gas chromatography Hydrogen Generat
- Page 209 and 210:
gas chromatography Zero Air Generat
- Page 211 and 212:
gas chromatography JUN-AIR ® Oil-L
- Page 213 and 214:
gas chromatography Grace ® GC Capi
- Page 215 and 216:
gas chromatography Alltech ® Custo
- Page 217 and 218:
gas chromatography Heliflex ® AT
- Page 219 and 220:
gas chromatography Heliflex ® AT-5
- Page 221 and 222:
gas chromatography Heliflex ® AT
- Page 223 and 224:
gas chromatography Heliflex ® AT
- Page 225 and 226:
gas chromatography Heliflex ® AT
- Page 227 and 228:
gas chromatography Heliflex ® AT
- Page 229 and 230:
gas chromatography Heliflex ® USP
- Page 231 and 232:
gas chromatography Heliflex ® AT
- Page 233 and 234:
gas chromatography Alltech Column G
- Page 235 and 236:
gas chromatography Astec Chiraldex
- Page 237 and 238:
gas chromatography SGE ® BPX Capil
- Page 239 and 240:
gas chromatography Alltech ® Custo
- Page 241 and 242:
gas chromatography Alltech ® GC Pa
- Page 243 and 244:
gas chromatography Alltech ® GC Pa
- Page 245 and 246:
gas chromatography Alltech ® Popul
- Page 247 and 248:
gas chromatography Pretested GC Pac
- Page 249 and 250:
gas chromatography Custom Coated Pa
- Page 251 and 252:
gas chromatography GC Supports Chro
- Page 253 and 254:
gas chromatography GC Packings Sili
- Page 255 and 256:
gas chromatography Graphitized Carb
- Page 257 and 258:
gas chromatography GC Packings Haye
- Page 259 and 260:
gas chromatography Capillary Connec
- Page 261 and 262: gas chromatography Capillary Access
- Page 263 and 264: gas chromatography Packing Accessor
- Page 265 and 266: gas chromatography Flowmeters Aalbo
- Page 267 and 268: gas chromatography Gas Leak Detecti
- Page 269 and 270: gas chromatography Physical Charact
- Page 271 and 272: gas chromatography Oxygen Traps Pro
- Page 273 and 274: gas chromatography Alltech ® Gas P
- Page 275 and 276: gas chromatography Purifier Accesso
- Page 277 and 278: gas chromatography Gas Sampling Bag
- Page 279 and 280: gas chromatography Gas Sampling Acc
- Page 281 and 282: gas chromatography GC Ferrules (con
- Page 283 and 284: gas chromatography Parker Fittings
- Page 285 and 286: gas chromatography Swagelok ® Fitt
- Page 287 and 288: gas chromatography Deactivated SGE
- Page 289 and 290: gas chromatography Septa Introducti
- Page 291 and 292: gas chromatography Septa General Pu
- Page 293 and 294: gas chromatography Flow Control Val
- Page 295 and 296: General Chromatography SPE . . . .
- Page 297 and 298: general chromatography SPE Introduc
- Page 299 and 300: general chromatography SPE Introduc
- Page 301 and 302: general chromatography Alltech ® S
- Page 303 and 304: general chromatography Alltech ® E
- Page 305 and 306: general chromatography Alltech ® E
- Page 307 and 308: general chromatography Alltech ® M
- Page 309 and 310: general chromatography Alltech ® M
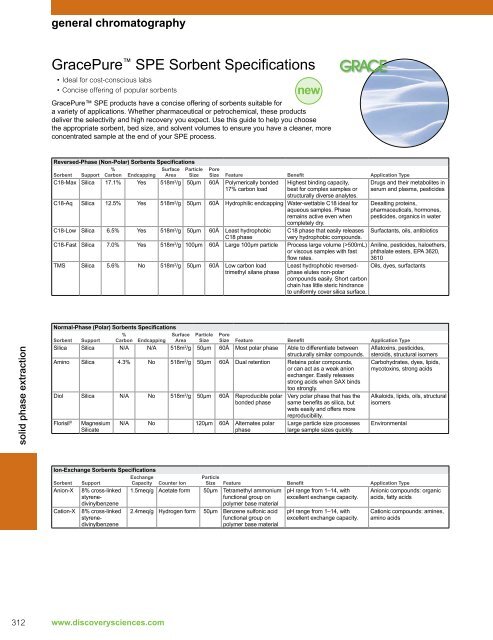
- Page 311: general chromatography Alltech ® 9
- Page 315 and 316: general chromatography Manifold Acc
- Page 317 and 318: general chromatography Filtration I
- Page 319 and 320: general chromatography Syringe Filt
- Page 321 and 322: general chromatography 2mL Centrifu
- Page 323 and 324: general chromatography Recommended
- Page 325 and 326: general chromatography Individual S
- Page 327 and 328: general chromatography Acylation Ac
- Page 329 and 330: general chromatography Gas Standard
- Page 331 and 332: general chromatography Special Gas
- Page 333 and 334: general chromatography Hydrocarbons
- Page 335 and 336: general chromatography Alltech ® I
- Page 337 and 338: general chromatography Hamilton ®
- Page 339 and 340: general chromatography Hamilton ®
- Page 341 and 342: general chromatography Hamilton ®
- Page 343 and 344: general chromatography Vici ® Prec
- Page 345 and 346: general chromatography SGE ® Syrin
- Page 347 and 348: general chromatography Popper Glass
- Page 349 and 350: general chromatography Vial Introdu
- Page 351 and 352: general chromatography 15x45mm 4mL
- Page 353 and 354: general chromatography Vials by Aut
- Page 355 and 356: general chromatography 12x32mm R.A.
- Page 357 and 358: general chromatography 12x32mm Scre
- Page 359 and 360: general chromatography 12x32mm Crim
- Page 361 and 362: general chromatography Limited Volu
- Page 363 and 364:
general chromatography 15x45mm Crim
- Page 365 and 366:
general chromatography 20mm Seals a
- Page 367 and 368:
general chromatography Silanized Gl
- Page 369 and 370:
general chromatography Screw Thread
- Page 371 and 372:
general chromatography Aluminum Sea
- Page 373 and 374:
general chromatography Polypropylen
- Page 375 and 376:
general chromatography Mini-Vials,
- Page 377 and 378:
general chromatography EPA Vials fo
- Page 379 and 380:
general chromatography 96-Well Prod
- Page 381 and 382:
general chromatography Racks and St
- Page 383 and 384:
general chromatography Crimpers and
- Page 385 and 386:
general chromatography Flex-Connect
- Page 387 and 388:
general chromatography Low-Pressure
- Page 389 and 390:
general chromatography Glass-Lined
- Page 391 and 392:
general chromatography Tubing Cutte
- Page 393 and 394:
general chromatography Tools Magnif
- Page 395 and 396:
hplc applications Analgesics Anti-I
- Page 397 and 398:
hplc applications Antidepressants T
- Page 399 and 400:
hplc applications Barbiturates 2 4
- Page 401 and 402:
hplc applications Anesthetics 1 + 2
- Page 403 and 404:
hplc applications Anti-Asthmatics M
- Page 405 and 406:
hplc applications Antibiotics Antib
- Page 407 and 408:
hplc applications Bacitracin Bacitr
- Page 409 and 410:
hplc applications Taxols Taxol ® a
- Page 411 and 412:
hplc applications 0 Ginseng 1 2 Gin
- Page 413 and 414:
hplc applications Chinese Pharmacop
- Page 415 and 416:
hplc applications Vitamins 1 2 3 5
- Page 417 and 418:
hplc applications 1 2 b-Carotenes 3
- Page 419 and 420:
hplc applications Carbohydrates 1 C
- Page 421 and 422:
hplc applications 3 1 2 4 Conquista
- Page 423 and 424:
hplc applications Organic Acids 1 8
- Page 425 and 426:
hplc applications Oils / Lipids 2 S
- Page 427 and 428:
hplc applications Oils / Lipids 1 2
- Page 429 and 430:
hplc applications Proteins & Peptid
- Page 431 and 432:
hplc applications Proteins & Peptid
- Page 433 and 434:
hplc applications Proteins & Peptid
- Page 435 and 436:
hplc applications Proteins & Peptid
- Page 437 and 438:
hplc applications Proteins & Peptid
- Page 439 and 440:
hplc applications Purification of T
- Page 441 and 442:
hplc applications 1) Cystine 2) Cys
- Page 443 and 444:
hplc applications Miscellaneous Pho
- Page 445 and 446:
hplc applications 1 Organochlorine
- Page 447 and 448:
hplc applications Water Pollutants
- Page 449 and 450:
hplc applications Polymers Polyuret
- Page 451 and 452:
hplc applications Biofuels Triacylg
- Page 453 and 454:
hplc applications Fuels Petrochemic
- Page 455 and 456:
ic applications 2 Anions 13033 2 Ba
- Page 457 and 458:
ic applications 3 Anions with pHBA
- Page 459 and 460:
ic applications Cations Rapid Analy
- Page 461 and 462:
ic applications Surfactants 1 2 Sho
- Page 463 and 464:
gc applications Ephedra Standards v
- Page 465 and 466:
gc applications Organic Volatile Im
- Page 467 and 468:
gc applications Fast GC Drug Analys
- Page 469 and 470:
gc applications
- Page 471 and 472:
gc applications Semivolatiles Colu
- Page 473 and 474:
gc applications Volatiles 5,6 Aroma
- Page 475 and 476:
gc applications EPA Method 624 —
- Page 477 and 478:
gc applications Alcohols The Glenli
- Page 479 and 480:
gc applications Essential Oils 1 2
- Page 481 and 482:
gc applications FAMEs 1 3 4 5 Sesam
- Page 483 and 484:
gc applications Fuel Texas Crude Oi
- Page 485 and 486:
gc applications Gases Scott Mix 216
- Page 487 and 488:
gc applications Amines Polyamines 2
- Page 489 and 490:
gc applications Gases 1 5 MAPP Gas
- Page 491 and 492:
gc applications Solvents Volatile O
- Page 493 and 494:
gc applications Test Mixes AT-
- Page 495 and 496:
spe applications Diuretics Procedur
- Page 497 and 498:
spe applications Additives Procedur
- Page 499 and 500:
spe applications Pesticides Procedu
- Page 501 and 502:
spe applications PAHs Procedure usi