Microcomputer Circuits and Processes
Microcomputer Circuits and Processes
Microcomputer Circuits and Processes
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
16<br />
address bus a<br />
=l~<br />
II ./<br />
0 board select ..•. I<br />
E<br />
C<br />
0<br />
0<br />
256-byte<br />
I<br />
I<br />
CPU E<br />
R<br />
readlwrite<br />
In<br />
memory<br />
board<br />
RD<br />
WR<br />
I<br />
I /~<br />
~~ "',,)"<br />
data bus<br />
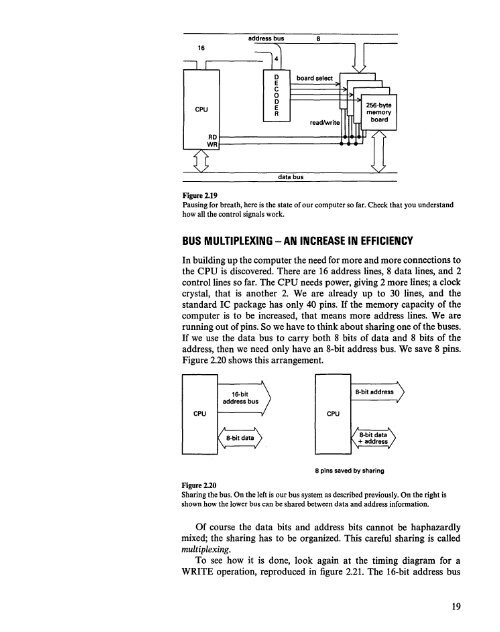
Figure 2.19<br />
Pausing for breath, here is the state of our computer so far. Check that you underst<strong>and</strong><br />
how all the control signals work.<br />
BUS MULTIPLEXING - AN INCREASE IN EFFICIENCY<br />
In building up the computer the need for more <strong>and</strong> more connections to<br />
the CPU is discovered. There are 16 address lines, 8 data lines, <strong>and</strong> 2<br />
control lines so far. The CPU needs power, giving 2 more lines; a clock<br />
crystal, that is another 2. We are already up to 30 lines, <strong>and</strong> the<br />
st<strong>and</strong>ard Ie package has only 40 pins. If the memory capacity of the<br />
computer is to be increased, that means more address lines. We are<br />
running out of pins. So we have to think about sharing one of the buses.<br />
If we use the data bus to carry both 8 bits of data <strong>and</strong> 8 bits of the<br />
address, then we need only have an 8-bit address bus. We save 8 pins.<br />
Figure 2.20 shows this arrangement.<br />
cPU<br />
16·bit<br />
address bus<br />
CPU<br />
a·bit address<br />
a pins saved by sharing<br />
Figure 2.20<br />
Sharing the bus. On the left is our bus system as described previously. On the right is<br />
shown how the lower bus can be shared between data <strong>and</strong> address information.<br />
Of course the data bits <strong>and</strong> address bits cannot be haphazardly<br />
mixed; the sharing has to be organized. This careful sharing is called<br />
multiplexing.<br />
To see how it is done, look again at the timing diagram for a<br />
WRITE operation, reproduced in figure 2.21. The 16-bit address bus<br />
19