You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
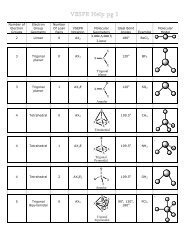
Key LightWave Terms and ConceptsIn the Appendices you will find an extensive Glossary of termsused in 3D graphics. The following are a brief selection of somecommon terms and concepts used with LightWave that will helpyou to get started. These are also covered in the Glossary, insome cases at greater length.Animation Channel — Animation Channel refers to the differentPosition, Rotation, and Scaling settings an item can have in Layout.It can also refer to other envelopeable elements like light intensity.See also motion channel.Axis — Axis refers to the XYZ coordinates used as the basisfor positioning elements in LightWave’s 3D space. It issomewhat like the concept of left/right, up/down, and near/far.Chapter 1: LightWave 3D Getting Started 7Normal — A polygon normal is the imaginary line projectingout perpendicular to a surface at any point indicatingthe direction of the polygon. A polygon surface normalis represented as dashed lines on selected polygons in<strong>Modeler</strong>. LightWave sees polygons or faces of an object onlyfrom the surface normal side. A single-sided polygon (like apiece of paper) with its normal facing away from the camerawill be invisible to the camera from that viewpoint (unlessthe surface is using the Double Sided option). A vertexnormal’s direction is the average of the polygon normals it isconnected to.Null Object — A null object is an object that contains no geometryand will not show up in a rendered image. Nulls are usefulfor tracking, grouping (parenting), and using with inversekinematics functions. They are also commonly used tocontrol plug-ins.Bone — For any object, you can define a skeletal systemcomposed of bones. By moving bones around, you canchange the shape of an object.Bounding Box — A Bounding Box is a six-sided box conforming tothe outer dimensions of an object. It is commonly used as aquickly drawn stand-in for a more complex object.Camera — As in real life, a camera records events. Lookingthrough LightWave’s camera shows you the view as it will begenerated.Control Mesh — A Control Mesh is a cage of points used to shapeSubPatches.Endomorph — An Endomorph is an object containing one or moreMorph Maps.Envelope — An envelope is a way of setting a particular value thatusually changes over time using a graphical input mode.Frames — LightWave works with frames. A frame is one image outof many that define an animation. There are 25 frames persecond in PAL video, approximately 30 frames per second inNTSC video, and 24 frames per second in film.Geometry — Geometry refers to the positional layout of points andpolygons that define an object.Item — An item in Layout refers to an object, bone, light, orcamera.Keyframe (Also known as just a key) — A keyframe is a frame forwhich you define a value for an animation channel(s) (e.g.,position or rotation) for an item in Layout. Animations arecomposed of a beginning keyframe, an ending keyframe andusually some number of keyframes in between. See alsotween, in the Glossary.Light — A light in LightWave is generally used just like a light inreal life. Lights illuminate a scene and allow you to see theobjects within it.LScript — This is LightWave’s built-in scripting language. LScriptscan be installed and used just like plugins.Motion Channel — Motion Channel is generally the same asAnimation Channel, but refers only to position, rotation, andscale. (i.e., not light intensity.)Object — An object is composed of points and faces. Pointsconnected together to form a polygon define a face. Facesjoined together form an object.Parenting — Parenting refers to LightWave’s ability to sethierarchical associations between items in a Scene.Generally, the parent item will have some level of influenceon its child, whether it is position, rotation, size, etc. The childcan also be a parent to another item.Particles — Usually refers to animated points used for sparks, fire,and even liquid. LightWave’s particle engine is called ParticleFX.Pivot Point — The position in an object that acts as the center ofrotation and position reference.Pixel — A pixel is the smallest unit of measurement in an imageand is used to describe the image’s width and height.Plane — A plane refers to a two-dimensional (i.e., flat and level)surface. You might want to think of a plane as a piece ofglass that is infinitely large, but has no depth.Plug-in — A plug-in is a program that works with and extends thefunctionality of LightWave.Render — Rendering is the computer’s process of calculating andgenerating an image based on the values you have selectedfor the different options in LightWave.Scene — A Scene is a LightWave project defining the objectsloaded and their motions, the number of lights and theirvalues/motions, the resolution of the final image, specialeffects, Camera settings, and so on. This ASCII text file isgenerally saved from Layout.Session — A session is a single use of an application. A sessionstarts when you first boot the application and ends when youexit.Spline (Curves) — LightWave uses splines or curved paths betweenkeys while moving items about.When modeling, splines refer to open or closed curves.SubPatch — SubPatch is a modeling mode where polygonsbecome a cage that controls an underlying mesh of NURBS.