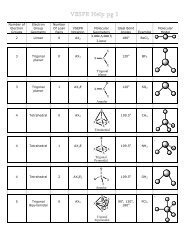
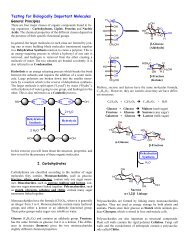
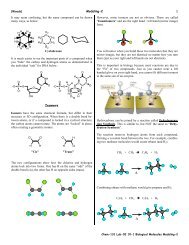
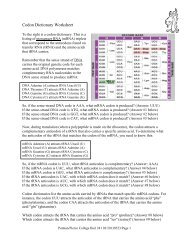
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
GlossaryvBump Map — Creates the illusion of three-dimensionality ofa surface (protrusions and cavities) by recalculating thenormals of the object, without changing the mesh itself. Itis very common in 3D renderings and suitable for creatingeffects like wrinkles, creases, crumples, cracks, seams etc.The silhouette of a bump mapped object is a give-awaysince, in these areas, it is obvious that the mesh is leftunaffected (if trying to create an orange by using a perfectsphere with an orange peel texture applied to it for bumpmapping it will still have an impeccably round silhouette).In LightWave areas in a bump map that are black areunaffected and areas that are white are raised.Byte — 8 bits. Multiples of bytes make up the terms kilobyte (1024bytes), megabytes (1024 kilobytes) and gigabyte (1024megabytes).CAD — Computer Aided Drafting (or Design); A system that lets adesigner use a computer screen instead of a drafting tableto make plans and blueprints. However, CAD packagesdon’t often have superb rendering abilities, so packages likeLightWave are turned to, for their abilities.CAM — Computer Aided Manufacturing; the process of usinga computer to create a physical product from a computercreateddesign. CAM is usually used to control robots thatperform tasks that would be tedious or dangerous to humanworkers. See also Rapid Prototyping.Camera — An apparatus for taking photographs, generallyconsisting of a lightproof enclosure having an aperturewith a shuttered lens through which the image of an objectis focused and recorded on a photosensitive film or plate.Digital cameras use CCDs to focus light and create a digitalpicture that can be seen and transferred to a computerimmediately. In LightWave, the camera is the conduit throughwhich objects and scenes are turned into still images oranimations.Capping — Surface closing the upper and/or bottom side of anobject such as a cylinder.Cartesian Coordinate — Mathematical representation of Euclideanspace. Every point can be described by three coordinates(X, Y, Z) representing the position along the orthogonal X, Y,and Z axes. The point (0, 0, 0) is called the origin, which isthe global center of the 3D world.Cartesian Space — A space in which positions are denoted by athree-coordinate system (x, y, and z coordinates) relating toa central origin (0,0,0).Catacorner — Slanted across a polygon on a diagonal line; “set offin a catty-corner direction across the vacant lot”. syn: catacornered,catercorner, cater-cornered, catty-corner, cattycornered,kitty-corner, kitty-cornered.Cattiwompus — Weird. Mixed up. Unusual. Distorted.Caustics — Light pattern created by specular reflection orrefraction of light, such as the patterns of light on the bottomof a swimming pool, or light through a glass of wine.CD — Compact Disc storage media. Also the chemical symbolfor Cadmium and the sticker on the back of a car with thediplomatic corps.Center of Projection — The point in perspective projection whereall projectors intersect.Center of the World — Is the absolute center of a 3D space,represented by X, Y, and Z points (0, 0, 0). Also referred toas the Origin.CenterPoint — A point that represents the center of an object. Thispoint is used in some programs for a point of reference forrotation and position. The center point of a polygon is wherethe line representing the normal comes out from.Chamfer — To cut off the edges of the geometry with a planar cut,creating a more blunt shape, typically at a 45 degree angle.A bevelled edge or corner between two intersecting lines orsurfaces.Child — An object whose movements are influenced by anotherobject, called the “parent”.Chord Length Parametrisation — See Non-UniformParametrisation.Clean Modeling — Refers to the practice of removing geometryfrom a model that is not wanted or needed. Also refers tothe use of proper geometry construction techniques, suchas creating continuous surfaces, minimising narrow faces,and avoiding small corner angles, that facilitates downstreamprocesses.Clipping — More often than not, much of the graphics drawn fora specific scene does not fit into the viewport of the camera.Accordingly, those which fall outside of the viewport must beclipped so as they are not drawn. Depending on the natureof the application, there are two kinds of clipping: 2D and 3D.The earlier simply compares each pixel against the extentsof the rendering viewport, while the latter technique usesthe six sides of the view frustum to determine whether a 3Dvertex is inside the viewport or not.Clone — This tool creates copies of an object based on userdefinedparameters for offset, motions, morphing, shadows,etc. This tool can be used to make ordered sets of objects,but is different from the array command because not all newobjects need be exactly the same as the original.Cloud of Points, or Point Cloud — A set of x-y-z coordinatesobtained from a 3D scanner or digitiser. The data can thenbe turned into a continuous surface and used as a 3D model.CODEC — Short for “COmpressor/DECompressor”. This is theterm used to reference the way that software programshandle different movie files, such as Quick Time, AVI, etc.The CODEC can control image quality, and can assign theamount of space given to the movie file. First, a multimediapublisher uses a codec to squeeze more sound and videointo less file space. These compressed files are easier tofit on a CD-ROM and transfer to your computer. Then, yourcomputer uses a codec to expand these files back to theiroriginal size and replay them on screen.Coincidence — Refers to geometry that occupies the same spatiallocation. For example, coincident vertices are points thatoccupy the same x, y, and z coordinates. Coincident linescan have differing lengths while one occupies the samelocation as the other.