A history of Greek mathematics Vol.II from Aristarchus to Diophantus by Heath, Thomas Little, Sir, 1921
MACEDONIA is GREECE and will always be GREECE- (if they are desperate to steal a name, Monkeydonkeys suits them just fine) ΚΑΤΩ Η ΣΥΓΚΥΒΕΡΝΗΣΗ ΤΩΝ ΠΡΟΔΟΤΩΝ!!! ΦΕΚ,ΚΚΕ,ΚΝΕ,ΚΟΜΜΟΥΝΙΣΜΟΣ,ΣΥΡΙΖΑ,ΠΑΣΟΚ,ΝΕΑ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ,ΕΓΚΛΗΜΑΤΑ,ΔΑΠ-ΝΔΦΚ, MACEDONIA,ΣΥΜΜΟΡΙΤΟΠΟΛΕΜΟΣ,ΠΡΟΣΦΟΡΕΣ,ΥΠΟΥΡΓΕΙΟ,ΕΝΟΠΛΕΣ ΔΥΝΑΜΕΙΣ,ΣΤΡΑΤΟΣ, ΑΕΡΟΠΟΡΙΑ,ΑΣΤΥΝΟΜΙΑ,ΔΗΜΑΡΧΕΙΟ,ΝΟΜΑΡΧΙΑ,ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ,ΛΟΓΟΤΕΧΝΙΑ,ΔΗΜΟΣ,LIFO,ΛΑΡΙΣΑ, ΠΕΡΙΦΕΡΕΙΑ,ΕΚΚΛΗΣΙΑ,ΟΝΝΕΔ,ΜΟΝΗ,ΠΑΤΡΙΑΡΧΕΙΟ,ΜΕΣΗ ΕΚΠΑΙΔΕΥΣΗ,ΙΑΤΡΙΚΗ,ΟΛΜΕ,ΑΕΚ,ΠΑΟΚ,ΦΙΛΟΛΟΓΙΚΑ,ΝΟΜΟΘΕΣΙΑ,ΔΙΚΗΓΟΡΙΚΟΣ,ΕΠΙΠΛΟ, ΣΥΜΒΟΛΑΙΟΓΡΑΦΙΚΟΣ,ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΑ,ΜΑΘΗΜΑΤΙΚΑ,ΝΕΟΛΑΙΑ,ΟΙΚΟΝΟΜΙΚΑ,ΙΣΤΟΡΙΑ,ΙΣΤΟΡΙΚΑ,ΑΥΓΗ,ΤΑ ΝΕΑ,ΕΘΝΟΣ,ΣΟΣΙΑΛΙΣΜΟΣ,LEFT,ΕΦΗΜΕΡΙΔΑ,ΚΟΚΚΙΝΟ,ATHENS VOICE,ΧΡΗΜΑ,ΟΙΚΟΝΟΜΙΑ,ΕΝΕΡΓΕΙΑ, ΡΑΤΣΙΣΜΟΣ,ΠΡΟΣΦΥΓΕΣ,GREECE,ΚΟΣΜΟΣ,ΜΑΓΕΙΡΙΚΗ,ΣΥΝΤΑΓΕΣ,ΕΛΛΗΝΙΣΜΟΣ,ΕΛΛΑΔΑ, ΕΜΦΥΛΙΟΣ,ΤΗΛΕΟΡΑΣΗ,ΕΓΚΥΚΛΙΟΣ,ΡΑΔΙΟΦΩΝΟ,ΓΥΜΝΑΣΤΙΚΗ,ΑΓΡΟΤΙΚΗ,ΟΛΥΜΠΙΑΚΟΣ, ΜΥΤΙΛΗΝΗ,ΧΙΟΣ,ΣΑΜΟΣ,ΠΑΤΡΙΔΑ,ΒΙΒΛΙΟ,ΕΡΕΥΝΑ,ΠΟΛΙΤΙΚΗ,ΚΥΝΗΓΕΤΙΚΑ,ΚΥΝΗΓΙ,ΘΡΙΛΕΡ, ΠΕΡΙΟΔΙΚΟ,ΤΕΥΧΟΣ,ΜΥΘΙΣΤΟΡΗΜΑ,ΑΔΩΝΙΣ ΓΕΩΡΓΙΑΔΗΣ,GEORGIADIS,ΦΑΝΤΑΣΤΙΚΕΣ ΙΣΤΟΡΙΕΣ, ΑΣΤΥΝΟΜΙΚΑ,ΦΙΛΟΣΟΦΙΚΗ,ΦΙΛΟΣΟΦΙΚΑ,ΙΚΕΑ,ΜΑΚΕΔΟΝΙΑ,ΑΤΤΙΚΗ,ΘΡΑΚΗ,ΘΕΣΣΑΛΟΝΙΚΗ,ΠΑΤΡΑ, ΙΟΝΙΟ,ΚΕΡΚΥΡΑ,ΚΩΣ,ΡΟΔΟΣ,ΚΑΒΑΛΑ,ΜΟΔΑ,ΔΡΑΜΑ,ΣΕΡΡΕΣ,ΕΥΡΥΤΑΝΙΑ,ΠΑΡΓΑ,ΚΕΦΑΛΟΝΙΑ, ΙΩΑΝΝΙΝΑ,ΛΕΥΚΑΔΑ,ΣΠΑΡΤΗ,ΠΑΞΟΙ
MACEDONIA is GREECE and will always be GREECE- (if they are desperate to steal a name, Monkeydonkeys suits them just fine)
ΚΑΤΩ Η ΣΥΓΚΥΒΕΡΝΗΣΗ ΤΩΝ ΠΡΟΔΟΤΩΝ!!!
ΦΕΚ,ΚΚΕ,ΚΝΕ,ΚΟΜΜΟΥΝΙΣΜΟΣ,ΣΥΡΙΖΑ,ΠΑΣΟΚ,ΝΕΑ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ,ΕΓΚΛΗΜΑΤΑ,ΔΑΠ-ΝΔΦΚ, MACEDONIA,ΣΥΜΜΟΡΙΤΟΠΟΛΕΜΟΣ,ΠΡΟΣΦΟΡΕΣ,ΥΠΟΥΡΓΕΙΟ,ΕΝΟΠΛΕΣ ΔΥΝΑΜΕΙΣ,ΣΤΡΑΤΟΣ, ΑΕΡΟΠΟΡΙΑ,ΑΣΤΥΝΟΜΙΑ,ΔΗΜΑΡΧΕΙΟ,ΝΟΜΑΡΧΙΑ,ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ,ΛΟΓΟΤΕΧΝΙΑ,ΔΗΜΟΣ,LIFO,ΛΑΡΙΣΑ, ΠΕΡΙΦΕΡΕΙΑ,ΕΚΚΛΗΣΙΑ,ΟΝΝΕΔ,ΜΟΝΗ,ΠΑΤΡΙΑΡΧΕΙΟ,ΜΕΣΗ ΕΚΠΑΙΔΕΥΣΗ,ΙΑΤΡΙΚΗ,ΟΛΜΕ,ΑΕΚ,ΠΑΟΚ,ΦΙΛΟΛΟΓΙΚΑ,ΝΟΜΟΘΕΣΙΑ,ΔΙΚΗΓΟΡΙΚΟΣ,ΕΠΙΠΛΟ, ΣΥΜΒΟΛΑΙΟΓΡΑΦΙΚΟΣ,ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΑ,ΜΑΘΗΜΑΤΙΚΑ,ΝΕΟΛΑΙΑ,ΟΙΚΟΝΟΜΙΚΑ,ΙΣΤΟΡΙΑ,ΙΣΤΟΡΙΚΑ,ΑΥΓΗ,ΤΑ ΝΕΑ,ΕΘΝΟΣ,ΣΟΣΙΑΛΙΣΜΟΣ,LEFT,ΕΦΗΜΕΡΙΔΑ,ΚΟΚΚΙΝΟ,ATHENS VOICE,ΧΡΗΜΑ,ΟΙΚΟΝΟΜΙΑ,ΕΝΕΡΓΕΙΑ, ΡΑΤΣΙΣΜΟΣ,ΠΡΟΣΦΥΓΕΣ,GREECE,ΚΟΣΜΟΣ,ΜΑΓΕΙΡΙΚΗ,ΣΥΝΤΑΓΕΣ,ΕΛΛΗΝΙΣΜΟΣ,ΕΛΛΑΔΑ, ΕΜΦΥΛΙΟΣ,ΤΗΛΕΟΡΑΣΗ,ΕΓΚΥΚΛΙΟΣ,ΡΑΔΙΟΦΩΝΟ,ΓΥΜΝΑΣΤΙΚΗ,ΑΓΡΟΤΙΚΗ,ΟΛΥΜΠΙΑΚΟΣ, ΜΥΤΙΛΗΝΗ,ΧΙΟΣ,ΣΑΜΟΣ,ΠΑΤΡΙΔΑ,ΒΙΒΛΙΟ,ΕΡΕΥΝΑ,ΠΟΛΙΤΙΚΗ,ΚΥΝΗΓΕΤΙΚΑ,ΚΥΝΗΓΙ,ΘΡΙΛΕΡ, ΠΕΡΙΟΔΙΚΟ,ΤΕΥΧΟΣ,ΜΥΘΙΣΤΟΡΗΜΑ,ΑΔΩΝΙΣ ΓΕΩΡΓΙΑΔΗΣ,GEORGIADIS,ΦΑΝΤΑΣΤΙΚΕΣ ΙΣΤΟΡΙΕΣ, ΑΣΤΥΝΟΜΙΚΑ,ΦΙΛΟΣΟΦΙΚΗ,ΦΙΛΟΣΟΦΙΚΑ,ΙΚΕΑ,ΜΑΚΕΔΟΝΙΑ,ΑΤΤΙΚΗ,ΘΡΑΚΗ,ΘΕΣΣΑΛΟΝΙΚΗ,ΠΑΤΡΑ, ΙΟΝΙΟ,ΚΕΡΚΥΡΑ,ΚΩΣ,ΡΟΔΟΣ,ΚΑΒΑΛΑ,ΜΟΔΑ,ΔΡΑΜΑ,ΣΕΡΡΕΣ,ΕΥΡΥΤΑΝΙΑ,ΠΑΡΓΑ,ΚΕΦΑΛΟΝΙΑ, ΙΩΑΝΝΙΝΑ,ΛΕΥΚΑΔΑ,ΣΠΑΡΤΗ,ΠΑΞΟΙ
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
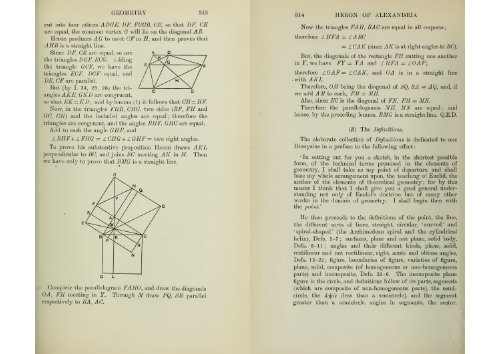
cut in<strong>to</strong><br />
GEOMETRY 313<br />
four others ADGE, I)F, FGGB, GE, so that DF, GE<br />
are equal, the common vertex G will lie on the diagonal AB.<br />
Heron produces AG <strong>to</strong> meet GF in H, and then proves that<br />
AHB is a straight line.<br />
Since DF, GE are equal, so are<br />
the triangles D GF, EGG. A dding<br />
the triangle GGF, we have the<br />
triangles EGF, JDGF equal, and<br />
DE, GF are parallel.<br />
But (<strong>by</strong> I. 34, 29, 26) the triangles<br />
AKE, GKD are congruent,<br />
so that EK=KD<br />
; and <strong>by</strong> lemma ( 1) it follows that CH=HF.<br />
Now, in the triangles FHB, CHG, two sides (BF, FH and<br />
GC, GH) and the included angles are equal ; therefore the<br />
triangles are congruent, and the angles BHF, GHG are equal.<br />
Add <strong>to</strong> each the angle GHF, and<br />
Z BHF+ Z FHG = Z CHG + Z GHF = two right angles.<br />
To prove his substantive proposition Heron draws AKL<br />
Then<br />
perpendicular <strong>to</strong> BG, and joins EG meeting AK in M.<br />
we have only <strong>to</strong> prove that BMG is a straight line.<br />
Complete the parallelogram FAHG, and draw the diagonals<br />
OA, FH meeting in F. Through M draw PQ, SR parallel<br />
respectively <strong>to</strong> BA, AG.<br />
314 HERON OF ALEXANDRIA<br />
Now the triangles FAH, BAG are equal in all respects<br />
IHFA = I ABC<br />
= Z CAR (since AK is at right angles <strong>to</strong> BG).<br />
therefore<br />
But, the diagonals <strong>of</strong> the rectangle FH cutting one another<br />
in Y, we have FY = YA and L.HFA = LOAF;<br />
therefore LOAF — AGAK, and OA is in a straight line<br />
. with AKL.<br />
Therefore, OM being the diagonal <strong>of</strong> SQ, SA — AQ. and, if<br />
we add AM <strong>to</strong> each, FM = MH. .<br />
Also, since EG is the diagonal <strong>of</strong> FN, FM — MN.<br />
Therefore the parallelograms MH, MN are equal ; and<br />
hence, <strong>by</strong> the preceding lemma, BMG is a straight line.<br />
(ft)<br />
The Definitions.<br />
Q.E.D.<br />
The elaborate collection <strong>of</strong> Definitions is dedicated <strong>to</strong> one<br />
Dionysius in a preface <strong>to</strong> the following effect<br />
'In setting out for you a sketch, in<br />
the shortest possible<br />
form, <strong>of</strong> the technical terms premised in the elements <strong>of</strong><br />
geometry, I shall take as my point <strong>of</strong> departure, and shall<br />
base my whole arrangement upon, the teaching <strong>of</strong> Euclid, the<br />
author <strong>of</strong> the elements <strong>of</strong> theoretical geometry ; for <strong>by</strong> this<br />
means I think that I shall give you a good general understanding<br />
not only <strong>of</strong> Euclid's doctrine but <strong>of</strong> many other<br />
works in the domain <strong>of</strong> geometiy. I shall begin then with<br />
the 'point!<br />
He then proceeds <strong>to</strong> the definitions <strong>of</strong> the point, the line,<br />
the different sorts <strong>of</strong> lines, straight, circular, ' curved ' and<br />
'<br />
spiral-shaped ' (the Archimedean spiral and the cylindrical<br />
helix), Defs. 1-7 ; surfaces, plane and not plane, solid body,<br />
Defs. 8-11; angles and their different kinds, plane, solid,<br />
rectilinear and not rectilinear, right, acute and obtuse angles,<br />
Defs. 12-22; figure, boundaries <strong>of</strong> figure, varieties <strong>of</strong> figure,<br />
plane, solid, composite (<strong>of</strong> homogeneous or non-homogeneous<br />
parts) and incomposite, Defs. 23-6. The incomposite plane<br />
figure is the circle, and definitions follow <strong>of</strong> its parts, segments<br />
(which are composite <strong>of</strong> non-homogeneous parts), the semicircle,<br />
the a\jfis (less than a semicircle), and the segment<br />
greater than a semicircle, angles in segments, the sec<strong>to</strong>r,