MS AR 2018 (1)
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
45.2 Liquidity risk<br />
Liquidity risk is the risk that the Company will not be able to meet its financial obligations as they fall due. The<br />
Company’s approach to managing liquidity is to ensure, as far as possible, that it will always have sufficient<br />
liquidity to meet its liabilities when due, under both normal and stressed conditions, without incurring unacceptable<br />
losses or risking damage to the Company’s reputation. The Company uses different methods which assists it<br />
in monitoring cash flow requirements. Typically the Company ensures that it has sufficient cash on demand to<br />
meet expected operational expenses for a reasonable period, including the servicing of financial obligation; this<br />
excludes the potential impact of extreme circumstances that cannot reasonably be predicted, such as natural<br />
disasters by maintaining adequate reserves, banking facilities and reserve borrowing facilities and continuously<br />
monitoring forecast and actual cash flows and matching the maturity profiles of financial assets and liabilities.<br />
Included in note. 26.1 to the financial statements is a detail of additional undrawn facilities that the Company has<br />
at its disposal to further reduce liquidity risk.<br />
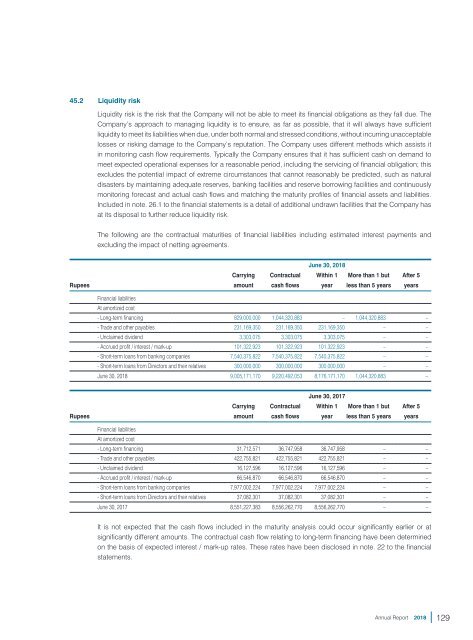
The following are the contractual maturities of financial liabilities including estimated interest payments and<br />
excluding the impact of netting agreements.<br />
June 30, <strong>2018</strong><br />
Carrying Contractual Within 1 More than 1 but After 5<br />
Rupees amount cash flows year less than 5 years years<br />
Financial liabilities<br />
At amortized cost<br />
- Long-term financing 829,000,000 1,044,320,883 – 1,044,320,883 –<br />
- Trade and other payables 231,169,350 231,169,350 231,169,350 – –<br />
- Unclaimed dividend 3,303,075 3,303,075 3,303,075 – –<br />
- Accrued profit / interest / mark-up 101,322,923 101,322,923 101,322,923 – –<br />
- Short-term loans from banking companies 7,540,375,822 7,540,375,822 7,540,375,822 – –<br />
- Short-term loans from Directors and their relatives 300,000,000 300,000,000 300,000,000 – –<br />
June 30, <strong>2018</strong> 9,005,171,170 9,220,492,053 8,176,171,170 1,044,320,883 –<br />
June 30, 2017<br />
Carrying Contractual Within 1 More than 1 but After 5<br />
Rupees amount cash flows year less than 5 years years<br />
Financial liabilities<br />
At amortized cost<br />
- Long-term financing 31,712,571 36,747,958 36,747,958 – –<br />
- Trade and other payables 422,755,821 422,755,821 422,755,821 – –<br />
- Unclaimed dividend 16,127,596 16,127,596 16,127,596 – –<br />
- Accrued profit / interest / mark-up 66,546,870 66,546,870 66,546,870 – –<br />
- Short-term loans from banking companies 7,977,002,224 7,977,002,224 7,977,002,224 – –<br />
- Short-term loans from Directors and their relatives 37,082,301 37,082,301 37,082,301 – –<br />
June 30, 2017 8,551,227,383 8,556,262,770 8,556,262,770 – –<br />
It is not expected that the cash flows included in the maturity analysis could occur significantly earlier or at<br />
significantly different amounts. The contractual cash flow relating to long-term financing have been determined<br />
on the basis of expected interest / mark-up rates. These rates have been disclosed in note. 22 to the financial<br />
statements.<br />
Annual Report <strong>2018</strong><br />
129