Business Potential for Agricultural Biotechnology - Asian Productivity ...
Business Potential for Agricultural Biotechnology - Asian Productivity ...
Business Potential for Agricultural Biotechnology - Asian Productivity ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Business</strong> <strong>Potential</strong> <strong>for</strong> <strong>Agricultural</strong> <strong>Biotechnology</strong> Products in the Philippines<br />
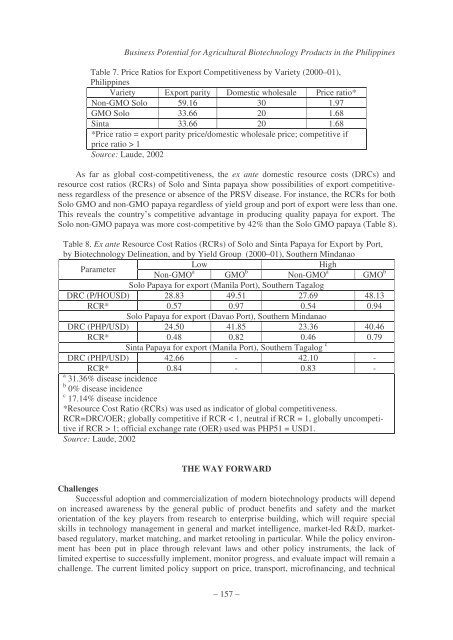
Table 7. Price Ratios <strong>for</strong> Export Competitiveness by Variety (2000–01),<br />
Philippines<br />
Variety Export parity Domestic wholesale Price ratio*<br />
Non-GMO Solo 59.16 30 1.97<br />
GMO Solo 33.66 20 1.68<br />
Sinta 33.66 20 1.68<br />
*Price ratio = export parity price/domestic wholesale price; competitive if<br />
price ratio > 1<br />
Source: Laude, 2002<br />
As far as global cost-competitiveness, the ex ante domestic resource costs (DRCs) and<br />
resource cost ratios (RCRs) of Solo and Sinta papaya show possibilities of export competitiveness<br />
regardless of the presence or absence of the PRSV disease. For instance, the RCRs <strong>for</strong> both<br />
Solo GMO and non-GMO papaya regardless of yield group and port of export were less than one.<br />
This reveals the country’s competitive advantage in producing quality papaya <strong>for</strong> export. The<br />
Solo non-GMO papaya was more cost-competitive by 42% than the Solo GMO papaya (Table 8).<br />
Table 8. Ex ante Resource Cost Ratios (RCRs) of Solo and Sinta Papaya <strong>for</strong> Export by Port,<br />
by <strong>Biotechnology</strong> Delineation, and by Yield Group (2000–01), Southern Mindanao<br />
Low High<br />
Parameter<br />
Non-GMO a GMO b Non-GMO a GMO b<br />
Solo Papaya <strong>for</strong> export (Manila Port), Southern Tagalog<br />
DRC (P/HOUSD) 28.83 49.51 27.69 48.13<br />
RCR* 0.57 0.97 0.54 0.94<br />
Solo Papaya <strong>for</strong> export (Davao Port), Southern Mindanao<br />
DRC (PHP/USD) 24.50 41.85 23.36 40.46<br />
RCR* 0.48 0.82 0.46 0.79<br />
Sinta Papaya <strong>for</strong> export (Manila Port), Southern Tagalog c<br />
DRC (PHP/USD) 42.66 - 42.10 -<br />
RCR*<br />
a<br />
31.36% disease incidence<br />
b<br />
0% disease incidence<br />
c<br />
17.14% disease incidence<br />
0.84 - 0.83 -<br />
*Resource Cost Ratio (RCRs) was used as indicator of global competitiveness.<br />
RCR=DRC/OER; globally competitive if RCR < 1, neutral if RCR = 1, globally uncompetitive<br />
if RCR > 1; official exchange rate (OER) used was PHP51 = USD1.<br />
Source: Laude, 2002<br />
THE WAY FORWARD<br />
Challenges<br />
Successful adoption and commercialization of modern biotechnology products will depend<br />
on increased awareness by the general public of product benefits and safety and the market<br />
orientation of the key players from research to enterprise building, which will require special<br />
skills in technology management in general and market intelligence, market-led R&D, marketbased<br />
regulatory, market matching, and market retooling in particular. While the policy environment<br />
has been put in place through relevant laws and other policy instruments, the lack of<br />
limited expertise to successfully implement, monitor progress, and evaluate impact will remain a<br />
challenge. The current limited policy support on price, transport, microfinancing, and technical<br />
– 157 –