A Review of Highway Agencies in the South Asia Region
A Review of Highway Agencies in the South Asia Region
A Review of Highway Agencies in the South Asia Region
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
A <strong>Review</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Highway</strong> <strong>Agencies</strong> <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>South</strong> <strong>Asia</strong> <strong>Region</strong><br />
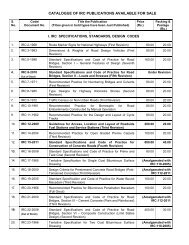
Table A6: Computation <strong>of</strong> NQI<br />
<strong>in</strong> millimeter (mm) per km <strong>of</strong> road. The follow<strong>in</strong>g steps can be used to compute <strong>the</strong> NQI <strong>of</strong><br />
<strong>the</strong> network.<br />
Step 1: The roughness levels may be measured all along <strong>the</strong> CRN once a year; divide <strong>the</strong><br />
network <strong>in</strong>to <strong>the</strong> follow<strong>in</strong>g categories:<br />
(a) Length where roughness is up to 3,000 mm/km<br />
(b) Length where roughness is between 3,000 and 4,000 mm/km<br />
(c) Length where roughness is more than 4,000 mm/km<br />
Step 2: Tabulate <strong>the</strong> results and compute <strong>the</strong> NQI consider<strong>in</strong>g <strong>the</strong> extent <strong>of</strong> roughness on<br />
<strong>the</strong> network as <strong>in</strong>dicated <strong>in</strong> Table A6.<br />
Roughness Level Percent Length <strong>of</strong> CRN Relative Score Weighted Score<br />
Up to 3,000 mm/km x 1 100 x 1 = WS 1<br />
Between 3,000 and 4,000 mm/km x 2 80 0.80 x 2 = WS 2<br />
More than 4,000 mm/km x 3 50 0.50 x 3 = WS 3<br />
Network Quality Index WS 1 + WS 2 + WS 3<br />
Table A7: Result <strong>of</strong> analysis <strong>in</strong> Step 1<br />
Higher <strong>the</strong> value <strong>of</strong> NQI, better <strong>the</strong> performance <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> highway agency.<br />
An example to illustrate <strong>the</strong> computation <strong>of</strong> NQI follows.<br />
(i) Let us assume that, as a result <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> analysis carried out <strong>in</strong> Step 1, <strong>the</strong> follow<strong>in</strong>g picture<br />
emerges (Table A7):<br />
Roughness Length Percent Length<br />
Length where roughness is up to 3,000 mm/km 4,000 km (33.33%)<br />
Length where roughness is between 3,000 and 4,000 mm/km 6,000 km (50.00%)<br />
Length where roughness is more than 4,000 mm/km 2,000 km (16.67%)<br />
Total 12,000 km 100.00<br />
Table A8: Computation <strong>of</strong> NQI<br />
(ii) Computation <strong>of</strong> NQI<br />
Roughness Level Percent Length <strong>of</strong> CRN Relative Score Weighted Score<br />
Length where roughness 33.33 100 33.33<br />
is up to 3,000 mm/km<br />
Length where roughness 50.00 80 0.80 x 50.00 = 40.00<br />
is between 3,000 and<br />
4,000 mm/km<br />
Length where roughness is<br />
more than 4,000 mm/km 16.67 50 0.50 x 16.67 = 8.33<br />
Network Quality Index 81.66, say 82<br />
84