The role of contractual arrangements in improving health sector ...
The role of contractual arrangements in improving health sector ...
The role of contractual arrangements in improving health sector ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Jordan<br />
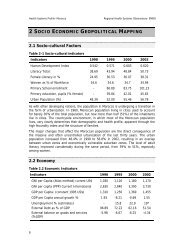
region. This, coupled with the cont<strong>in</strong>ued decl<strong>in</strong>e <strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong>fant mortality (22 deaths per<br />
1000 live births for 2002) and the rise <strong>in</strong> life expectancy at birth (70.6 and 72.4 years<br />
for males and females, respectively), represents a significant social and economic<br />
challenge to the government (M<strong>in</strong>istry <strong>of</strong> Health Annual Book, 2002).<br />
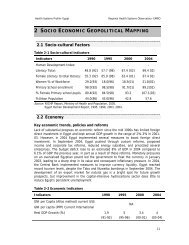
Jordan has a small economy with limited natural resources, arid land mostly<br />
unsuitable for agriculture, and chronic water shortages. It imports most <strong>of</strong> the energy<br />
it consumes. <strong>The</strong> economic situation is aggravated by the political environment,<br />
which makes efforts to revive the economy difficult task. Although the GDP growth<br />
rate slightly improved between 2001 and 2002 (4.2% versus 4%), the cost <strong>of</strong> liv<strong>in</strong>g<br />
also <strong>in</strong>creased. <strong>The</strong> unemployment figure is still high between 14.7%–16% accord<strong>in</strong>g<br />
to different estimates. Nearly 12% <strong>of</strong> the Jordanian population is below the national<br />
poverty l<strong>in</strong>e (World Bank Group, 2002).<br />
Based on the commonly used development <strong>in</strong>dicators, Jordan fares better than<br />
most countries <strong>in</strong> the low–middle <strong>in</strong>come category. <strong>The</strong> majority <strong>of</strong> the population<br />
has access to basic <strong>in</strong>frastructure such as safe water, sanitation and electricity, and<br />
lives <strong>in</strong> permanent dwell<strong>in</strong>g structures. Government commitments to improve the<br />
overall quality <strong>of</strong> life and the social standards <strong>of</strong> its people have borne impressive<br />
results. Primary and secondary <strong>health</strong> care services are distributed all over the country<br />
with 98% to 100% population access to local <strong>health</strong> services (WHO, Country<br />
Pr<strong>of</strong>iles, 2003). <strong>The</strong> total literacy rate is 89.7% and Jordan has a well developed<br />
human resource base.<br />
Health <strong>sector</strong> brief<br />
Jordan has one <strong>of</strong> the most modern <strong>health</strong> care <strong>in</strong>frastructures <strong>in</strong> the Middle<br />
East. Jordan’s <strong>health</strong> system is a complex amalgam <strong>of</strong> three major <strong>sector</strong>s: public,<br />
private and donors. <strong>The</strong> public <strong>sector</strong> consists <strong>of</strong> two major public programmes that<br />
f<strong>in</strong>ance as well as deliver care: the M<strong>in</strong>istry <strong>of</strong> Health and Royal Medical Services.<br />
Other smaller public programmes <strong>in</strong>clude several university-based programmes, such<br />
as Jordan University Hospital <strong>in</strong> Amman and K<strong>in</strong>g Abdullah Hospital <strong>in</strong> Irbid. In<br />
2001, the total expenditure on <strong>health</strong> services accounted for about JD 598 million,<br />
9.5% <strong>of</strong> the GDP. Health expenditure per capita was JD 115 (Jordan’s National Health<br />
Accounts, Draft Report, 2004). Each <strong>of</strong> the <strong>health</strong> care sub-<strong>sector</strong>s has its own<br />
f<strong>in</strong>anc<strong>in</strong>g and delivery system that reflects directly on <strong>contractual</strong> <strong>arrangements</strong><br />
among these <strong>sector</strong>s. <strong>The</strong> follow<strong>in</strong>g description gives an <strong>in</strong>stitutional overview <strong>of</strong> the<br />
<strong>health</strong> care f<strong>in</strong>anc<strong>in</strong>g and delivery <strong>of</strong> each <strong>sector</strong>.<br />
M<strong>in</strong>istry <strong>of</strong> Health<br />
<strong>The</strong> M<strong>in</strong>istry <strong>of</strong> Health is the major s<strong>in</strong>gle <strong>in</strong>stitution f<strong>in</strong>ancer and provider <strong>of</strong><br />
<strong>health</strong> care services <strong>in</strong> Jordan. It is the largest <strong>in</strong> terms <strong>of</strong> the size <strong>of</strong> its operation and<br />
utilization as compared to Royal Medical Services, Jordan University Hospital, K<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Abdullah Hospital, or others <strong>in</strong> the private <strong>sector</strong>. <strong>The</strong> M<strong>in</strong>istry owns and operates 27<br />
hospitals <strong>in</strong> 11 governorates, with 3462 hospital beds account<strong>in</strong>g for 37% <strong>of</strong> total<br />
108