Tutorials Manual
Tutorials Manual
Tutorials Manual
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Chemkin 4.1.1<br />
Chapter 2: Combustion in Gas-phase Processes<br />
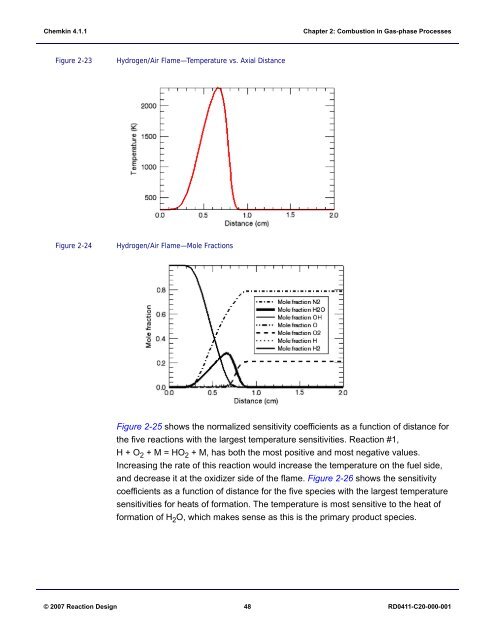
Figure 2-23<br />
Hydrogen/Air Flame—Temperature vs. Axial Distance<br />
Figure 2-24<br />
Hydrogen/Air Flame—Mole Fractions<br />
Figure 2-25 shows the normalized sensitivity coefficients as a function of distance for<br />
the five reactions with the largest temperature sensitivities. Reaction #1,<br />
H+O 2 +M=HO 2 + M, has both the most positive and most negative values.<br />
Increasing the rate of this reaction would increase the temperature on the fuel side,<br />
and decrease it at the oxidizer side of the flame. Figure 2-26 shows the sensitivity<br />
coefficients as a function of distance for the five species with the largest temperature<br />
sensitivities for heats of formation. The temperature is most sensitive to the heat of<br />
formation of H 2 O, which makes sense as this is the primary product species.<br />
© 2007 Reaction Design 48 RD0411-C20-000-001