Plutonium Biokinetics in Human Body A. Luciani - Kit-Bibliothek - FZK
Plutonium Biokinetics in Human Body A. Luciani - Kit-Bibliothek - FZK
Plutonium Biokinetics in Human Body A. Luciani - Kit-Bibliothek - FZK
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
HPGe crystals are produced <strong>in</strong> cyl<strong>in</strong>drical shape (called coaxial) for the detection of<br />
high energy photons emitters (typically for energy higher then 100 keV): their large volume<br />
enhances the probability of <strong>in</strong>teraction of the penetrat<strong>in</strong>g energetic photons with the crystal.<br />
For the detection of low energy photon emitters (typically for energy lower then 100 keV)<br />
planar shaped Germanium detectors are normally used because low penetrat<strong>in</strong>g photons have<br />
high probability of <strong>in</strong>teract<strong>in</strong>g, i.e. of be<strong>in</strong>g detected, already with th<strong>in</strong> Germanium crystals.<br />
At <strong>FZK</strong> coaxial and planar HPGe detectors are coupled: a coaxial detector is placed back to<br />
the planar detector <strong>in</strong> order that high energy photons cross the planar detector and can be<br />
detected by the coaxial detector. They can operate as a antico<strong>in</strong>cidence guard for background<br />
suppression purposes of high energy photons, <strong>in</strong> the same way as a phoswich detector. Both<br />
the detectors are cooled by means of a cool<strong>in</strong>g rod with an extremity dipped <strong>in</strong> the liquid<br />
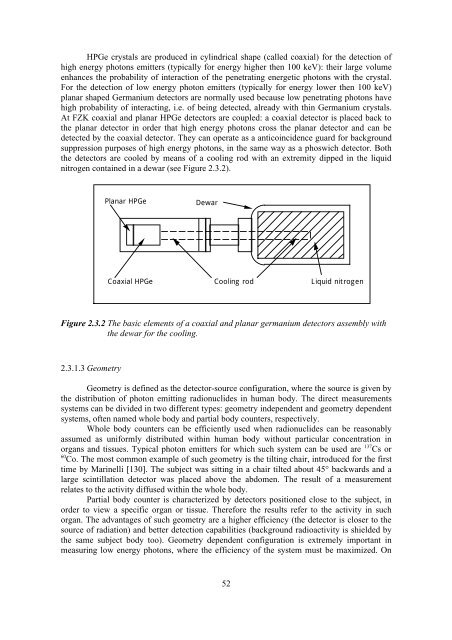
nitrogen conta<strong>in</strong>ed <strong>in</strong> a dewar (see Figure 2.3.2).<br />
Figure 2.3.2 The basic elements of a coaxial and planar germanium detectors assembly with<br />
the dewar for the cool<strong>in</strong>g.<br />
2.3.1.3 Geometry<br />
Planar HPGe<br />
Dewar<br />
Coaxial HPGe Cool<strong>in</strong>g rod<br />
Geometry is def<strong>in</strong>ed as the detector-source configuration, where the source is given by<br />
the distribution of photon emitt<strong>in</strong>g radionuclides <strong>in</strong> human body. The direct measurements<br />
systems can be divided <strong>in</strong> two different types: geometry <strong>in</strong>dependent and geometry dependent<br />
systems, often named whole body and partial body counters, respectively.<br />
Whole body counters can be efficiently used when radionuclides can be reasonably<br />
assumed as uniformly distributed with<strong>in</strong> human body without particular concentration <strong>in</strong><br />
organs and tissues. Typical photon emitters for which such system can be used are 137 Cs or<br />
60 Co. The most common example of such geometry is the tilt<strong>in</strong>g chair, <strong>in</strong>troduced for the first<br />
time by Mar<strong>in</strong>elli [130]. The subject was sitt<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> a chair tilted about 45° backwards and a<br />
large sc<strong>in</strong>tillation detector was placed above the abdomen. The result of a measurement<br />
relates to the activity diffused with<strong>in</strong> the whole body.<br />
Partial body counter is characterized by detectors positioned close to the subject, <strong>in</strong><br />
order to view a specific organ or tissue. Therefore the results refer to the activity <strong>in</strong> such<br />
organ. The advantages of such geometry are a higher efficiency (the detector is closer to the<br />
source of radiation) and better detection capabilities (background radioactivity is shielded by<br />
the same subject body too). Geometry dependent configuration is extremely important <strong>in</strong><br />
measur<strong>in</strong>g low energy photons, where the efficiency of the system must be maximized. On<br />
52<br />
Liquid nitrogen











![{A1[]Sp - Bibliothek](https://img.yumpu.com/21908054/1/184x260/a1sp-bibliothek.jpg?quality=85)




