programming with max/msp - Virtual Sound
programming with max/msp - Virtual Sound
programming with max/msp - Virtual Sound
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Chapter 2P - Additive and vector synthesis 2P<br />
ACTIVITIES<br />
Using the patch 02_01_additive.<strong>max</strong>pat, create two presets, one that has the<br />
amplitudes of the odd harmonics set to 1, and those of the even harmonics set<br />
to 0. Apart from timbre, what is the obvious difference? Why?<br />
Continuing to use 02_01_additive.<strong>max</strong>pat (and referring to the discussion of<br />
missing fundamentals in Section 2.1T), begin <strong>with</strong> a spectrum in which the<br />
amplitudes of all harmonics are 1, and then zero out the amplitude of the<br />
fundamental. Listen for the illusion that the zeroed fundamental appears to be<br />
present. Try reducing the amplitude of successive harmonics, one by one. At<br />
what point can you no longer perceive the fundamental?<br />
PHASE<br />
We now take on a topic discussed at length in Section 2.1T (Section 2.1 of<br />
Chapter 2T), the phase of a periodic waveform. It is a basic concept that will<br />
develop over many chapters; because of this, it is important to understand<br />
how phase is managed using Max/MSP. Probably you have noticed that the<br />
cycle~ object has two inlets: the left, as we already know, allows us to set<br />
the frequency, and the right allows us to set the normalized phase, a phase<br />
that is expressed as a value between 0 and 1 (rather than a value between 0<br />
and 360 degrees or between 0 and 2π radians, both of which we encountered<br />
in the box dedicated to phase in Section 2.1T).<br />
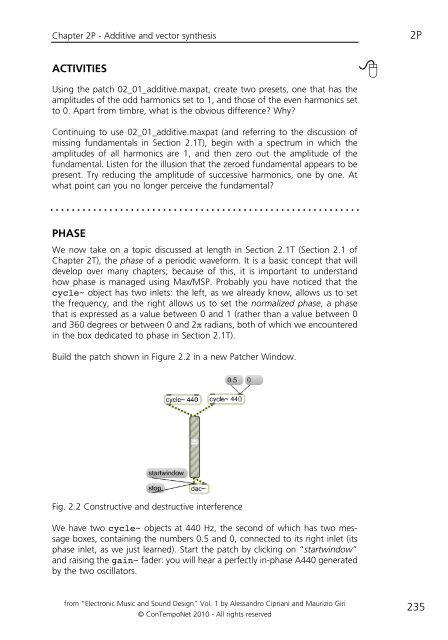
Build the patch shown in Figure 2.2 in a new Patcher Window.<br />
Fig. 2.2 Constructive and destructive interference<br />
We have two cycle~ objects at 440 Hz, the second of which has two message<br />
boxes, containing the numbers 0.5 and 0, connected to its right inlet (its<br />
phase inlet, as we just learned). Start the patch by clicking on “startwindow”<br />
and raising the gain~ fader: you will hear a perfectly in-phase A440 generated<br />
by the two oscillators.<br />
from “Electronic Music and <strong>Sound</strong> Design” Vol. 1 by Alessandro Cipriani and Maurizio Giri<br />
© ConTempoNet 2010 - All rights reserved<br />
8<br />
235