Inclination sensors
Inclination sensors
Inclination sensors
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
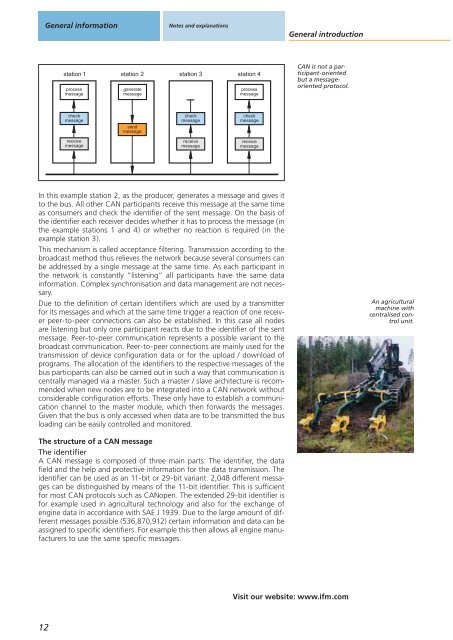
General informationNotes and explanationsGeneral introductionstation 1 station 2 station 3 station 4processmessagegeneratemessageprocessmessageCAN is not a participant-orientedbut a messageorientedprotocol.checkmessagesendmessagecheckmessagecheckmessagereceivemessagereceivemessagereceivemessageIn this example station 2, as the producer, generates a message and gives itto the bus. All other CAN participants receive this message at the same timeas consumers and check the identifier of the sent message. On the basis ofthe identifier each receiver decides whether it has to process the message (inthe example stations 1 and 4) or whether no reaction is required (in theexample station 3).This mechanism is called acceptance filtering. Transmission according to thebroadcast method thus relieves the network because several consumers canbe addressed by a single message at the same time. As each participant inthe network is constantly “listening” all participants have the same datainformation. Complex synchronisation and data management are not necessary.Due to the definition of certain identifiers which are used by a transmitterfor its messages and which at the same time trigger a reaction of one receiverpeer-to-peer connections can also be established. In this case all nodesare listening but only one participant reacts due to the identifier of the sentmessage. Peer-to-peer communication represents a possible variant to thebroadcast communication. Peer-to-peer connections are mainly used for thetransmission of device configuration data or for the upload / download ofprograms. The allocation of the identifiers to the respective messages of thebus participants can also be carried out in such a way that communication iscentrally managed via a master. Such a master / slave architecture is recommendedwhen new nodes are to be integrated into a CAN network withoutconsiderable configuration efforts. These only have to establish a communicationchannel to the master module, which then forwards the messages.Given that the bus is only accessed when data are to be transmitted the busloading can be easily controlled and monitored.An agriculturalmachine withcentralised controlunit.The structure of a CAN messageThe identifierA CAN message is composed of three main parts: The identifier, the datafield and the help and protective information for the data transmission. Theidentifier can be used as an 11-bit or 29-bit variant. 2,048 different messagescan be distinguished by means of the 11-bit identifier. This is sufficientfor most CAN protocols such as CANopen. The extended 29-bit identifier isfor example used in agricultural technology and also for the exchange ofengine data in accordance with SAE J 1939. Due to the large amount of differentmessages possible (536,870,912) certain information and data can beassigned to specific identifiers. For example this then allows all engine manufacturersto use the same specific messages.Visit our website: www.ifm.com12