Environmental & Social Management Framework - About ...
Environmental & Social Management Framework - About ...
Environmental & Social Management Framework - About ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
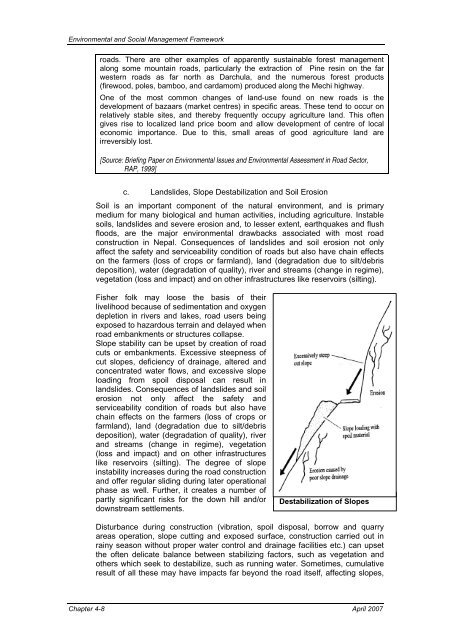
<strong>Environmental</strong> and <strong>Social</strong> <strong>Management</strong> <strong>Framework</strong>roads. There are other examples of apparently sustainable forest managementalong some mountain roads, particularly the extraction of Pine resin on the farwestern roads as far north as Darchula, and the numerous forest products(firewood, poles, bamboo, and cardamom) produced along the Mechi highway.One of the most common changes of land-use found on new roads is thedevelopment of bazaars (market centres) in specific areas. These tend to occur onrelatively stable sites, and thereby frequently occupy agriculture land. This oftengives rise to localized land price boom and allow development of centre of localeconomic importance. Due to this, small areas of good agriculture land areirreversibly lost.[Source: Briefing Paper on <strong>Environmental</strong> Issues and <strong>Environmental</strong> Assessment in Road Sector,RAP, 1999]c. Landslides, Slope Destabilization and Soil ErosionSoil is an important component of the natural environment, and is primarymedium for many biological and human activities, including agriculture. Instablesoils, landslides and severe erosion and, to lesser extent, earthquakes and flushfloods, are the major environmental drawbacks associated with most roadconstruction in Nepal. Consequences of landslides and soil erosion not onlyaffect the safety and serviceability condition of roads but also have chain effectson the farmers (loss of crops or farmland), land (degradation due to silt/debrisdeposition), water (degradation of quality), river and streams (change in regime),vegetation (loss and impact) and on other infrastructures like reservoirs (silting).Fisher folk may loose the basis of theirlivelihood because of sedimentation and oxygendepletion in rivers and lakes, road users beingexposed to hazardous terrain and delayed whenroad embankments or structures collapse.Slope stability can be upset by creation of roadcuts or embankments. Excessive steepness ofcut slopes, deficiency of drainage, altered andconcentrated water flows, and excessive slopeloading from spoil disposal can result inlandslides. Consequences of landslides and soilerosion not only affect the safety andserviceability condition of roads but also havechain effects on the farmers (loss of crops orfarmland), land (degradation due to silt/debrisdeposition), water (degradation of quality), riverand streams (change in regime), vegetation(loss and impact) and on other infrastructureslike reservoirs (silting). The degree of slopeinstability increases during the road constructionand offer regular sliding during later operationalphase as well. Further, it creates a number ofpartly significant risks for the down hill and/ordownstream settlements.Destabilization of SlopesDisturbance during construction (vibration, spoil disposal, borrow and quarryareas operation, slope cutting and exposed surface, construction carried out inrainy season without proper water control and drainage facilities etc.) can upsetthe often delicate balance between stabilizing factors, such as vegetation andothers which seek to destabilize, such as running water. Sometimes, cumulativeresult of all these may have impacts far beyond the road itself, affecting slopes,Chapter 4-8 April 2007


![j:6 ]zg cfof ]hgf](https://img.yumpu.com/51286794/1/190x245/j6-zg-cfof-hgf.jpg?quality=85)

![x'nfsL /fhdfu { cfof ]hgf](https://img.yumpu.com/50581959/1/190x245/xnfsl-fhdfu-cfof-hgf.jpg?quality=85)










