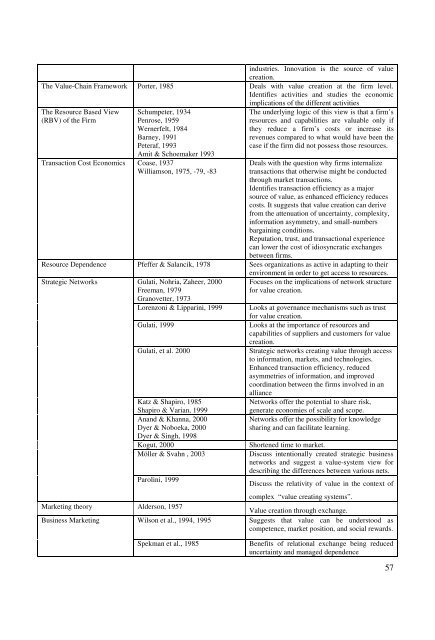
<strong>in</strong>dustries. Innovation is the source of valuecreation.The <strong>Value</strong>-Cha<strong>in</strong> Framework Porter, 1985 Deals with value creation at the firm level.Identifies activities and studies the economicimplications of the different activitiesThe Resource Based View(RBV) of the FirmSchumpeter, 1934Penrose, 1959Wernerfelt, 1984Barney, 1991Peteraf, 1993Amit & Schoemaker 1993The underly<strong>in</strong>g logic of this view is that a firm’ sresources and capabilities are valuable only ifthey reduce a firm’ s costs or <strong>in</strong>crease itsrevenues compared to what would have been thecase if the firm did not possess those resources.Transaction <strong>Co</strong>st Economics <strong>Co</strong>ase, 1937Williamson, 1975, -79, -83Deals with the question why firms <strong>in</strong>ternalizetransactions that otherwise might be conductedthrough market transactions.Identifies transaction efficiency as a majorsource of value, as enhanced efficiency reducescosts. It suggests that value creation can derivefrom the attenuation of uncerta<strong>in</strong>ty, complexity,<strong>in</strong>formation asymmetry, and small-numbersbarga<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g conditions.Reputation, trust, and transactional experiencecan lower the cost of idiosyncratic exchangesbetween firms.Resource Dependence Pfeffer & Salancik, 1978 Sees organizations as active <strong>in</strong> adapt<strong>in</strong>g to theirenvironment <strong>in</strong> order to get access to resources.Strategic NetworksGulati, Nohria, Zaheer, 2000Freeman, 1979Granovetter, 1973Lorenzoni & Lippar<strong>in</strong>i, 1999Gulati, 1999Gulati, et al. 2000Katz & Shapiro, 1985Shapiro & Varian, 1999Anand & Khanna, 2000Dyer & Noboeka, 2000Dyer & S<strong>in</strong>gh, 1998Kogut, 2000Möller & Svahn , 2003Parol<strong>in</strong>i, 1999Market<strong>in</strong>g theory Alderson, 1957Bus<strong>in</strong>ess Market<strong>in</strong>gWilson et al., 1994, 1995Focuses on the implications of network structurefor value creation.Looks at governance mechanisms such as trustfor value creation.Looks at the importance of resources andcapabilities of suppliers and customers for valuecreation.Strategic networks creat<strong>in</strong>g value through accessto <strong>in</strong>formation, markets, and technologies.Enhanced transaction efficiency, reducedasymmetries of <strong>in</strong>formation, and improvedcoord<strong>in</strong>ation between the firms <strong>in</strong>volved <strong>in</strong> anallianceNetworks offer the potential to share risk,generate economies of scale and scope.Networks offer the possibility for knowledgeshar<strong>in</strong>g and can facilitate learn<strong>in</strong>g.Shortened time to market.Discuss <strong>in</strong>tentionally created strategic bus<strong>in</strong>essnetworks and suggest a value-system view fordescrib<strong>in</strong>g the differences between various nets.Discuss the relativity of value <strong>in</strong> the context ofcomplex “ value creat<strong>in</strong>g systems” .<strong>Value</strong> creation through exchange.Suggests that value can be understood ascompetence, market position, and social rewards.Spekman et al., 1985Benefits of relational exchange be<strong>in</strong>g reduceduncerta<strong>in</strong>ty and managed dependence57
Dwyer et al., 1987Anderson & Narus, 1998, 1999,2004Snehota, 1990Benefits of buyer-seller relations <strong>in</strong> achiev<strong>in</strong>ggoals as a result of effective communication andcollaboration<strong>Co</strong>nceptualizes customer value by discuss<strong>in</strong>gvalue and price of offer<strong>in</strong>gs provided bysuppliers to customers.<strong>Value</strong> as the realization of the potential services<strong>in</strong> resources through bus<strong>in</strong>ess exchange.Gadde & Snehota, 2000 Discusses benefits and costs of supplierrelationships where costs are; direct procurementcosts, transaction costs, relationship handl<strong>in</strong>gcosts, and supply handl<strong>in</strong>g costs. Benefits <strong>in</strong> turnare divided <strong>in</strong>to cost benefits and revenuebenefits.De Chernatory et al., 2000 <strong>Value</strong> as a trade off between total benefits andsacrificesWalter el al., 2001Discusses functions of a customer relationship;direct functions: profit function, the volumefunction and the safeguard function. Indirectfunctions: the <strong>in</strong>novation function, the marketfunction, the scout function and the accessfunction. Supplier-perceived value consists offunctions of a customer relationshipUlaga, 2001Discusses customer value by us<strong>in</strong>g threedifferent perspectives: the “ buyer perspective” ,“ the supplier perspective” and “ the buyer-sellerperspective” .Gadde et al., 2002Discusses price as an aspect of cost and revenue<strong>in</strong> the exchange processSelnes & Johnson, 2004Presents a typology for value creation <strong>in</strong> anexchange relationship by us<strong>in</strong>g parity value,differentiated value and customized value.Håkansson & Prenkert, 2004 Dist<strong>in</strong>guishes between exchange value and usevalue.Table 3.1: Summary of conceptualizations of valueGiven the above literature review on value and the summarization above it can clearly beseen that value can be thought of <strong>in</strong> a number of different ways, depend<strong>in</strong>g on the context.As mentioned earlier value is relative and should be treated as such. In this study, which isan exploratory case study, the stated aim is to review how value has been used theoreticallyand to explore empirically how it is perceived <strong>in</strong> a buyer-seller dyad. For this purpose Ibelieve that a loose conceptual framework is the most suitable for this study. A looseframework will give room for the empirical material to speak. In this way exploration willbe possible <strong>in</strong>stead of be<strong>in</strong>g locked <strong>in</strong> a rigid pre-understand<strong>in</strong>g of what could be perceivedas value <strong>in</strong> this particular context.58
- Page 1 and 2:
Birgitta ForsströmValue Co-Creatio
- Page 3 and 4:
VALUE CO-CREATION IN INDUSTRIAL BUY
- Page 5 and 6:
CIP Cataloguing in PublicationForss
- Page 7 and 8:
Suokannas and Annica Isacsson my de
- Page 9 and 10:
3.3 The use of the value concept in
- Page 11 and 12:
7.2.1 Price as a benefit and a sacr
- Page 13 and 14: Figure 8.1: Interdependence, involv
- Page 15 and 16: 81. INTRODUCTIONEconomic theory rel
- Page 17 and 18: Portfolio management and key accoun
- Page 19 and 20: value - ways to understand and thin
- Page 21 and 22: creation in a world of relationship
- Page 23 and 24: Möller and Halinen-Kaila (1999) cr
- Page 25 and 26: Value of a Relationship: When discu
- Page 27 and 28: 1.3 Outline of the studyThe study s
- Page 30 and 31: in such relationships, and on how t
- Page 32 and 33: 2.2 Research approach“ Human gras
- Page 34 and 35: “ In case study both the research
- Page 36 and 37: interview ended up being different
- Page 38 and 39: simplifying and combining observati
- Page 40 and 41: the purpose of why it is studied an
- Page 42 and 43: started paying attention to issues
- Page 44 and 45: The analysis of the material was an
- Page 47: are: setting the boundaries of the
- Page 50 and 51: Critical events during the process
- Page 52 and 53: interviewing, observing, reading, r
- Page 54 and 55: unit. Going even further back in hi
- Page 56 and 57: 3.4.1 Overview of the use of the va
- Page 58 and 59: ç-è1éWèê9ë ì9í!î¹ï5ðWí
- Page 60 and 61: argumentation alters the traditiona
- Page 62 and 63: zG{\| }C~t s oHpaqfrRs t s qXu2vs y
- Page 66 and 67: ôô3.7 SummaryThe assessment of va
- Page 68 and 69: 4. A RELATIONAL APPROACH TO VALUE C
- Page 70 and 71: est way to organize, any way of org
- Page 72 and 73: 4.2 The IMP view on relationships a
- Page 74 and 75: The focus and unit of analysis of t
- Page 76 and 77: ecent book discuss how creating val
- Page 78 and 79: not simply mutual dependence betwee
- Page 80 and 81: 3n3465-7 89;:=©:¡?@95AB
- Page 82 and 83: interdependence is associated with
- Page 84 and 85: “ The performance of supplier arr
- Page 86 and 87: Figure 4.5: Different value creatin
- Page 88 and 89: “ organizational arrangements tha
- Page 90 and 91: There is no simple or universal def
- Page 92 and 93: The question of win-win in partners
- Page 94 and 95: The following chapter, number five,
- Page 96 and 97: The world cruise industry is domina
- Page 98 and 99: Figure 5.2: The actors and the setu
- Page 100 and 101: ù õ ñ ù õ ó*ÿ¡ ÷£¢ ñ¤
- Page 102 and 103: :: ]:: ]In normal cases the Seller
- Page 104 and 105: the top 10 suppliers for the cruise
- Page 106 and 107: 6. THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE RELATIONS
- Page 108 and 109: In 1997 when Mr BR9 got the positio
- Page 110 and 111: The relationship between the compan
- Page 112 and 113: ” He (BR9) often talks about the
- Page 114 and 115:
With some years of experience with
- Page 116 and 117:
offering, the Buyer still sees the
- Page 118 and 119:
When the Seller realized that they
- Page 120 and 121:
we have a new development in the pr
- Page 122 and 123:
to serving the customers - the part
- Page 124 and 125:
” This is the most problematic ag
- Page 126 and 127:
• Optimize operations i.e. fuel o
- Page 128 and 129:
They also commented that the person
- Page 130 and 131:
6.7.5 Comments on internal issuesAt
- Page 132 and 133:
changes, and that the Seller would
- Page 134 and 135:
survey 14 that the Seller had condu
- Page 136 and 137:
uuuuuuu uuuuuuuuuuuuuuue¦f¨gh ijk
- Page 138 and 139:
Seller. At present there are three
- Page 140 and 141:
15 - a factor that should not be ne
- Page 142 and 143:
elationship and the people interact
- Page 144 and 145:
+ K !ñ ú ê ñ ê ö ë î ñ ï
- Page 146 and 147:
7.1 Perceived value as a prerequisi
- Page 148 and 149:
” We are in the process of develo
- Page 150 and 151:
and that is insane. We must be able
- Page 152 and 153:
è èèèè èèèè èè èè èè
- Page 154 and 155:
We learn their way of handling thin
- Page 156 and 157:
Price receivedThe price received ca
- Page 158 and 159:
partnership with the Seller, the as
- Page 160 and 161:
In the light of this, one could say
- Page 162 and 163:
dependence. If managers were not ab
- Page 164 and 165:
¥(¦§¨&©G§ªG¦(£(«¬¨$Z
- Page 166 and 167:
Seller’ s products and concepts,
- Page 168 and 169:
forth between the companies. This h
- Page 170 and 171:
What I found even more interesting
- Page 172 and 173:
The Buyer sees that the interest fo
- Page 174 and 175:
decision to pursue a collaborative
- Page 176 and 177:
methodology. I will also direct som
- Page 178 and 179:
years to come. Consequently the par
- Page 180 and 181:
€‚ƒ‡ ˆ„~„| }~different
- Page 182 and 183:
Question 1: How is the value concep
- Page 184 and 185:
exists, the value co-creation poten
- Page 186 and 187:
partnering and cooperating are so o
- Page 188 and 189:
process of analyzing the material s
- Page 190 and 191:
Barney, JB. (1991). Firms resources
- Page 192 and 193:
Forsström, B., (1998). Trouble & S
- Page 194 and 195:
Katz, M & Shapiro, C (1985). Networ
- Page 196 and 197:
Shapiro, B.P., Rangan V.K., Moriart
- Page 198 and 199:
Interviews:Interview: Buyer 1Interv
- Page 201:
Relationships between buyers and se