Review and Critical Analysis of International UHI Studies
Review and Critical Analysis of International UHI Studies
Review and Critical Analysis of International UHI Studies
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
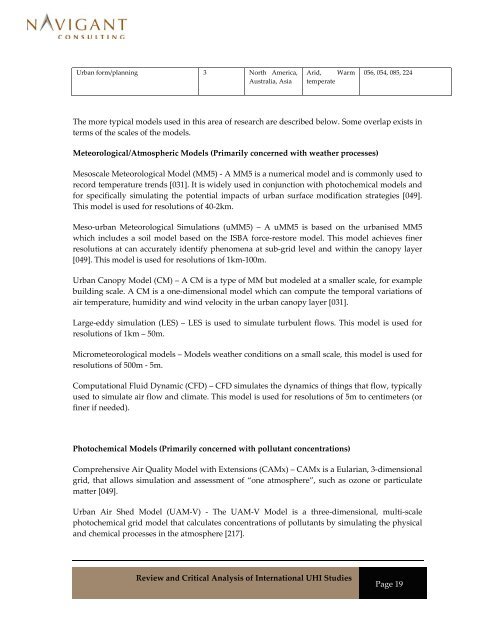
Urban form/planning 3 North America,<br />
Australia, Asia<br />
Arid, Warm<br />
temperate<br />
<strong>Review</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Critical</strong> <strong>Analysis</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>International</strong> <strong>UHI</strong> <strong>Studies</strong><br />
056, 054, 085, 224<br />
The more typical models used in this area <strong>of</strong> research are described below. Some overlap exists in<br />
terms <strong>of</strong> the scales <strong>of</strong> the models.<br />
Meteorological/Atmospheric Models (Primarily concerned with weather processes)<br />
Mesoscale Meteorological Model (MM5) ‐ A MM5 is a numerical model <strong>and</strong> is commonly used to<br />
record temperature trends [031]. It is widely used in conjunction with photochemical models <strong>and</strong><br />
for specifically simulating the potential impacts <strong>of</strong> urban surface modification strategies [049].<br />
This model is used for resolutions <strong>of</strong> 40‐2km.<br />
Meso‐urban Meteorological Simulations (uMM5) – A uMM5 is based on the urbanised MM5<br />
which includes a soil model based on the ISBA force‐restore model. This model achieves finer<br />
resolutions at can accurately identify phenomena at sub‐grid level <strong>and</strong> within the canopy layer<br />
[049]. This model is used for resolutions <strong>of</strong> 1km‐100m.<br />
Urban Canopy Model (CM) – A CM is a type <strong>of</strong> MM but modeled at a smaller scale, for example<br />
building scale. A CM is a one‐dimensional model which can compute the temporal variations <strong>of</strong><br />
air temperature, humidity <strong>and</strong> wind velocity in the urban canopy layer [031].<br />
Large‐eddy simulation (LES) – LES is used to simulate turbulent flows. This model is used for<br />
resolutions <strong>of</strong> 1km – 50m.<br />
Micrometeorological models – Models weather conditions on a small scale, this model is used for<br />
resolutions <strong>of</strong> 500m ‐ 5m.<br />
Computational Fluid Dynamic (CFD) – CFD simulates the dynamics <strong>of</strong> things that flow, typically<br />
used to simulate air flow <strong>and</strong> climate. This model is used for resolutions <strong>of</strong> 5m to centimeters (or<br />
finer if needed).<br />
Photochemical Models (Primarily concerned with pollutant concentrations)<br />
Comprehensive Air Quality Model with Extensions (CAMx) – CAMx is a Eularian, 3‐dimensional<br />
grid, that allows simulation <strong>and</strong> assessment <strong>of</strong> “one atmosphere”, such as ozone or particulate<br />
matter [049].<br />
Urban Air Shed Model (UAM‐V) ‐ The UAM‐V Model is a three‐dimensional, multi‐scale<br />
photochemical grid model that calculates concentrations <strong>of</strong> pollutants by simulating the physical<br />
<strong>and</strong> chemical processes in the atmosphere [217].<br />
Page 19