Proceedings in pdf format. - Sociotechnical Systems Engineering ...
Proceedings in pdf format. - Sociotechnical Systems Engineering ...
Proceedings in pdf format. - Sociotechnical Systems Engineering ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
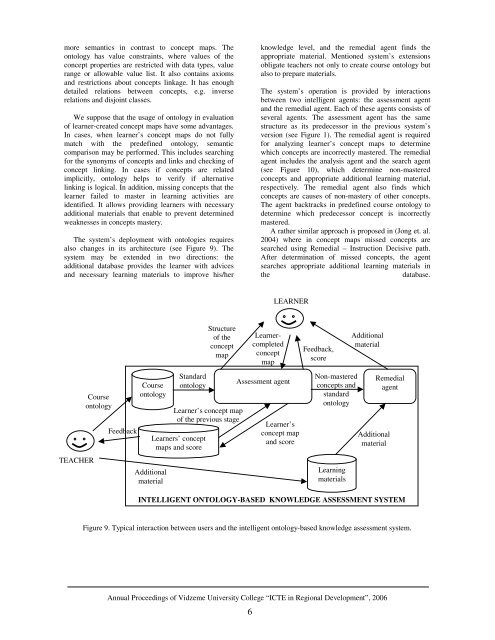
more semantics <strong>in</strong> contrast to concept maps. Theontology has value constra<strong>in</strong>ts, where values of theconcept properties are restricted with data types, valuerange or allowable value list. It also conta<strong>in</strong>s axiomsand restrictions about concepts l<strong>in</strong>kage. It has enoughdetailed relations between concepts, e.g. <strong>in</strong>verserelations and disjo<strong>in</strong>t classes.We suppose that the usage of ontology <strong>in</strong> evaluationof learner-created concept maps have some advantages.In cases, when learner’s concept maps do not fullymatch with the predef<strong>in</strong>ed ontology, semanticcomparison may be performed. This <strong>in</strong>cludes search<strong>in</strong>gfor the synonyms of concepts and l<strong>in</strong>ks and check<strong>in</strong>g ofconcept l<strong>in</strong>k<strong>in</strong>g. In cases if concepts are relatedimplicitly, ontology helps to verify if alternativel<strong>in</strong>k<strong>in</strong>g is logical. In addition, miss<strong>in</strong>g concepts that thelearner failed to master <strong>in</strong> learn<strong>in</strong>g activities areidentified. It allows provid<strong>in</strong>g learners with necessaryadditional materials that enable to prevent determ<strong>in</strong>edweaknesses <strong>in</strong> concepts mastery.The system’s deployment with ontologies requiresalso changes <strong>in</strong> its architecture (see Figure 9). Thesystem may be extended <strong>in</strong> two directions: theadditional database provides the learner with advicesand necessary learn<strong>in</strong>g materials to improve his/herknowledge level, and the remedial agent f<strong>in</strong>ds theappropriate material. Mentioned system’s extensionsobligate teachers not only to create course ontology butalso to prepare materials.The system’s operation is provided by <strong>in</strong>teractionsbetween two <strong>in</strong>telligent agents: the assessment agentand the remedial agent. Each of these agents consists ofseveral agents. The assessment agent has the samestructure as its predecessor <strong>in</strong> the previous system’sversion (see Figure 1). The remedial agent is requiredfor analyz<strong>in</strong>g learner’s concept maps to determ<strong>in</strong>ewhich concepts are <strong>in</strong>correctly mastered. The remedialagent <strong>in</strong>cludes the analysis agent and the search agent(see Figure 10), which determ<strong>in</strong>e non-masteredconcepts and appropriate additional learn<strong>in</strong>g material,respectively. The remedial agent also f<strong>in</strong>ds whichconcepts are causes of non-mastery of other concepts.The agent backtracks <strong>in</strong> predef<strong>in</strong>ed course ontology todeterm<strong>in</strong>e which predecessor concept is <strong>in</strong>correctlymastered.A rather similar approach is proposed <strong>in</strong> (Jong et. al.2004) where <strong>in</strong> concept maps missed concepts aresearched us<strong>in</strong>g Remedial – Instruction Decisive path.After determ<strong>in</strong>ation of missed concepts, the agentsearches appropriate additional learn<strong>in</strong>g materials <strong>in</strong>thedatabase.LEARNERTEACHERCourseontologyFeedbackCourseontologyAdditionalmaterialStandardontologyLearners’ conceptmaps and scoreStructureof theconceptmapLearner’s concept mapof the previous stageLearnercompletedconceptmapAssessment agentLearner’sconcept mapand scoreFeedback,scoreNon-masteredconcepts andstandardontologyLearn<strong>in</strong>gmaterialsAdditionalmaterialAdditionalmaterialRemedialagentINTELLIGENT ONTOLOGY-BASED KNOWLEDGE ASSESSMENT SYSTEMFigure 9. Typical <strong>in</strong>teraction between users and the <strong>in</strong>telligent ontology-based knowledge assessment system.Annual <strong>Proceed<strong>in</strong>gs</strong> of Vidzeme University College “ICTE <strong>in</strong> Regional Development”, 20066