mag
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Malaysia Water Research Journal<br />
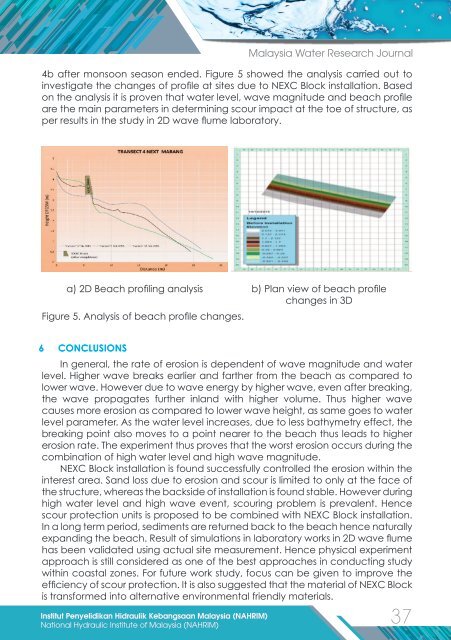
4b after monsoon season ended. Figure 5 showed the analysis carried out to<br />
investigate the changes of profile at sites due to NEXC Block installation. Based<br />
on the analysis it is proven that water level, wave <strong>mag</strong>nitude and beach profile<br />
are the main parameters in determining scour impact at the toe of structure, as<br />
per results in the study in 2D wave flume laboratory.<br />
a) 2D Beach profiling analysis b) Plan view of beach profile<br />
changes in 3D<br />
Figure 5. Analysis of beach profile changes.<br />
6 CONCLUSIONS<br />
In general, the rate of erosion is dependent of wave <strong>mag</strong>nitude and water<br />
level. Higher wave breaks earlier and farther from the beach as compared to<br />
lower wave. However due to wave energy by higher wave, even after breaking,<br />
the wave propagates further inland with higher volume. Thus higher wave<br />
causes more erosion as compared to lower wave height, as same goes to water<br />
level parameter. As the water level increases, due to less bathymetry effect, the<br />
breaking point also moves to a point nearer to the beach thus leads to higher<br />
erosion rate. The experiment thus proves that the worst erosion occurs during the<br />
combination of high water level and high wave <strong>mag</strong>nitude.<br />
NEXC Block installation is found successfully controlled the erosion within the<br />
interest area. Sand loss due to erosion and scour is limited to only at the face of<br />
the structure, whereas the backside of installation is found stable. However during<br />
high water level and high wave event, scouring problem is prevalent. Hence<br />
scour protection units is proposed to be combined with NEXC Block installation.<br />
In a long term period, sediments are returned back to the beach hence naturally<br />
expanding the beach. Result of simulations in laboratory works in 2D wave flume<br />
has been validated using actual site measurement. Hence physical experiment<br />
approach is still considered as one of the best approaches in conducting study<br />
within coastal zones. For future work study, focus can be given to improve the<br />
efficiency of scour protection. It is also suggested that the material of NEXC Block<br />
is transformed into alternative environmental friendly materials.<br />
Institut Penyelidikan Hidraulik Kebangsaan Malaysia (NAHRIM)<br />
37<br />
National Hydraulic Institute of Malaysia (NAHRIM)