3. FOOD ChEMISTRy & bIOTEChNOLOGy 3.1. Lectures
3. FOOD ChEMISTRy & bIOTEChNOLOGy 3.1. Lectures
3. FOOD ChEMISTRy & bIOTEChNOLOGy 3.1. Lectures
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Chem. Listy, 102, s265–s1311 (2008) Food Chemistry & Biotechnology<br />
HO HO<br />
OH<br />
O<br />
OH<br />
R= α/β-H 1a<br />
α-CH3 1b<br />
OR<br />
HO O<br />
HO HO<br />
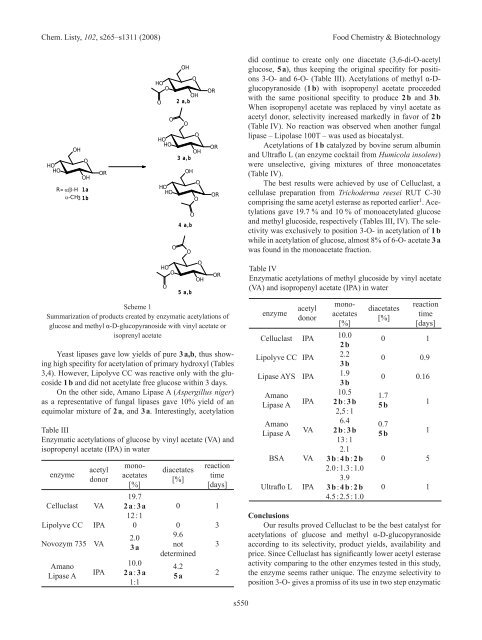
Yeast lipases gave low yields of pure 3 a,b, thus showing<br />
high specifity for acetylation of primary hydroxyl (Tables<br />
3,4). However, Lipolyve CC was reactive only with the glucoside<br />
1 b and did not acetylate free glucose within 3 days.<br />
On the other side, Amano Lipase A (Aspergillus niger)<br />
as a representative of fungal lipases gave 10% yield of an<br />
equimolar mixture of 2 a, and 3 a. Interestingly, acetylation<br />
O<br />
O<br />
HO HO<br />
O<br />
HO O<br />
O<br />
OH<br />
O<br />
O<br />
OH<br />
2 a,b<br />
O<br />
OH<br />
3 a,b<br />
OH<br />
4 a,b<br />
O<br />
5 a ,b<br />
Scheme 1<br />
Summarization of products created by enzymatic acetylations of<br />
glucose and methyl α-D-glucopyranoside with vinyl acetate or<br />
isoprenyl acetate<br />
Table III<br />
Enzymatic acetylations of glucose by vinyl acetate (VA) and<br />
isopropenyl acetate (IPA) in water<br />
enzyme<br />
acetyl<br />
donor<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
OH<br />
OR<br />
OR<br />
OR<br />
OR<br />
mono-<br />
diacetates reaction<br />
acetates<br />
[%]<br />
time<br />
[%] [days]<br />
Celluclast VA<br />
19.7<br />
2 a : 3 a<br />
12 : 1<br />
0 1<br />
Lipolyve CC IPA 0 0 3<br />
novozym 735 VA<br />
2.0<br />
9.6<br />
3 a<br />
3<br />
not<br />
determined<br />
Amano<br />
Lipase A<br />
IPA<br />
10.0<br />
2 a : 3 a<br />
1:1<br />
4.2<br />
5 a<br />
2<br />
s550<br />
did continue to create only one diacetate (3,6-di-O-acetyl<br />
glucose, 5 a), thus keeping the original specifity for positions<br />
3-O- and 6-O- (Table III). Acetylations of methyl α-Dglucopyranoside<br />
(1 b) with isopropenyl acetate proceeded<br />
with the same positional specifity to produce 2 b and 3 b.<br />
When isopropenyl acetate was replaced by vinyl acetate as<br />
acetyl donor, selectivity increased markedly in favor of 2 b<br />
(Table IV). no reaction was observed when another fungal<br />
lipase – Lipolase 100T – was used as biocatalyst.<br />
Acetylations of 1 b catalyzed by bovine serum albumin<br />
and Ultraflo L (an enzyme cocktail from Humicola insolens)<br />
were unselective, giving mixtures of three monoacetates<br />
(Table IV).<br />
The best results were achieved by use of Celluclast, a<br />
cellulase preparation from Trichoderma reesei RUT C-30<br />
comprising the same acetyl esterase as reported earlier 1 . Acetylations<br />
gave 19.7 % and 10 % of monoacetylated glucose<br />
and methyl glucoside, respectively (Tables III, IV). The selectivity<br />
was exclusively to position 3-O- in acetylation of 1 b<br />
while in acetylation of glucose, almost 8% of 6-O- acetate 3 a<br />
was found in the monoacetate fraction.<br />
Table IV<br />
Enzymatic acetylations of methyl glucoside by vinyl acetate<br />
(VA) and isopropenyl acetate (IPA) in water<br />
enzyme<br />
acetyl<br />
donor<br />
Celluclast IPA<br />
10.0<br />
2 b<br />
Lipolyve CC IPA<br />
2.2<br />
3 b<br />
Lipase AYS IPA<br />
1.9<br />
3 b<br />
Amano<br />
Lipase A<br />
IPA<br />
10.5<br />
2 b : 3 b<br />
2,5 : 1<br />
Amano<br />
Lipase A<br />
VA<br />
6.4<br />
2 b : 3 b<br />
13 : 1<br />
2.1<br />
BSA VA 3 b : 4 b : 2 b<br />
2.0 : 1.3 : 1.0<br />
<strong>3.</strong>9<br />
Ultraflo L IPA 3 b : 4 b : 2 b<br />
4.5 : 2.5 : 1.0<br />
mono-<br />
diacetates<br />
reaction<br />
acetates<br />
[%]<br />
time<br />
[%] [days]<br />
0 1<br />
0 0.9<br />
0 0.16<br />
1.7<br />
5 b<br />
0.7<br />
5 b<br />
Conclusions<br />
Our results proved Celluclast to be the best catalyst for<br />
acetylations of glucose and methyl α-D-glucopyranoside<br />
according to its selectivity, product yields, availability and<br />
price. Since Celluclast has significantly lower acetyl esterase<br />
activity comparing to the other enzymes tested in this study,<br />
the enzyme seems rather unique. The enzyme selectivity to<br />
position 3-O- gives a promiss of its use in two step enzymatic<br />
1<br />
1<br />
0 5<br />
0 1